Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... For every 1 point rise 30 times the energy is released. Magnitude - Height of a line traced on a seismogram. ...
... For every 1 point rise 30 times the energy is released. Magnitude - Height of a line traced on a seismogram. ...
Slide 1
... a) Is a landform made of magma that hardened in a volcanoes pipe and later was exposed by erosion b) Weathering and erosion work constantly to wear away the volcanoes c) When a volcanoes activity ends, magma remaining in the pipe hardens to form igneous rock ...
... a) Is a landform made of magma that hardened in a volcanoes pipe and later was exposed by erosion b) Weathering and erosion work constantly to wear away the volcanoes c) When a volcanoes activity ends, magma remaining in the pipe hardens to form igneous rock ...
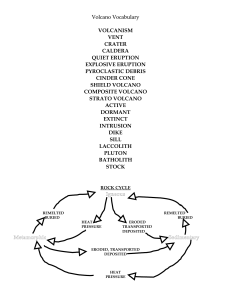
volcanism vent crater caldera quiet eruption explosive
... The height is usually less than 600 feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crate ...
... The height is usually less than 600 feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crate ...
Volcano Vocabulary - watertown.k12.wi.us
... The height is usually less than 600 feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crate ...
... The height is usually less than 600 feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crate ...
2. Volcanoes
... Hood explosive eruption due to type of magma: higher viscosity, 700 C; contains gases; from melting of lithosphere: more silica Eruptions unpredictable and hazardous to a region Can sometimes cause short time cooling events, e.g. Pinatubo d) Calderas: large bowl-shaped depression left after a compos ...
... Hood explosive eruption due to type of magma: higher viscosity, 700 C; contains gases; from melting of lithosphere: more silica Eruptions unpredictable and hazardous to a region Can sometimes cause short time cooling events, e.g. Pinatubo d) Calderas: large bowl-shaped depression left after a compos ...
_____ 1. What happens to the atmosphere after large
... nonexplosive eruptions _____ 5. made of pyroclastic material usually produced from moderately explosive eruptions _____ 6. formed from explosive eruptions of pyroclastic material followed by quieter flows of lava; also called stratovolcanoes ...
... nonexplosive eruptions _____ 5. made of pyroclastic material usually produced from moderately explosive eruptions _____ 6. formed from explosive eruptions of pyroclastic material followed by quieter flows of lava; also called stratovolcanoes ...
Unit 4 Chapter
... & cracks, you know, the internal arrangement of its atoms. You can find this anywhere, Iceland, New York, California, etc. ...
... & cracks, you know, the internal arrangement of its atoms. You can find this anywhere, Iceland, New York, California, etc. ...
VOLCANOES form where molten rock is vented at Earth`s surface.
... • Word is from the Island of Vulcano off Sicily • Ancient people from the area believed that Vulcano was the chimney of the forge of Vulcan (blacksmith of the Roman gods) • They thought hot lava fragments and clouds of dust erupting from Vulcano came from Vulcan's forge as he beat out thunderbolts f ...
... • Word is from the Island of Vulcano off Sicily • Ancient people from the area believed that Vulcano was the chimney of the forge of Vulcan (blacksmith of the Roman gods) • They thought hot lava fragments and clouds of dust erupting from Vulcano came from Vulcan's forge as he beat out thunderbolts f ...
Types of Volcanoes
... • Explosive eruptions that throw lava and rocks high into the air • These bits of rock and hardened lava are called tephra – Tephra layers build up to form steep sided volcanoes ...
... • Explosive eruptions that throw lava and rocks high into the air • These bits of rock and hardened lava are called tephra – Tephra layers build up to form steep sided volcanoes ...
Volcanoes
... ancient Roman island of Vulcano. The Romans believed that Vulcan, the god of Fire and the maker of weapons, used the volcano on that island to forge his weapons. ...
... ancient Roman island of Vulcano. The Romans believed that Vulcan, the god of Fire and the maker of weapons, used the volcano on that island to forge his weapons. ...
Volcanic Acid-Base Reaction
... 1 and 6. Bases range from 8 to 14. Seven on the pH scale is pure water, which is devoid of either acidity or alkalinity. Some examples of acids are citric acid (from certain fruits and veggies), vinegar, carbonic acid (from carbonation of soft drinks), and lactic acid (in butter milk). Some examples ...
... 1 and 6. Bases range from 8 to 14. Seven on the pH scale is pure water, which is devoid of either acidity or alkalinity. Some examples of acids are citric acid (from certain fruits and veggies), vinegar, carbonic acid (from carbonation of soft drinks), and lactic acid (in butter milk). Some examples ...
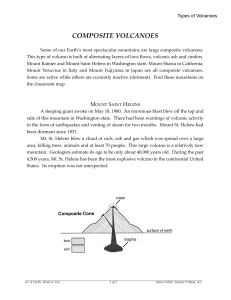
composite volcanoes - Mesa Public Schools
... A sleeping giant awoke on May 18, 1980. An enormous blast blew off the top and side of this mountain in Washington state. There had been warnings of volcanic activity in the form of earthquakes and venting of steam for two months. Mount St. Helens had been dormant since 1831. Mt. St. Helens blew a c ...
... A sleeping giant awoke on May 18, 1980. An enormous blast blew off the top and side of this mountain in Washington state. There had been warnings of volcanic activity in the form of earthquakes and venting of steam for two months. Mount St. Helens had been dormant since 1831. Mt. St. Helens blew a c ...
Volcanoes form as molten rock erupts.
... Earth’s thin outer layer is made of cool rock, but most of Earth is made of extremely hot rock and molten metal. Some of the heat inside Earth escapes to the surface through volcanoes. A volcano is an opening in Earth’s crust through which molten rock, rock fragments, and hot gases erupt. A mountain ...
... Earth’s thin outer layer is made of cool rock, but most of Earth is made of extremely hot rock and molten metal. Some of the heat inside Earth escapes to the surface through volcanoes. A volcano is an opening in Earth’s crust through which molten rock, rock fragments, and hot gases erupt. A mountain ...
HST_CRF_04_02_03.qxd
... 1. Volcanic eruptions can be times stronger than the explosion produced by the first atomic bomb. 2. What is magma? 3. Magma that flows onto the Earth’s surface is called . 4. What is a volcano? ...
... 1. Volcanic eruptions can be times stronger than the explosion produced by the first atomic bomb. 2. What is magma? 3. Magma that flows onto the Earth’s surface is called . 4. What is a volcano? ...
Volcanoes - LambertEarth
... blasted into the air and hardens. Volcano’s eruptions may alternate between lava ...
... blasted into the air and hardens. Volcano’s eruptions may alternate between lava ...
Shapes of igneous bodies
... Extrusive bodies – Fissure Landforms Feeder dikes (regional extension - MOR) Flood basalts Extrusive bodies – Pyroclastic Landforms Pyroclastic Deposits include – volcaniclastic – formed by volcano (process irrelevant) - pyroclastic – formed from magma/lava aerially expelled from vent - lahar – volc ...
... Extrusive bodies – Fissure Landforms Feeder dikes (regional extension - MOR) Flood basalts Extrusive bodies – Pyroclastic Landforms Pyroclastic Deposits include – volcaniclastic – formed by volcano (process irrelevant) - pyroclastic – formed from magma/lava aerially expelled from vent - lahar – volc ...
Volcanoes
... the edifice and destroyed Armero and Chinchina. The footage of rescue efforts after the lahar were devastating and heartbreaking. Sadly, this disaster was mostly preventable as the citizens of these towns could have had at least an hour's warning to walk to higher ground, but the Colombian governmen ...
... the edifice and destroyed Armero and Chinchina. The footage of rescue efforts after the lahar were devastating and heartbreaking. Sadly, this disaster was mostly preventable as the citizens of these towns could have had at least an hour's warning to walk to higher ground, but the Colombian governmen ...
Earth Science--Ch 9 Volcanoes Review Guide
... like/shape, how they erupt, what types of materials they are primarily made of, where they tend to form.) ...
... like/shape, how they erupt, what types of materials they are primarily made of, where they tend to form.) ...
Section 1 - kjpederson
... caused by the impact of a meteroid 2. dormant: a volcano that is not currently active, but that may become active in the future 3. extinct: a volcano that is no longer active and is unlikely to erupt again 4. lava flow: liquid magma that reaches the surface; also the rock formed when liquid lava har ...
... caused by the impact of a meteroid 2. dormant: a volcano that is not currently active, but that may become active in the future 3. extinct: a volcano that is no longer active and is unlikely to erupt again 4. lava flow: liquid magma that reaches the surface; also the rock formed when liquid lava har ...
Answering: What Happens When A Volcano Erupts?
... passage of time, the winds can carry the volcanic gases around a large area. The ash elements obstruct the air traffic, and create breathing complications in the near vicinity. The ash particles produce a layer that is hard to remove. In combination with water, the ash develops into a mud like mass. ...
... passage of time, the winds can carry the volcanic gases around a large area. The ash elements obstruct the air traffic, and create breathing complications in the near vicinity. The ash particles produce a layer that is hard to remove. In combination with water, the ash develops into a mud like mass. ...
magma and lava
... Name __________________________________ Period ______Date___________ Volcano Review Sheet Please use your notes, textbook and any diagrams that you may have to help you complete this review sheet. 1. Molten rock underground is called magma. 2. Mafic magma has low silica and is dark in color. 3. Fels ...
... Name __________________________________ Period ______Date___________ Volcano Review Sheet Please use your notes, textbook and any diagrams that you may have to help you complete this review sheet. 1. Molten rock underground is called magma. 2. Mafic magma has low silica and is dark in color. 3. Fels ...
Build a Volcano
... Volcanoes are built by the accumulation of their own eruptive products—lava, bombs (crusted over ash flows), and tephra (airborne ash and dust). A volcano is most commonly a conical hill or mountain built around a vent that connects with reservoirs of molten rock below the surface of Earth. The term ...
... Volcanoes are built by the accumulation of their own eruptive products—lava, bombs (crusted over ash flows), and tephra (airborne ash and dust). A volcano is most commonly a conical hill or mountain built around a vent that connects with reservoirs of molten rock below the surface of Earth. The term ...