* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes Igneous Activity
Mono–Inyo Craters wikipedia , lookup
Axial Seamount wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Itcha Range wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Level Mountain wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Lascar (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Blanco (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Silverthrone Caldera wikipedia , lookup
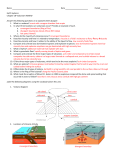
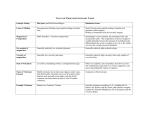
Igneous Activity 10.1 Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Eruptions A. Factors that determine the violence of an eruption 1. 2. 3. B. Composition (Si, Fe, Mg) Temperature Dissolved gases Viscosity of magma 1. A measure of a materials resistance to flow – (how “thick” it is) B. Viscosity of Magma (con’t.) 2) Factors affecting viscosity a. Temperature (high = easy flow= low viscosity Low temp = flows slowly =high viscosity b. Composition 1. Amt of silica is high, then,Viscosity - high, example – felsic granite or rhyolite 2. Amt of silica is low Viscosity is low, example– mafic basalt or gabbro B. Viscosity of Magma 2. Factors affecting viscosity (con’t) Gases trapped Felsic rock c. Dissolved gases 1. H2O & CO2 2. Expand as they near the surface 3. Gases easily Escape Mafic rock (The power to explode) 4. The violence of the eruption is related to how easily gases can escape a. Fluid magma=Easy escape b. viscous magma = violent eruptions Materials Associated with volcanic eruptions A. Lava flows Pahoehoe lava Aa lava 1. Basaltic -Fluid (dark, dense) 2. Types of basaltic(mafic) lava flows a. Pahoehoe – rope like texture (typically seen) b. aa- jagged, sharp edges B. Gases 1. 1-5 % of weight Materials associated w/volcanic eruptions 2. Types of pyroclastics a. b. c. d. e. Ash – very fine glassy fragments Pumice – “frothy lava” gas escapes at surface, leaving holes Lapilli – walnut sized pieces Cinders – pea sized pieces Larger than lapilli 1. 2. Lava blocks – hardened chunks of lava Lava bombs – molten lava often streamlined as it falls through the air. Ash Cloud Micro view of ash Cinders Lapilli Lava blocks and bombs Note the aerodynamic shape They take on as they fall Through the air Volcanoes A. General features 1. Opening at the top a. Crater steep, walled depression b. Caldera – same as crater, but larger (1 km or more in diameter Sunset Crater Yellowstone Caldera is known as a “Super Volcano” (Note the size of the caldera and how far there would be significant ash deposit ) 2. Vent- the tunnel (conduit) that connects magma chamber to surface (crater) Ancient vent Tourists near multiple small vents Underwater vent Volcanoes B. Types of volcanoes 1. Shield a. Broad, slightly domed b. Primarily basaltic lava c. Very large (large area, not height above sea level) d. Produces large volume of lava e. Example: Mona Loa, Hawaii Shield Volcano Mona Loa 2. Composite or (Strato) a. b. c. d. e. Very large, very high elevation, symmetrical, and usually snow capped Interbedded layers of lava and pyroclastics Most violent due to its felsic composition Produces a Nuee ardente – fiery cloud of hot gases infused with ash. Flows down at great speeds exceeding 200 km/hr Produces a Lahar – huge mud slide produced when snow at peak is melted quickly Nuee Ardente-firey cloud a pyroclastic flow traveling at Speeds past 400mph and at Temperatures that exceed 1500 degrees F Very powerful, very fast, difficult to escape Steel re-bar bent by the blast of a nuee ardante https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8f9TbC88-40 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u2vvKFkuPbk Lahar - mudflow or debris flow composed of a slurry of pyroclastic material, rocky debris, and water. The material flows down from a volcano, typically along . a river valley Often the “killer” Part of a volcano https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3XMS-quxdGg Volcanoes 3. Cinder Cone a. Built from ejected lava material a. Steep slope, small in size b. Frequently occurs in groups surrounding a large stratovolcano c. Sunset Crater, Flagstaff, AZ Sunset Crater Paracutin in Mexico Paracutin At the beginning of the eruptions After the eruptions in 1943 By 1952 the volcano became dormant Distribution of Igneous Activity Volcanoes are found Along Plate Margins Famous examples: Japan – Mt. Fuji Philippines – Mt. Pinatubo Mt. mayon Indonesia - Tambora, Krakatau, Ocean to Ocean Plate Boundary Famous Examples: El Chicon, Villarrica Mt. St. Helens, & Mt. Rainer Ocean to continent plate boundary Ring of Fire- the Pacific Rim is encircled by volcanic activity Intraplate Volcanism- volcano erupts in the middle of a plate Hawaiian Islands Known as “Hot Spots” in the middle of a tectonic plate Unusual “hot spot” on a plate boundary Iceland Azores