* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Faizan - WordPress.com
Mono–Inyo Craters wikipedia , lookup
Lōʻihi Seamount wikipedia , lookup
Axial Seamount wikipedia , lookup
Itcha Range wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Blanco (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Level Mountain wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Volcanology of Io wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
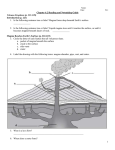
Presented by Rana Faizan Saleem Roll.No (10) VOLCANOES AND ITS LANDFORMS THIS PRESENTATION EXPLAINS YOU Volcanoes Structure of a Volcano Volcanism and its Types Types of Volcanoes Landforms from Lava Landforms from Magma Benefits of Volcanoes VOLCANOES Introduction: Word Volcano taken from: Roman god of fire, Vulcan What is a Volcano? Volcano – a weak spot in the earth’s crust where molten material (magma), comes to the surface. How do Volcanoes formed? When rock from the mantle melts, moves to the surface through the crust, and releases pent-up gases, volcanoes erupt. Extremely high temperature and pressure cause the rock to melt and become liquid rock or magma. When a large body of magma has formed, it rises through the denser rock layers toward Earth's surface. WHAT HAPPENS AS A VOLCANO ERUPTS? As magma rises toward the surface, the pressure decreases allowing the dissolved gases to separate out forming bubbles These materials erupts: i. ii. iii. Lava:(Liquid) Volcanic Ash:(The Solid) Volcanic Bomb: (Like Ash but large) STRUCTURE OF A VOLCANO Magma: Molten mixture of rock-forming substances, gases, and water from the mantle. Lava: When magma reaches the surface it is called Lava. Magma Chamber: The pocket beneath a volcano where magma collects Conduit Pipe: A long tube through which magma moves from the magma chamber to the Earth’s surface Vent: An opening where magma and gas leave the volcano Crater: Mouth of a volcano - surrounds a volcanic vent. Throat: Entrance of a volcano. The part of the conduit that ejects lava and volcanic ash. Flank: The side of a Volcano Lava flow: A lava flow is basically a stream of lava on the surface. Summit: Highest point Ash: Fragments of lava or rock smaller than 2 mm in size that are blasted into the air by volcanic explosions. Ash Cloud: A cloud of ash formed by volcanic explosions. Parasitic Cone: A small cone-shaped volcano formed by an accumulation of volcanic debris. VOLCANISM AND ITS TYPES Volcanism: When hot molten magma escapes from the Earth’s core becoming cooler, and forming hard rocks, we refer to this process as volcanism. Volcanism takes place both above the surface of Earth, as well as beneath its surface. Extrusive Volcanism When molten lava escapes the Earth and reaches the surface geologists say that it is extrusive volcanism. Intrusive Volcanism When molten magma cools and hardens beneath the surface of the Earth, we say that it is intrusive volcanism. VOLCANIC LANDFORMS TYPES ON THE BASIS OF ERUPTION Active Volcano: An active volcano is a volcano that erupts regularly. about 1510 active volcanoes in the world. (Pacific Ring of Fire):- The ring of fire is a circle around the edges of the pacific ocean where half the worlds valcanoes are located . Dormant Volcano: A dormant volcano is a volcano that is not erupting, but supposed to erupt again. Extinct Volcano: An extinct volcano has not had an eruption and is not expected to erupt again. TYPES ON THE BASIS OF SHAPES Following types on Shape basis: Sheild Volcano Composite (or Stratovolcano) Cinder Cones Lava Dome Sheild Volcano: A bowl or sheild shaped Volcano in the middle with long-gentle slopes made by basaltic lava flows,called flood basalt. Shield volcanoes created the Hawaiian Islands HAWAIIAN ISLAND Composite Volcano: A composite volcano is built up from alternate layers of ash, high viscosity lava and rock debris. It has steep sides because when it erupts it lava is thick and viscous meaning that it does not travel great distances and stays on the side of the volcano. MOUNT FUJI Cinder Cones: Erupts violently Cinder cones form around a volcanic vent. Lava explodes into the air and cools very quickly forming accumulating a ring of volcanic fragments. Lava Dome: A dome volcano is a round shaped mountain made of viscous lava. The lava has a high silica content that prevents the lava from flowing very far from its vent. Most domes are formed by dacite and rhyolite lavas. Mount Myoko Japan is example. LANDFORMS FROM LAVA Lava Plateau: A lava plateau is a plateau formed by low-viscous lava through numerous vents, during quiet eruptions. Caldera: The main volcano vent dries out and the top of the volcano collapses into it. Volcanic Neck: A volcanic neck forms when the magma inside a volcano turns into rock and the outside of a volcano wears away, leaving the spiky-shaped rock magma LAVA PLATEAU CALDERA LANDFORMS FROM MAGMA Dike: Magma hardens in a vertical crack Sill: Magma hardens in a horizontal crack Batholith: A large deposit of magma that cools underground. BENEFITS OF VOLCANOES Benefits of volcanoes Soils Energy from heat Rock (Pumice) Gases for industry