specific defenses: the immune system
... the following questions. 1. Label each part of the figure in the spaces provided. a ...
... the following questions. 1. Label each part of the figure in the spaces provided. a ...
Document
... thought to form pores in cell membranes that allow antigens to gain access to the endogenous presentation pathway resulting in presentation by MHC class I and hence CTL activation. ...
... thought to form pores in cell membranes that allow antigens to gain access to the endogenous presentation pathway resulting in presentation by MHC class I and hence CTL activation. ...
Antigens and Antibodies, Cell Receptors
... FV region, variable loops of β-strands, three each on VL and VH Fc region - ensures that each antibody generates an ...
... FV region, variable loops of β-strands, three each on VL and VH Fc region - ensures that each antibody generates an ...
IMMUNE SYSTEM:
... 2. If pathogens get past the barrier of your skin, the inflammatory response helps attack the pathogens. It is called the body’s general defense. 3. A white blood cell that surrounds the pathogen and destroys it is called a phagocyte. 4. If the inflammatory response is not enough to overcome the pat ...
... 2. If pathogens get past the barrier of your skin, the inflammatory response helps attack the pathogens. It is called the body’s general defense. 3. A white blood cell that surrounds the pathogen and destroys it is called a phagocyte. 4. If the inflammatory response is not enough to overcome the pat ...
1133693644_460426
... • Antigen presenting cells (APCs) – Macrophages and dendritic cells kill microbes – Present intruding microorganisms to T cells ...
... • Antigen presenting cells (APCs) – Macrophages and dendritic cells kill microbes – Present intruding microorganisms to T cells ...
Natural (Innate) Immunity
... Historical background 1798, Jenner Cowpox vaccines, induced immunity against smallpox 1885, Louis Pasteur Vaccine against rabies • Other used Inactivated diphtheria toxins as a vaccine against diphtheria (the protective effect were found to be in the serum) • Serum factor called Antibody ...
... Historical background 1798, Jenner Cowpox vaccines, induced immunity against smallpox 1885, Louis Pasteur Vaccine against rabies • Other used Inactivated diphtheria toxins as a vaccine against diphtheria (the protective effect were found to be in the serum) • Serum factor called Antibody ...
IMMUNOLOGY 2010™ Poster Symposia Schedule
... CD8 T Cell Memory and Plasma Cell Responses Chemokines and Their Receptors in Health and Disease Cytokines II: Immunomodulatory Cytokines Effector Cells and Tissue Damage in Autoimmunity Host Defense: Innate Immune Receptors and Signal Transduction Immune Regulation of Host Immunity during Viral Inf ...
... CD8 T Cell Memory and Plasma Cell Responses Chemokines and Their Receptors in Health and Disease Cytokines II: Immunomodulatory Cytokines Effector Cells and Tissue Damage in Autoimmunity Host Defense: Innate Immune Receptors and Signal Transduction Immune Regulation of Host Immunity during Viral Inf ...
Chapter 21 The Immune System
... • New Terms: – Antigen: usually a protein found on the cell membrane of the pathogen that has attacked the body – Antibody: protein (nonliving) that reacts w/ antigen to mark the pathogen allowing it to be recognized & then eaten by a phagocyte ...
... • New Terms: – Antigen: usually a protein found on the cell membrane of the pathogen that has attacked the body – Antibody: protein (nonliving) that reacts w/ antigen to mark the pathogen allowing it to be recognized & then eaten by a phagocyte ...
Aspirations Diploma Plus High School
... Directions: Answer the questions below using your notes and knowledge of Biology 1. Some human white blood cells help destroy pathogenic bacteria by (1) causing mutations in the bacteria (3) producing toxins that compete with bacterial toxins (2) engulfing and digesting the bacteria (4) inserting pa ...
... Directions: Answer the questions below using your notes and knowledge of Biology 1. Some human white blood cells help destroy pathogenic bacteria by (1) causing mutations in the bacteria (3) producing toxins that compete with bacterial toxins (2) engulfing and digesting the bacteria (4) inserting pa ...
ch 40.2 notes - 4J Blog Server
... Specific defenses (immune response) Like security guard – deals with specific ...
... Specific defenses (immune response) Like security guard – deals with specific ...
Immunity Ch. 11.1-6
... 11.3 Antigen-presenting B & T cells • Recognizes antigens derived from pathogens. • If you have a secondary infection from the same or a similar pathogen, memory B and T cells will give you immunity. • This natural process of creating immunity is enhanced artificially by the use of vaccines. ...
... 11.3 Antigen-presenting B & T cells • Recognizes antigens derived from pathogens. • If you have a secondary infection from the same or a similar pathogen, memory B and T cells will give you immunity. • This natural process of creating immunity is enhanced artificially by the use of vaccines. ...
Acquired immunity
... Various specialized regions in the body produce immune system components. Humoral immunity is part of acquired immunity and relies on production of antibodies to attack pathogens. A small number of “memory” cells continually patrol the blood and produce antibodies in case of later infection. Cell- ...
... Various specialized regions in the body produce immune system components. Humoral immunity is part of acquired immunity and relies on production of antibodies to attack pathogens. A small number of “memory” cells continually patrol the blood and produce antibodies in case of later infection. Cell- ...
Section Assignment 1.3 Part C: Defence Systems
... White blood cells that kill virus-infected cells and tumor cells by cell-to-cell combat Digested invaders and fragments of white blood cells Promotes production of antibodies without causing disease Disease-causing agent, such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi Unicellular organisms that are neither pl ...
... White blood cells that kill virus-infected cells and tumor cells by cell-to-cell combat Digested invaders and fragments of white blood cells Promotes production of antibodies without causing disease Disease-causing agent, such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi Unicellular organisms that are neither pl ...
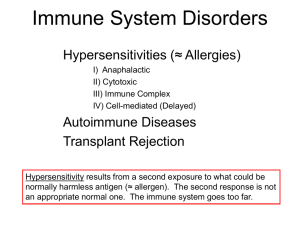
Immune System Disorders (Hypersensitivities ≈ Allergies)
... • IgG and IgM antibodies bind to foreign antigens on the surface of otherwise healthy human blood cell types. • This results in activation of the complement cascade via the classic pathway, which leads to cytolysis of blood cells with the foreign antigen. • Further antibody and complement C3b bindin ...
... • IgG and IgM antibodies bind to foreign antigens on the surface of otherwise healthy human blood cell types. • This results in activation of the complement cascade via the classic pathway, which leads to cytolysis of blood cells with the foreign antigen. • Further antibody and complement C3b bindin ...
Q9 Describe how the body defends against infection
... o Skin (prevents bacterial entry and growth) o Normal flora (prevent transient pathogenic organisms from colonizing the skin surface by competing for nutrients or secreting protective enzymes) o Mucous (traps bacteri ...
... o Skin (prevents bacterial entry and growth) o Normal flora (prevent transient pathogenic organisms from colonizing the skin surface by competing for nutrients or secreting protective enzymes) o Mucous (traps bacteri ...
Another person Direct contact: shaking hands 1. 2. Contaminated
... 7. What are four major groups of human pathogens? ...
... 7. What are four major groups of human pathogens? ...
Oral Delivery of the Factor VIII Gene: Immunotherapy for Hemophilia A
... administered in a canine hemophilia model to study therapeutic efficacy and immune modulation in parallel. Feeding of antigen can activate CD4+ T cells, generating an immune regulatory and anti-inflammatory response. Intestinal regulatory T cells such as CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ cells, Th3, or Tr1 cells secr ...
... administered in a canine hemophilia model to study therapeutic efficacy and immune modulation in parallel. Feeding of antigen can activate CD4+ T cells, generating an immune regulatory and anti-inflammatory response. Intestinal regulatory T cells such as CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ cells, Th3, or Tr1 cells secr ...
Helminth derived Immunodmodulator A therapeutic for immune-related diseases Overview
... Helminth derived Immunodmodulator A therapeutic for immune-related diseases Overview The technology relates to novel compositions and methods for modulating an immune response in order to prevent or treat disease and/or conditions where T lymphocyte cells have a pathogenic role, such as Th1 or ThIL- ...
... Helminth derived Immunodmodulator A therapeutic for immune-related diseases Overview The technology relates to novel compositions and methods for modulating an immune response in order to prevent or treat disease and/or conditions where T lymphocyte cells have a pathogenic role, such as Th1 or ThIL- ...