* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PS1 Study Guide - Dublin City Schools
Passive solar building design wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic insulation wikipedia , lookup
Solar water heating wikipedia , lookup
Heat exchanger wikipedia , lookup
Thermal comfort wikipedia , lookup
Intercooler wikipedia , lookup
Building insulation materials wikipedia , lookup
Heat equation wikipedia , lookup
Thermal conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Copper in heat exchangers wikipedia , lookup
Cogeneration wikipedia , lookup
Solar air conditioning wikipedia , lookup
R-value (insulation) wikipedia , lookup
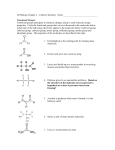
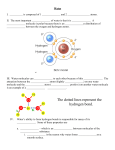
Name _______________________ Study Guide: Light and Sound Check-in 1: What is energy? What is thermal energy? Vocabulary: Energy- The ability to do work and cause a change in matter. Thermal Energy- Heat energy Temperature- The measure of thermal energy or how cool or warm things are. Conduction- Process by which heat or electricity is transferred through an object. Conductor- Materials where heat or electricity flows easily from molecule to molecule. Insulator- Material where heat does not flow easily from molecule to molecule. Key Concepts: • Heat, light, and sound forces are different types of energy. • Temperature is measured in degrees Fahrenheit and/or degrees Celsius. • Temperature is measured using a thermometer. As heat increases, the molecules of the colored liquid inside the thermometer expand, causing the liquid to rise. • Examples of good conductors are iron, aluminum, copper, some other metals, and water. • Examples of good insulators are plastic, rubber, air, wood, cork, chalk, etc. • Molecules speed up and move farther apart when heated. • Molecules slow down and move closer together when cooled. • Heat moves from warmer to cooler objects Name _______________________ Study Guide: Light and Sound Check-in 1: What is energy? What is thermal energy? Vocabulary: Energy- The ability to do work and cause a change in matter. Thermal Energy- Heat energy Temperature- The measure of thermal energy or how cool or warm things are. Conduction- Process by which heat or electricity is transferred through an object. Conductor- Materials where heat or electricity flows easily from molecule to molecule. Insulator- Material where heat does not flow easily from molecule to molecule. Key Concepts: • Heat, light, and sound forces are different types of energy. • Temperature is measured in degrees Fahrenheit and/or degrees Celsius. • Temperature is measured using a thermometer. As heat increases, the molecules of the colored liquid inside the thermometer expand, causing the liquid to rise. • Examples of good conductors are iron, aluminum, copper, some other metals, and water. • Examples of good insulators are plastic, rubber, air, wood, cork, chalk, etc. • Molecules speed up and move farther apart when heated. • Molecules slow down and move closer together when cooled. • Heat moves from warmer to cooler objects