Cornell Notes Template
... Steep slopes Medium-high viscosity lava Explosive eruptions that occur suddenly after years of being inactive Made of alternate layers of pyroclastic material and lava o Examples- Mount St. Helens (deadliest and most economically destructive volcanic event in U.S. history) ...
... Steep slopes Medium-high viscosity lava Explosive eruptions that occur suddenly after years of being inactive Made of alternate layers of pyroclastic material and lava o Examples- Mount St. Helens (deadliest and most economically destructive volcanic event in U.S. history) ...
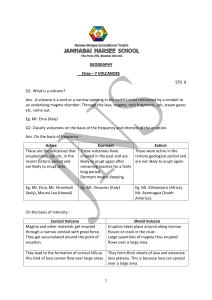
GEOGRAPHY Chap – 7 VOLCANOES STD. 8 Q1. What is a volcano
... Magma and other materials get erupted through a narrow conduit with great force. They get accumulated around the point of eruption. ...
... Magma and other materials get erupted through a narrow conduit with great force. They get accumulated around the point of eruption. ...
Hawaii Volcanoes National Park
... flows, they continue to destroy whatever is remaining in the path of the lava. Many plants may become extinct because there are not as many as there used to be and the animals continue to eat whatever is remaining for food. Once the plants stop growing or become extinct, animals that eat the plants ...
... flows, they continue to destroy whatever is remaining in the path of the lava. Many plants may become extinct because there are not as many as there used to be and the animals continue to eat whatever is remaining for food. Once the plants stop growing or become extinct, animals that eat the plants ...
Notes 13.2 Studying the composition of rocks, scientists determine
... Hot mafic lava flows out of the vent, hardens and builds up to form the cone. Hawaiian Islands chain of shield volcanoes o CINDER CONE Steep slopes Rarely more than a few 100 m high Small explosive eruptions Made of pyroclastic material o COMPOSITE VOLCANO Made of alternating layer of ha ...
... Hot mafic lava flows out of the vent, hardens and builds up to form the cone. Hawaiian Islands chain of shield volcanoes o CINDER CONE Steep slopes Rarely more than a few 100 m high Small explosive eruptions Made of pyroclastic material o COMPOSITE VOLCANO Made of alternating layer of ha ...
VOLCANOES form where molten rock is vented at Earth`s surface.
... form where molten rock is vented at Earth’s surface. ...
... form where molten rock is vented at Earth’s surface. ...
Ch. 7.2 Volcanic Eruptions
... Pyroclastic material results from exploded felsic lava. The type of ...
... Pyroclastic material results from exploded felsic lava. The type of ...
Volcano - Greenwich Central School
... The opening through which molten rock and gas leave the volcano. ...
... The opening through which molten rock and gas leave the volcano. ...
lesson 24 effects of ash fall
... Magma is buoyont, and lighter than the solid rock that surrounds it, which is why it rises. ...
... Magma is buoyont, and lighter than the solid rock that surrounds it, which is why it rises. ...
No Slide Title
... • Growth of Hawaii – 1980’s & 90’s 1.5 billion cubic meters • Geothermal energy- New Zealand; California • Effect on climate- 1816 “year without summer” • Volcanic catastrophies – Mt. St. Helens 1980 – Vesuvius 79 AD – Krakatoa 1883 – Crater Lake 6,600 y.b.p. ...
... • Growth of Hawaii – 1980’s & 90’s 1.5 billion cubic meters • Geothermal energy- New Zealand; California • Effect on climate- 1816 “year without summer” • Volcanic catastrophies – Mt. St. Helens 1980 – Vesuvius 79 AD – Krakatoa 1883 – Crater Lake 6,600 y.b.p. ...
Volcanoes - Travelling across time
... 1. Magma rises through cracks or weaknesses in the Earth's crust. 2. Pressure builds up inside the Earth. 3. When this pressure is released, eg as a result of plate movement, magma explodes to the surface causing a volcanic eruption. 4. The lava from the eruption cools to form new crust. 5. Over tim ...
... 1. Magma rises through cracks or weaknesses in the Earth's crust. 2. Pressure builds up inside the Earth. 3. When this pressure is released, eg as a result of plate movement, magma explodes to the surface causing a volcanic eruption. 4. The lava from the eruption cools to form new crust. 5. Over tim ...
Non explosive volcanoes - Garfield Gifts and Talents
... St. Helens, Washington . It doesn’t do much damage because the lava gets pushed out very slowly. ...
... St. Helens, Washington . It doesn’t do much damage because the lava gets pushed out very slowly. ...
VOLCANOES!!!
... More than 36,000 people killed Area around the volcano was in completely dark for about 24 hours. ...
... More than 36,000 people killed Area around the volcano was in completely dark for about 24 hours. ...
Document
... b. A small amount of volcanic ash and gases are ejected into the upper atmosphere. c. Volcanic ash and gases are ejected directly above the volcano. d. Enormous amounts of volcanic ash and gases are ejected into the upper atmosphere. _____ 2. As volcanic ash and gases spread throughout the atmospher ...
... b. A small amount of volcanic ash and gases are ejected into the upper atmosphere. c. Volcanic ash and gases are ejected directly above the volcano. d. Enormous amounts of volcanic ash and gases are ejected into the upper atmosphere. _____ 2. As volcanic ash and gases spread throughout the atmospher ...
Chapter 9 Section 1 Notes
... 2. These eruptions produce relatively calm flows of ______________. Explosive Eruptions 1. ________________________ eruptions are much rarer than nonexplosive eruptions. 2. During an explosive eruption, clouds of hot debris, ____________, and ______________ rapidly shoot out from a volcano. What Is ...
... 2. These eruptions produce relatively calm flows of ______________. Explosive Eruptions 1. ________________________ eruptions are much rarer than nonexplosive eruptions. 2. During an explosive eruption, clouds of hot debris, ____________, and ______________ rapidly shoot out from a volcano. What Is ...
Volcanoes
... • A vent that lets out heat from inside the Earth , spewing out lava and eventually forming a mountain. • 3 classifications of volcanic activity: extinct (does not erupt), dormant (sleeping), and active (currently erupting). • The most active volcano on the Earth is Kilauea on the big island of Hawa ...
... • A vent that lets out heat from inside the Earth , spewing out lava and eventually forming a mountain. • 3 classifications of volcanic activity: extinct (does not erupt), dormant (sleeping), and active (currently erupting). • The most active volcano on the Earth is Kilauea on the big island of Hawa ...
Volcano Making - Manchester Museum
... you shake it up before you open it!). The way that a volcano erupts depends on how runny the magma is and much pressure has built up before the magma breaks through the surface. ...
... you shake it up before you open it!). The way that a volcano erupts depends on how runny the magma is and much pressure has built up before the magma breaks through the surface. ...
Volcanoes: The Fire Within
... • A vent that lets out heat from inside the Earth , spewing out lava (molten rock on the surface) and eventually forming a mountain. • 3 classifications of volcanic activity: extinct (does not erupt), dormant (sleeping), and active (currently erupting). • The most active volcano on the Earth is Kila ...
... • A vent that lets out heat from inside the Earth , spewing out lava (molten rock on the surface) and eventually forming a mountain. • 3 classifications of volcanic activity: extinct (does not erupt), dormant (sleeping), and active (currently erupting). • The most active volcano on the Earth is Kila ...
Notes Igneous Activity
... Lava bombs – molten lava often streamlined as it falls through the air. ...
... Lava bombs – molten lava often streamlined as it falls through the air. ...
File
... Crater – a deep hollow at the top of a volcano Crust – The top layer of the Earth Eruption – the release of gases, magma and rock from a volcano Lava – melted rock that flows down the volcano Magma – melted rock inside the Earth Molten – melted, liquid Vent – a crack on the side of a volcano where m ...
... Crater – a deep hollow at the top of a volcano Crust – The top layer of the Earth Eruption – the release of gases, magma and rock from a volcano Lava – melted rock that flows down the volcano Magma – melted rock inside the Earth Molten – melted, liquid Vent – a crack on the side of a volcano where m ...
Volcanoes and Earthquakes
... • Explosive eruptions have released enough gases and ash into the atmosphere to effect weather globally by blocking the sun’s heat ...
... • Explosive eruptions have released enough gases and ash into the atmosphere to effect weather globally by blocking the sun’s heat ...
EandV_Exam2_StudyGui..
... What is its plate tectonic cause? What type of eruption was it? What was it’s magma composition? (Study Hint: the last three are closely related to each other) What was the impact of this eruption (i.e. approx. deaths/hazards)? What is notable about this volcano? Why do you think this volcano was me ...
... What is its plate tectonic cause? What type of eruption was it? What was it’s magma composition? (Study Hint: the last three are closely related to each other) What was the impact of this eruption (i.e. approx. deaths/hazards)? What is notable about this volcano? Why do you think this volcano was me ...
Directions: Read the information below. Use this information and
... from a single vent and accumulate around the vent when they fall back to earth. Cinder cones grow rapidly and soon approach their maximum size. They rarely exceed 250m in height and 500m in diameter. Shield volcanoes are huge in size. They are built by many layers of runny lava flows. Lava spills ou ...
... from a single vent and accumulate around the vent when they fall back to earth. Cinder cones grow rapidly and soon approach their maximum size. They rarely exceed 250m in height and 500m in diameter. Shield volcanoes are huge in size. They are built by many layers of runny lava flows. Lava spills ou ...