Chapters 19&20
... • Kelvin scale is defined by the temperature of the triple point of pure water • Triple point – set of pressure and temperature values at which solid, liquid, and gas phases can coexist • International convention: T of the triple point of water is ...
... • Kelvin scale is defined by the temperature of the triple point of pure water • Triple point – set of pressure and temperature values at which solid, liquid, and gas phases can coexist • International convention: T of the triple point of water is ...
PS1 Study Guide - Dublin City Schools
... Energy- The ability to do work and cause a change in matter. Thermal Energy- Heat energy Temperature- The measure of thermal energy or how cool or warm things are. Conduction- Process by which heat or electricity is transferred through an object. Conductor- Materials where heat or electricity flows ...
... Energy- The ability to do work and cause a change in matter. Thermal Energy- Heat energy Temperature- The measure of thermal energy or how cool or warm things are. Conduction- Process by which heat or electricity is transferred through an object. Conductor- Materials where heat or electricity flows ...
Take Control of Your Thermostat – During the
... Take Control of Your Thermostat – During the Day and Night Although slight natural variations in our internal body temperature throughout the day are normal, our temperature should remain within the range of 98–102◦F (36.5-37.5 ). Temperature is lowest between 2 and 4 am and typically increases slig ...
... Take Control of Your Thermostat – During the Day and Night Although slight natural variations in our internal body temperature throughout the day are normal, our temperature should remain within the range of 98–102◦F (36.5-37.5 ). Temperature is lowest between 2 and 4 am and typically increases slig ...
Molar Heat of VaporizationREV
... absorbed by one mole of a substance in melting from a solid to a liquid q = mol x Hfus. (no temperature change) 2. Molar Heat of Solidification ( Hsolid.) = the heat lost when one mole of liquid solidifies (or freezes) to a solid q = mol x Hsolid. (no temperature change) ...
... absorbed by one mole of a substance in melting from a solid to a liquid q = mol x Hfus. (no temperature change) 2. Molar Heat of Solidification ( Hsolid.) = the heat lost when one mole of liquid solidifies (or freezes) to a solid q = mol x Hsolid. (no temperature change) ...
Heat Transfer/ Specific Heat Problems Worksheet
... heat of copper is 0.38452 J/g x oC). Place your answer in kJ. 3. The specific heat of iron is 0.4494 J/g x oC. How much heat is transferred when a 4.7 kg piece of iron is cooled from 180 oC to 13 oC? Remember you must use the same units so you will have to convert your mass to grams before you begin ...
... heat of copper is 0.38452 J/g x oC). Place your answer in kJ. 3. The specific heat of iron is 0.4494 J/g x oC. How much heat is transferred when a 4.7 kg piece of iron is cooled from 180 oC to 13 oC? Remember you must use the same units so you will have to convert your mass to grams before you begin ...
Chapter 3: Air Temperature
... • Human body stabilizes its T (i.e., prevents its T decrease) primarily by converting food into heat (metabolism) • The stronger the wind, the faster the body’s heat loss • High winds in below-freezing air can remove heat from exposed skin so quickly that the skin may actually freeze (called frostbi ...
... • Human body stabilizes its T (i.e., prevents its T decrease) primarily by converting food into heat (metabolism) • The stronger the wind, the faster the body’s heat loss • High winds in below-freezing air can remove heat from exposed skin so quickly that the skin may actually freeze (called frostbi ...
introduction - IIT Portal.com
... Triple Point[ Secondary Information]:- Unique set of pressure and temp. Exist at which are these states (solid, liquid and vapones) of a pure substance can exist orace in equilibrium. This temprature is called triple point of substance. Kelvin Scale: The celsius scale i9s defined such as T (K) = T ( ...
... Triple Point[ Secondary Information]:- Unique set of pressure and temp. Exist at which are these states (solid, liquid and vapones) of a pure substance can exist orace in equilibrium. This temprature is called triple point of substance. Kelvin Scale: The celsius scale i9s defined such as T (K) = T ( ...
habitat place where an organism lives and that
... multiply or in which a virus can hide until activated by environmental stimuli. the result of an unusually hot area at the boundary between Earth’s mantle and core that forms volcanoes when melted rock is forced upward and breaks through the crust. amount of water vapor held in the air. dark-colored ...
... multiply or in which a virus can hide until activated by environmental stimuli. the result of an unusually hot area at the boundary between Earth’s mantle and core that forms volcanoes when melted rock is forced upward and breaks through the crust. amount of water vapor held in the air. dark-colored ...
Heat Transfer Oil
... Heat Transfer Oil is a highly refined and stable paraffinic oil designed to be used as a heat transfer medium and quenching oil. In many industrial applications heating is provided indirectly by circulating hot oil through a heat exchanger, thus reducing hot spots and increasing the safety of the he ...
... Heat Transfer Oil is a highly refined and stable paraffinic oil designed to be used as a heat transfer medium and quenching oil. In many industrial applications heating is provided indirectly by circulating hot oil through a heat exchanger, thus reducing hot spots and increasing the safety of the he ...
f21/2509/2009 githua scolastica njoki heat and mass transfer
... Derive an expression for the critical radius of insulation for a radial system Adding insulation to a cylindrical piece or a spherical shell increases the conduction resistance of the insulation layer but decreases the convection resistance of the surface because of the increase in the outer surface ...
... Derive an expression for the critical radius of insulation for a radial system Adding insulation to a cylindrical piece or a spherical shell increases the conduction resistance of the insulation layer but decreases the convection resistance of the surface because of the increase in the outer surface ...
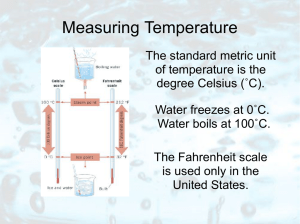
Measuring Temperature
... As the temperature of most substances increases, its molecules move faster and farther apart. Most substances expand when heated and contract when cooled. Extreme heat on a July day caused the buckling of these railroad tracks. ...
... As the temperature of most substances increases, its molecules move faster and farther apart. Most substances expand when heated and contract when cooled. Extreme heat on a July day caused the buckling of these railroad tracks. ...
14_Water Cooling System
... Burning of fuel Heat developed by compression of air Frictional heat ...
... Burning of fuel Heat developed by compression of air Frictional heat ...
Heat Transfer LAB
... substance gains heat, the particles making it up move faster. This increased movement in turn causes the substance to have an increased volume and decreased density – thermal expansion. When a substance loses heat, the particles making it up move slower. This decreased movement in turn causes the su ...
... substance gains heat, the particles making it up move faster. This increased movement in turn causes the substance to have an increased volume and decreased density – thermal expansion. When a substance loses heat, the particles making it up move slower. This decreased movement in turn causes the su ...
Powerpoint
... • Magma ocean may have been helped by thick early atmosphere (high surface temperatures) ...
... • Magma ocean may have been helped by thick early atmosphere (high surface temperatures) ...
Phy213_2 - Personal.psu.edu
... coefficient of thermal expansion for the material of which the rod is made of? The change in length for the rod is 20.11cm-20.05cm plus the expansion of the steel ruler at its 20.11cm mark: ∆Ls = Lss∆T = (20.11 cm)(11 x 10-6 /C˚)(270˚C-20˚C) ...
... coefficient of thermal expansion for the material of which the rod is made of? The change in length for the rod is 20.11cm-20.05cm plus the expansion of the steel ruler at its 20.11cm mark: ∆Ls = Lss∆T = (20.11 cm)(11 x 10-6 /C˚)(270˚C-20˚C) ...
4.5 THERMAL ENERGY AND HEAT . PRACTICE
... 7. An electric room heater is best placed near the floor. In this way, the warm air rising from the heater by convection has an opportunity to be distributed throughout the room. If placed near the ceiling, the warm air would simply stay near the ceiling. 8. In most eases, the density of a substance ...
... 7. An electric room heater is best placed near the floor. In this way, the warm air rising from the heater by convection has an opportunity to be distributed throughout the room. If placed near the ceiling, the warm air would simply stay near the ceiling. 8. In most eases, the density of a substance ...
Thermodynamics!!!
... COLD, only a lack of heat Temperature is the measurement of the average kinetic energy of the molecules of a substance Heat always moves from “warm to cold” meaning from something with a higher temperature to something with a lower temperature ...
... COLD, only a lack of heat Temperature is the measurement of the average kinetic energy of the molecules of a substance Heat always moves from “warm to cold” meaning from something with a higher temperature to something with a lower temperature ...
Conductive Thermal Transfer
... relatively high resolution (<1 km pixel) over the entire conterminous United States… Measurements are integrative so are representative of properties of surface rocks. Can these be used to draw inferences about deeper rocks also? ...
... relatively high resolution (<1 km pixel) over the entire conterminous United States… Measurements are integrative so are representative of properties of surface rocks. Can these be used to draw inferences about deeper rocks also? ...
Worksheet 6a
... standard enthalpy of formation – heat associated with the formation of one mole of a compound from its elements in their standard state (way they occur at 1 atm and 25 oC). ...
... standard enthalpy of formation – heat associated with the formation of one mole of a compound from its elements in their standard state (way they occur at 1 atm and 25 oC). ...
SPECIFIC HEAT
... CALORIMETRY & SPECIFIC HEAT THEORY Heat energy is defined as energy that flows from hot objects to cold objects. It can be measured in calories, kilocalories, or joules of energy. One calorie is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 C. One calorie i ...
... CALORIMETRY & SPECIFIC HEAT THEORY Heat energy is defined as energy that flows from hot objects to cold objects. It can be measured in calories, kilocalories, or joules of energy. One calorie is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 C. One calorie i ...
heat
... • How is energy being transferred from: (a) heating plate to beaker (b) beaker to water (c) water to thermometer (d) water to thermometer • Describe the color of the hot plate after boiling the water. • What form of energy transfer is causing the heating plate to change color? ...
... • How is energy being transferred from: (a) heating plate to beaker (b) beaker to water (c) water to thermometer (d) water to thermometer • Describe the color of the hot plate after boiling the water. • What form of energy transfer is causing the heating plate to change color? ...
Name - Net Start Class
... temperature of 25oC. The final temperature of both the metal and the water is 45oC. a. What will happen to the temperature of the piece of metal? decrease b. What will happen to the temperature of the water? increase c. What is the specific heat of the metal? Q = m Cp T 2500 g * 4.184 j/goC * 20oC ...
... temperature of 25oC. The final temperature of both the metal and the water is 45oC. a. What will happen to the temperature of the piece of metal? decrease b. What will happen to the temperature of the water? increase c. What is the specific heat of the metal? Q = m Cp T 2500 g * 4.184 j/goC * 20oC ...
Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia is elevated body temperature due to failed thermoregulation that occurs when a body produces or absorbs more heat than it dissipates. Extreme temperature elevation then becomes a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment to prevent disability or death.The most common causes include heat stroke and adverse reactions to drugs. The former is an acute temperature elevation caused by exposure to excessive heat, or combination of heat and humidity, that overwhelms the heat-regulating mechanisms. The latter is a relatively rare side effect of many drugs, particularly those that affect the central nervous system. Malignant hyperthermia is a rare complication of some types of general anesthesia.Hyperthermia differs from fever in that the body's temperature set point remains unchanged. The opposite is hypothermia, which occurs when the temperature drops below that required to maintain normal metabolism.