19. BG_7.20 GRAM PO..
... •α-hemolytic; optochin sensitivity •Quellung test or capsular swelling reaction ...
... •α-hemolytic; optochin sensitivity •Quellung test or capsular swelling reaction ...
Virus or Bacteria... which needs the iron?
... Disease producing bacteria can be transmitted sexually, by contaminated food or water, by insect bites, or by casual contact such as touching, kissing, drinking after or breathing air exhaled by an infected person. Harmful pathogens are able to infiltrate the body by attaching directly on the surfac ...
... Disease producing bacteria can be transmitted sexually, by contaminated food or water, by insect bites, or by casual contact such as touching, kissing, drinking after or breathing air exhaled by an infected person. Harmful pathogens are able to infiltrate the body by attaching directly on the surfac ...
Am I Well Enough guidelines
... appropriate antibiotic therapy. 2. Exclude from extracurricular activities. ...
... appropriate antibiotic therapy. 2. Exclude from extracurricular activities. ...
Unit 2.2.2 – Health and Disease Immunity
... from injury insofar as the latter is usually instantaneously acquired.” “An alteration of a living body that impairs its functioning” “A condition of being sick from a particular cause” ...
... from injury insofar as the latter is usually instantaneously acquired.” “An alteration of a living body that impairs its functioning” “A condition of being sick from a particular cause” ...
Chest Physiotherapy: Physio in-service:
... Chest physio is contra-indicated in presence of cavities, haemoptysis, severe respiratory distress or within the first 2 weeks of anti-TB drug therapy Precautions: Avoid percussion techniques due to risk of haemoptysis and pneumothorax Do not suction in pt with active TB IPPB should not be giv ...
... Chest physio is contra-indicated in presence of cavities, haemoptysis, severe respiratory distress or within the first 2 weeks of anti-TB drug therapy Precautions: Avoid percussion techniques due to risk of haemoptysis and pneumothorax Do not suction in pt with active TB IPPB should not be giv ...
PUO
... (up to 20%) (up to 15%) (up to 15%) (up to 10%) (up to 10%) (up to 5%) (up to 5%) (up to 5%) (up to 5%) (up to 5%) (up to 5%) (up to 1%) (up to 1%) (up to 1%) ...
... (up to 20%) (up to 15%) (up to 15%) (up to 10%) (up to 10%) (up to 5%) (up to 5%) (up to 5%) (up to 5%) (up to 5%) (up to 5%) (up to 1%) (up to 1%) (up to 1%) ...
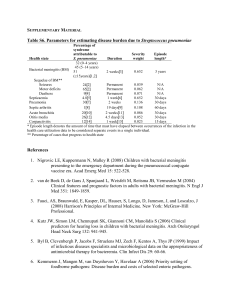
Table S6.
... * Episode length denotes the amount of time that must have elapsed between occurrences of the infection in the health care utilization data to be considered separate events in a single individual. ** Percentage of cases that progress to health state ...
... * Episode length denotes the amount of time that must have elapsed between occurrences of the infection in the health care utilization data to be considered separate events in a single individual. ** Percentage of cases that progress to health state ...
PLAGUES, PESTILENCE AND PUBLIC HEALTH
... hundreds as Europe's pestilential diseases were introduced, and by about 1520, most of them had crossed the Atlantic. These included measles, smallpox, typhus and influenza. Native Americans had their own diseases such as pinta, trypanosomiasis (Chagas' disease), bartonellosis (Carrion's disease, Or ...
... hundreds as Europe's pestilential diseases were introduced, and by about 1520, most of them had crossed the Atlantic. These included measles, smallpox, typhus and influenza. Native Americans had their own diseases such as pinta, trypanosomiasis (Chagas' disease), bartonellosis (Carrion's disease, Or ...
Document
... birth while its immune system develops. – Other example-rabies antibodies when you are bitten but you must get treatment shots to cure it ...
... birth while its immune system develops. – Other example-rabies antibodies when you are bitten but you must get treatment shots to cure it ...
3.1 Bacteria and viruses flashcards
... the disease from host to another? 77) What is an example of vector transmission? 78) What is an organism that causes disease? 79) The type of pathogen that only causes disease when they have an opportunity? 80) What are some STD viruses? 81) What is the virus that infects white blood cells? 82) What ...
... the disease from host to another? 77) What is an example of vector transmission? 78) What is an organism that causes disease? 79) The type of pathogen that only causes disease when they have an opportunity? 80) What are some STD viruses? 81) What is the virus that infects white blood cells? 82) What ...
Immune system
... (Steinman) Immune system the body defense against infections organisms and other invaders, the immune system is made up of a network of cells, tissues and organs that work together to protect the body. ...
... (Steinman) Immune system the body defense against infections organisms and other invaders, the immune system is made up of a network of cells, tissues and organs that work together to protect the body. ...
Holyrood Secondary School Higher Human Biology Unit 4
... (ii) The second injection caused a higher concentration of antibody to be produced than the first injection. Identify two other differences in the response to the second injection. ...
... (ii) The second injection caused a higher concentration of antibody to be produced than the first injection. Identify two other differences in the response to the second injection. ...
Treatment of Human Bites
... 2. Occlusive bites – bites that break the skin on a body part. Infection rates with these are usually lower than with fight bites. Occlusive bites, however, to the hand need greater attention, as infection rate tends to be higher with them than other occlusive bites. Human bites frequently cause inf ...
... 2. Occlusive bites – bites that break the skin on a body part. Infection rates with these are usually lower than with fight bites. Occlusive bites, however, to the hand need greater attention, as infection rate tends to be higher with them than other occlusive bites. Human bites frequently cause inf ...
History of Health Care - Lemon Bay High School
... • Priestly discovered the element oxygen. • Ben Franklin invented bifocals for glasses. • Lind prescribed limes to prevent scurvy. • Jenner developed first smallpox vaccine. • Average life span = 40 – 50 years. ...
... • Priestly discovered the element oxygen. • Ben Franklin invented bifocals for glasses. • Lind prescribed limes to prevent scurvy. • Jenner developed first smallpox vaccine. • Average life span = 40 – 50 years. ...
TOXOPLASMOSIS
... Tissue cysts: Tissue cysts are found most commonly in the brain and in skeletal and cardiac muscle but can occur in any organ ...
... Tissue cysts: Tissue cysts are found most commonly in the brain and in skeletal and cardiac muscle but can occur in any organ ...
Office hours
... Office hours: M 10-12; T 3:30-5; W 10-11:30 Lecture and Discussion: T R 10:00-11:40am, Sci II 180 ...
... Office hours: M 10-12; T 3:30-5; W 10-11:30 Lecture and Discussion: T R 10:00-11:40am, Sci II 180 ...
PDF
... antibiotic and in vivo studies have shown that this novel antibiotic is not affected by either beta-lactam or common macrolide resistance mechanisms. Positive results for a Phase II trial with NXL103 in the treatment of community acquired pneumonia (CAP) were reported towards the end of 2008. NXL103 ...
... antibiotic and in vivo studies have shown that this novel antibiotic is not affected by either beta-lactam or common macrolide resistance mechanisms. Positive results for a Phase II trial with NXL103 in the treatment of community acquired pneumonia (CAP) were reported towards the end of 2008. NXL103 ...
Diseases of molluscs Parasitic diseases—Infection with
... Differential diagnosis The differential diagnostic table and the list of similar diseases appearing at the bottom of each disease page refer only to the diseases covered by this field guide. Gross signs observed might well be representative of a wider range of diseases not included here. Therefore, ...
... Differential diagnosis The differential diagnostic table and the list of similar diseases appearing at the bottom of each disease page refer only to the diseases covered by this field guide. Gross signs observed might well be representative of a wider range of diseases not included here. Therefore, ...
Clostridial diseases - Victorian Farmers Federation
... soil or faeces. The bacterial spores may also occur naturally in the gastrointestinal tract or in the tissue of healthy animals. The bacteria may live in the animal with no consequences, are then excreted in the manure and able to infect the surrounding environment. The bacteria in the gut will only ...
... soil or faeces. The bacterial spores may also occur naturally in the gastrointestinal tract or in the tissue of healthy animals. The bacteria may live in the animal with no consequences, are then excreted in the manure and able to infect the surrounding environment. The bacteria in the gut will only ...
Regents Biology Jonas Salk Developed first vaccine against polio
... throat became swollen and she collapsed. This allergic reaction occurred because her body (1) recognized an antigen in peanut butter and produced antibiotics against it (2) digested the white blood cells that can recognize an antigen in peanut butter (3) did not recognize an antigen in peanut butter ...
... throat became swollen and she collapsed. This allergic reaction occurred because her body (1) recognized an antigen in peanut butter and produced antibiotics against it (2) digested the white blood cells that can recognize an antigen in peanut butter (3) did not recognize an antigen in peanut butter ...
Acquired immunity
... Various specialized regions in the body produce immune system components. Humoral immunity is part of acquired immunity and relies on production of antibodies to attack pathogens. A small number of “memory” cells continually patrol the blood and produce antibodies in case of later infection. Cell- ...
... Various specialized regions in the body produce immune system components. Humoral immunity is part of acquired immunity and relies on production of antibodies to attack pathogens. A small number of “memory” cells continually patrol the blood and produce antibodies in case of later infection. Cell- ...
Role of Gluten Peptides
... Kagnoff MF. 2007. Celiac Disease: Pathogenesis of a Model Immunogenetic Disease. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 117(1): 41-49. Pietzak MM. 2005. Follow-up of Patients with Celiac Disease: Achieving Compliance with Treatment. Gastroenterology 128: S135-S141. Walker MM, Murray JA. 2011. An upd ...
... Kagnoff MF. 2007. Celiac Disease: Pathogenesis of a Model Immunogenetic Disease. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 117(1): 41-49. Pietzak MM. 2005. Follow-up of Patients with Celiac Disease: Achieving Compliance with Treatment. Gastroenterology 128: S135-S141. Walker MM, Murray JA. 2011. An upd ...
987Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKp) in
... Conclusion. CRKp infections occur more frequently in children with comorbidities, prolonged hospital stays and prior antibiotic exposure. Mortality is high. A meropenem containing regimen seems to be the best choice in severely ill children. ...
... Conclusion. CRKp infections occur more frequently in children with comorbidities, prolonged hospital stays and prior antibiotic exposure. Mortality is high. A meropenem containing regimen seems to be the best choice in severely ill children. ...
Infection

Infection is the invasion of an organism's body tissues by disease-causing agents, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to these organisms and the toxins they produce. Infectious disease, also known as transmissible disease or communicable disease, is illness resulting from an infection.Infections are caused by infectious agents including viruses, viroids, prions, bacteria, nematodes such as parasitic roundworms and pinworms, arthropods such as ticks, mites, fleas, and lice, fungi such as ringworm, and other macroparasites such as tapeworms and other helminths.Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response.Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as Infectious Disease.