Make a Volcano Lesson Plan - Indiana 4-H
... It is the policy of the Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service that all persons have equal opportunity and access to its educational programs, services, activities, and facilities without regard to race, religion, color, sex, age, national origin or ancestry, marital status, parental status ...
... It is the policy of the Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service that all persons have equal opportunity and access to its educational programs, services, activities, and facilities without regard to race, religion, color, sex, age, national origin or ancestry, marital status, parental status ...
Problem 13 - Macmillan Learning
... average strain rate experienced by South America? Because your answer will be small, express it per year, rather than in the more conventional per seconds. Problem W13.2. Geology of the Island of Hawaii. Study the geologic map of the island of Hawaii (Figure WS13.1). Things to note: ...
... average strain rate experienced by South America? Because your answer will be small, express it per year, rather than in the more conventional per seconds. Problem W13.2. Geology of the Island of Hawaii. Study the geologic map of the island of Hawaii (Figure WS13.1). Things to note: ...
Make a Volcano Lesson Plan - Purdue Extension
... It is the policy of the Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service that all persons have equal opportunity and access to its educational programs, services, activities, and facilities without regard to race, religion, color, sex, age, national origin or ancestry, marital status, parental status ...
... It is the policy of the Purdue University Cooperative Extension Service that all persons have equal opportunity and access to its educational programs, services, activities, and facilities without regard to race, religion, color, sex, age, national origin or ancestry, marital status, parental status ...
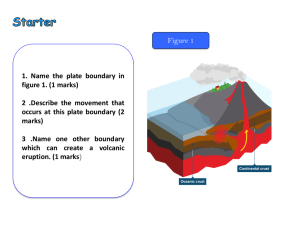
VOLCANOES
... Volcanoes erupt because of density and pressure. The lower density of the magma relative to the surrounding rocks causes it to rise. It will rise to the surface or to a depth that is determined by the density of the magma and the weight of the rocks above it. As the magma rises, bubbles start to for ...
... Volcanoes erupt because of density and pressure. The lower density of the magma relative to the surrounding rocks causes it to rise. It will rise to the surface or to a depth that is determined by the density of the magma and the weight of the rocks above it. As the magma rises, bubbles start to for ...
Virtual Volcano Lab Handout
... c. 2 famous cinder cone volcanoes & where they are located: i. _______________________________________________________ ii. _______________________________________________________ 3) Shield Volcano: a. How are they made?_____________________________________________ b. Look like—______________________ ...
... c. 2 famous cinder cone volcanoes & where they are located: i. _______________________________________________________ ii. _______________________________________________________ 3) Shield Volcano: a. How are they made?_____________________________________________ b. Look like—______________________ ...
Chapter 13 Section 2 Directed Reading
... ______ 7. Explosive eruptions are most likely to be caused by magma with a. small amounts of dissolved gases. b. large amounts of trapped, dissolved gases. c. any amount of dissolved gases. d. small amounts of dissolved rock. ______ 8. Oceanic volcanoes commonly form from a. mafic magma. b. felsic m ...
... ______ 7. Explosive eruptions are most likely to be caused by magma with a. small amounts of dissolved gases. b. large amounts of trapped, dissolved gases. c. any amount of dissolved gases. d. small amounts of dissolved rock. ______ 8. Oceanic volcanoes commonly form from a. mafic magma. b. felsic m ...
Virtual Volcano Lab
... c. 2 famous cinder cone volcanoes & where they are located: i. _______________________________________________________ ii. _______________________________________________________ 3) Shield Volcano: a. How are they made?_____________________________________________ b. Look like—______________________ ...
... c. 2 famous cinder cone volcanoes & where they are located: i. _______________________________________________________ ii. _______________________________________________________ 3) Shield Volcano: a. How are they made?_____________________________________________ b. Look like—______________________ ...
Monitoring Methods
... Gas — When molten material (magma) moves into a volcano it gives off volcanic gas emissions, sulphur dioxide (SO2), carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen sulphide (H2S) which are measured regularly at our volcanoes. There are several techniques which include measurement done from an aircraft and on the ...
... Gas — When molten material (magma) moves into a volcano it gives off volcanic gas emissions, sulphur dioxide (SO2), carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen sulphide (H2S) which are measured regularly at our volcanoes. There are several techniques which include measurement done from an aircraft and on the ...
Wk16-Volcanoes-p2
... • Mafic: refers to rocks and magma rich in iron and magnesium. • This type of lava that is very runny. • As magma nears the surface there is little pressure, causing gasses escape easily. • Magma low in Silica have quiet eruptions ...
... • Mafic: refers to rocks and magma rich in iron and magnesium. • This type of lava that is very runny. • As magma nears the surface there is little pressure, causing gasses escape easily. • Magma low in Silica have quiet eruptions ...
Volcanoes Week 2
... shapes and are solid. Some lava blocks are pieces of the volcano vent or sides of the volcano when it blows apart. The pieces can be as big as a small car. Lava blocks are the largest pieces of pyroclastic material ejected during a violent eruption. Pumice Pumice is light-colored igneous rock blown ...
... shapes and are solid. Some lava blocks are pieces of the volcano vent or sides of the volcano when it blows apart. The pieces can be as big as a small car. Lava blocks are the largest pieces of pyroclastic material ejected during a violent eruption. Pumice Pumice is light-colored igneous rock blown ...
Faizan - WordPress.com
... A cloud of ash formed by volcanic explosions. Parasitic Cone: A small cone-shaped volcano formed by an accumulation of volcanic debris. ...
... A cloud of ash formed by volcanic explosions. Parasitic Cone: A small cone-shaped volcano formed by an accumulation of volcanic debris. ...
Volcanoes Webquest - Mrs. Gomez`s Class
... Earth's tectonic plates collide and one dives into the mantle. What type of crystals are the authors analyzing from arc volcanoes? ...
... Earth's tectonic plates collide and one dives into the mantle. What type of crystals are the authors analyzing from arc volcanoes? ...
Volcanology - Departments
... • Island arcs • Destructive plate boundaries where oceanic crust is being destroyed and gases are being added ...
... • Island arcs • Destructive plate boundaries where oceanic crust is being destroyed and gases are being added ...
Chapter 6 Study Guide
... The molten mixture of rock – forming substance, gases, and water deep in Earth’s mantle is called ______________________. The belt around the rim of the Pacific Ocean is called ___________. Thicker magma contains more ______________________. What is a wide gently sloping mountain made of hardened la ...
... The molten mixture of rock – forming substance, gases, and water deep in Earth’s mantle is called ______________________. The belt around the rim of the Pacific Ocean is called ___________. Thicker magma contains more ______________________. What is a wide gently sloping mountain made of hardened la ...
Volcanoes - Types and structure
... These volcanoes are created at constructive margins. This is where two plates are moving apart from each other and magma moves to the surface through the gap. The emerging lava is more fluid and therefore the shape of the volcano is low and wide. This is why it is called a ‘shield’ volcano. ...
... These volcanoes are created at constructive margins. This is where two plates are moving apart from each other and magma moves to the surface through the gap. The emerging lava is more fluid and therefore the shape of the volcano is low and wide. This is why it is called a ‘shield’ volcano. ...
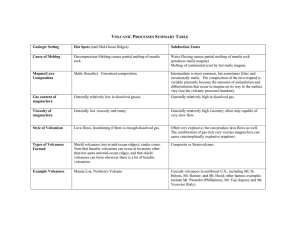
Geologic Setting Hot Spots (and Mid
... Generally relatively high viscosity; often only capable of very slow flow. ...
... Generally relatively high viscosity; often only capable of very slow flow. ...
Volcano
... pumice, and a small amount of stiff, silica lava (called rhyolite). This type of volcano can have eruptions accompanied by lahars -- deadly mudflows. Most volcanoes on Earth are of this type. Stratovolcanoes kill more people than any other type of volcanoes - this is because of their abundance on Ea ...
... pumice, and a small amount of stiff, silica lava (called rhyolite). This type of volcano can have eruptions accompanied by lahars -- deadly mudflows. Most volcanoes on Earth are of this type. Stratovolcanoes kill more people than any other type of volcanoes - this is because of their abundance on Ea ...
Chapter 13 Section 2 Review Page 330
... causing the volcanic cone to collapse in upon it, or when magma is ejected violently and the cone is destroyed. ...
... causing the volcanic cone to collapse in upon it, or when magma is ejected violently and the cone is destroyed. ...
Section 13
... causing the volcanic cone to collapse in upon it, or when magma is ejected violently and the cone is destroyed. ...
... causing the volcanic cone to collapse in upon it, or when magma is ejected violently and the cone is destroyed. ...
Volcano Jeopardy Round 1 Location, location, location! Most
... d. What is the process that melts rock when it rises inside the Earth? Decrease in pressure e. What is the most common way that melt is formed at subduction zones? Addition of water 5. Ashes, ashes, we all fall down! a. What electrical phenomenon can be caused by a volcanic eruption? Lightning ...
... d. What is the process that melts rock when it rises inside the Earth? Decrease in pressure e. What is the most common way that melt is formed at subduction zones? Addition of water 5. Ashes, ashes, we all fall down! a. What electrical phenomenon can be caused by a volcanic eruption? Lightning ...
Volcanic Landforms
... Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, composite volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places o ...
... Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, composite volcanoes, and lava plateaus. At some places o ...
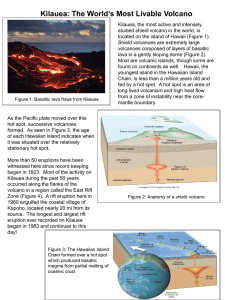
Kilauea: The World`s Most Livable Volcano
... Kapoho, located nearly 20 mi from its source. The longest and largest rift eruption ever recorded on Kilauea began in 1983 and continues to this day! ...
... Kapoho, located nearly 20 mi from its source. The longest and largest rift eruption ever recorded on Kilauea began in 1983 and continues to this day! ...
Volcanic Eruptions
... • Magma from the mantle rises up through the crust because it is less dense. • Magma becomes trapped beneath layers of rock. • Weak spots in the crust allow trapped magma to reach the surface, forming a volcano. ...
... • Magma from the mantle rises up through the crust because it is less dense. • Magma becomes trapped beneath layers of rock. • Weak spots in the crust allow trapped magma to reach the surface, forming a volcano. ...