Part 1 MRCSI (Ophth) regulations and guidance notes
... work under Full or Temporary/Limited Registration in Ireland or the United Kingdom. ...
... work under Full or Temporary/Limited Registration in Ireland or the United Kingdom. ...
Nivolumab in treating advanced melanoma
... immunotherapy is distinct to that previously encountered with other anti-neoplastic agents. The result of the activation of the immune system against auto-antigens can lead to immune-related adverse events (irAEs). When they occur with single PD-1 inhibitors, they are typically lowgrade and manageab ...
... immunotherapy is distinct to that previously encountered with other anti-neoplastic agents. The result of the activation of the immune system against auto-antigens can lead to immune-related adverse events (irAEs). When they occur with single PD-1 inhibitors, they are typically lowgrade and manageab ...
Gut associated lymphoid tissue
... o Also it is usually a slow or delayed hypersensitivity reaction. ...
... o Also it is usually a slow or delayed hypersensitivity reaction. ...
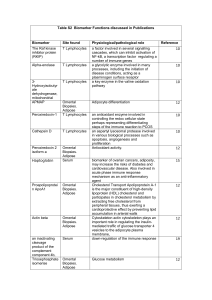
Table S2 Biomarker Functions discussed in Publications
... a factor involved in several signalling cascades, which can inhibit activation of NF-kB, a transcription factor regulating a number of immune genes a glycolytic enzyme involved in many processes, including the initiation of disease conditions, acting as a plasminogen surface receptor a key enzyme in ...
... a factor involved in several signalling cascades, which can inhibit activation of NF-kB, a transcription factor regulating a number of immune genes a glycolytic enzyme involved in many processes, including the initiation of disease conditions, acting as a plasminogen surface receptor a key enzyme in ...
Ch11AB
... Graded potentials are _________________, ____________________ changes in the membrane potential. Graded potentials can be __________________or _______________________. The ___________________ of a graded potential varies directly (is graded) with stimulus strength. (Slide 10) The ___________________ ...
... Graded potentials are _________________, ____________________ changes in the membrane potential. Graded potentials can be __________________or _______________________. The ___________________ of a graded potential varies directly (is graded) with stimulus strength. (Slide 10) The ___________________ ...
Richness and diversity of mammalian fungal communities shape
... the differentiation of naı̈ve T cells into effector Th-cell subtypes (Fig. 1). A healthy interaction between fungi and the host requires the interplay of several Ag-specific adaptive immune responses, the first step being the activation of the innate fungal detection system through the PRR. In tissu ...
... the differentiation of naı̈ve T cells into effector Th-cell subtypes (Fig. 1). A healthy interaction between fungi and the host requires the interplay of several Ag-specific adaptive immune responses, the first step being the activation of the innate fungal detection system through the PRR. In tissu ...
Document
... • Monoclonal antibodies are pure antibody preparations • Specific for a single antigenic determinant • Produced from descendents of a single cell • Hybridomas – cell hybrids made from a fusion of a tumor cell and a B cell • Have desirable properties of both parent cells – indefinite proliferation as ...
... • Monoclonal antibodies are pure antibody preparations • Specific for a single antigenic determinant • Produced from descendents of a single cell • Hybridomas – cell hybrids made from a fusion of a tumor cell and a B cell • Have desirable properties of both parent cells – indefinite proliferation as ...
Introduction to Psychology The Nervous System: Biological Control
... most important part of this lobe. This part of the brain plays an essential role in processing sensory information due to the eyes. Damage to this area can result in partial or complete blindness. The unlabeled parts of the brain not included with the lobes are known as the association areas. Th ...
... most important part of this lobe. This part of the brain plays an essential role in processing sensory information due to the eyes. Damage to this area can result in partial or complete blindness. The unlabeled parts of the brain not included with the lobes are known as the association areas. Th ...
The Lymphatic System
... • Lymph exits through efferent lymphatic vessels • Fewer efferent than afferent vessels causes flow to be slowed ...
... • Lymph exits through efferent lymphatic vessels • Fewer efferent than afferent vessels causes flow to be slowed ...
ISSN (Print): 2319-2526, Volume -3, Issue -1, 2014
... in wired local area networks. Their work is based on the negative selection part of the self-nonself model and some form of danger signal [11],[12]. TCP connections play the role of self and nonself cells. One connection is represented by a triplet encoding sender’s destination address, receiver’s d ...
... in wired local area networks. Their work is based on the negative selection part of the self-nonself model and some form of danger signal [11],[12]. TCP connections play the role of self and nonself cells. One connection is represented by a triplet encoding sender’s destination address, receiver’s d ...
The purpose of this summary is exclusively educational, to provide
... nickel activates TLR4 but not always induces hypersensitivity; imiquimod activates TLR7 but rarely induces hypersensitivity). ...
... nickel activates TLR4 but not always induces hypersensitivity; imiquimod activates TLR7 but rarely induces hypersensitivity). ...
Nervous System - The Beat@KUMC
... Performs surgical procedures on the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves ...
... Performs surgical procedures on the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves ...
Tilburg University Prenatal diethylstilbestrol
... persons with DES exposure. In addition, the number of reported colds, flu, and respiratory tract conditions proved to be three times as high as control groups. Noller (20) found three infectious conditions differing between the exposed and control group. Candida infections and otitis media were more ...
... persons with DES exposure. In addition, the number of reported colds, flu, and respiratory tract conditions proved to be three times as high as control groups. Noller (20) found three infectious conditions differing between the exposed and control group. Candida infections and otitis media were more ...
Stomatitis
... and is characterized by significant loss of surface gum tissue, frequently with inflammation (known as “ulcers”) • Oral eosinophilic granuloma (a mass or nodular lesion located in the mouth, containing a type of white-blood cell, called an eosinophil)—most commonly seen in the Siberian husky (may be ...
... and is characterized by significant loss of surface gum tissue, frequently with inflammation (known as “ulcers”) • Oral eosinophilic granuloma (a mass or nodular lesion located in the mouth, containing a type of white-blood cell, called an eosinophil)—most commonly seen in the Siberian husky (may be ...
Female sex hormones regulate the Th17 immune response to sperm
... of IL-17A and IL-22 by the splenocytes after sperm pulsing, whereas diestrus levels of E2 and/or P had no effect on the release of cytokines (Fig. 2A). We obtained similar results in the same experiments performed with C. albicans-pulsed splenocyte cultures (Fig. 2B). Therefore, E2 reduces secretion ...
... of IL-17A and IL-22 by the splenocytes after sperm pulsing, whereas diestrus levels of E2 and/or P had no effect on the release of cytokines (Fig. 2A). We obtained similar results in the same experiments performed with C. albicans-pulsed splenocyte cultures (Fig. 2B). Therefore, E2 reduces secretion ...
chapter 2 antigen/antibody interactions
... resistance to naïve recipients; such immunity is therefore not humoral.) This illustration also serves to define two distinct modes of adaptive immunity, namely ACTIVE IMMUNITY and PASSIVE IMMUNITY. Immunization of the mouse in the second line of Fig. 2-1 results in a state of "active" immunity; the ...
... resistance to naïve recipients; such immunity is therefore not humoral.) This illustration also serves to define two distinct modes of adaptive immunity, namely ACTIVE IMMUNITY and PASSIVE IMMUNITY. Immunization of the mouse in the second line of Fig. 2-1 results in a state of "active" immunity; the ...
Slide 1
... the eye by regulating nitric oxide, or NO. Varying concentrations of Leptin were tested for their ability to affect NO on certain cell lines. Each experiment yielded relatively similar results, showing that different concentrations of Leptin did not affect NO release from the cells. Therefore, our o ...
... the eye by regulating nitric oxide, or NO. Varying concentrations of Leptin were tested for their ability to affect NO on certain cell lines. Each experiment yielded relatively similar results, showing that different concentrations of Leptin did not affect NO release from the cells. Therefore, our o ...
Hormones
... Adrenal Medulla Adrenal medulla: Derived from embryonic neural crest ectoderm (same tissue that produces the sympathetic ganglia). Controlled by preganglionic sympathetic innervation (is like a postganglionic neuron!) Secretes adrenaline (aka epenephrine) (also secretes norepenephrine) ...
... Adrenal Medulla Adrenal medulla: Derived from embryonic neural crest ectoderm (same tissue that produces the sympathetic ganglia). Controlled by preganglionic sympathetic innervation (is like a postganglionic neuron!) Secretes adrenaline (aka epenephrine) (also secretes norepenephrine) ...
Introduction to Neurotransmitters
... Neurotransmission • When an electrical impulse travels down the axon of the neuron, it releases neurotransmitters which cross the synapse between the neurons • Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers which transmit information over the synapses from one neuron to another. ...
... Neurotransmission • When an electrical impulse travels down the axon of the neuron, it releases neurotransmitters which cross the synapse between the neurons • Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers which transmit information over the synapses from one neuron to another. ...
Psychoneuroimmunology

Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI), also referred to as psychoendoneuroimmunology (PENI), is the study of the interaction between psychological processes and the nervous and immune systems of the human body. PNI takes an interdisciplinary approach, incorporating psychology, neuroscience, immunology, physiology, genetics, pharmacology, molecular biology, psychiatry, behavioral medicine, infectious diseases, endocrinology, and rheumatology.The main interests of PNI are the interactions between the nervous and immune systems and the relationships between mental processes and health. PNI studies, among other things, the physiological functioning of the neuroimmune system in health and disease; disorders of the neuroimmune system (autoimmune diseases; hypersensitivities; immune deficiency); and the physical, chemical and physiological characteristics of the components of the neuroimmune system in vitro, in situ, and in vivo.