Questions and missing material
... • gain of function = adds the amount or activity of a protein – Dominant change – New function – More active than wild type • achondroplasia: defect in fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 – Produced more than normally • Expressed at the wrong time during development, in wrong tissues, in exceptional ...
... • gain of function = adds the amount or activity of a protein – Dominant change – New function – More active than wild type • achondroplasia: defect in fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 – Produced more than normally • Expressed at the wrong time during development, in wrong tissues, in exceptional ...
Hands-on Exercise: Locating Protein Information
... Locate five experimentally verified Ser/Thr/Tyr phosphorylation sites in this protein. ...
... Locate five experimentally verified Ser/Thr/Tyr phosphorylation sites in this protein. ...
Introduction Activity: From DNA to Protein File
... This overview provides a sequence of learning activities to help you understand that proteins and DNA are not just abstract concepts in biology textbooks, but rather crucial components of our bodies that affect functions and characteristics that you are familiar with. You will learn about the functi ...
... This overview provides a sequence of learning activities to help you understand that proteins and DNA are not just abstract concepts in biology textbooks, but rather crucial components of our bodies that affect functions and characteristics that you are familiar with. You will learn about the functi ...
The World of Chemistry
... 1. What are some of the ways mentioned that proteins are used in our bodies? ...
... 1. What are some of the ways mentioned that proteins are used in our bodies? ...
Syllabus
... This laboratory for majors in Chemical Biology and Biochemistry and Molecular Biology is designed to have students learn the theory and practicality of modern laboratory science by investigation of unknown properties of the yeast kinesin Cin8. The course breadth covers Molecular and Cell Biology wit ...
... This laboratory for majors in Chemical Biology and Biochemistry and Molecular Biology is designed to have students learn the theory and practicality of modern laboratory science by investigation of unknown properties of the yeast kinesin Cin8. The course breadth covers Molecular and Cell Biology wit ...
Notes from Lecture 1 - Tufts Computer Science
... Genes are the parts of the DNA that code for proteins. You can get different proteins from the same portion of DNA via splicing. ...
... Genes are the parts of the DNA that code for proteins. You can get different proteins from the same portion of DNA via splicing. ...
Bioinformatics Needs for the post
... differentiates into the ~300 different types of cells that make up an adult body. • With a few exceptions all of these cells contain the complete human genome, but express only a subset of the genes. • Gene expression patterns are determined largely by cell type, and vice versa. ...
... differentiates into the ~300 different types of cells that make up an adult body. • With a few exceptions all of these cells contain the complete human genome, but express only a subset of the genes. • Gene expression patterns are determined largely by cell type, and vice versa. ...
Key concepts_Protein processing and modification
... Much processing and modification occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum or the Golgi apparatus; this requires directed transport across membranes. Transport of proteins across membranes, known as translocation, utilizes multiprotein complexes called translocons. A number of different mechanisms are emp ...
... Much processing and modification occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum or the Golgi apparatus; this requires directed transport across membranes. Transport of proteins across membranes, known as translocation, utilizes multiprotein complexes called translocons. A number of different mechanisms are emp ...
Ribosomes 2
... Located on the Rough ER and in the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells and move freely in prokaryotic cells ...
... Located on the Rough ER and in the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells and move freely in prokaryotic cells ...
S1 Table - PLoS ONE
... regulator of cellular and systemic homeostatic response to hypoxia by activating transcription of many genes including those involved in energy metabolism, angiogenesis, apoptosis, and other genes whose protein products increase oxygen delivery or facilitate metabolic adaptation to hypoxia ...
... regulator of cellular and systemic homeostatic response to hypoxia by activating transcription of many genes including those involved in energy metabolism, angiogenesis, apoptosis, and other genes whose protein products increase oxygen delivery or facilitate metabolic adaptation to hypoxia ...
Protein Function Foldable Activity
... Proteins are essential for building up body tissues - including muscles! ...
... Proteins are essential for building up body tissues - including muscles! ...
Designer enzymes Donald Hilvert ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
... understand the rules of protein folding, and our knowledge of structure-function relationships in these macromolecules is at best incomplete. Nature has solved the problem of protein design through the mechanism of Darwinian evolution. From primitive precursors, recursive cycles of mutation, selecti ...
... understand the rules of protein folding, and our knowledge of structure-function relationships in these macromolecules is at best incomplete. Nature has solved the problem of protein design through the mechanism of Darwinian evolution. From primitive precursors, recursive cycles of mutation, selecti ...
3-in-1: A novel approach to study membrane protein pharmacology
... Membrane proteins make up about 25% of all proteins encoded by the human genome and are considered major drug targets. One type of membrane protein, the family of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs), mediates crucial functions in the nervous system and has been implicated a numerous diseases. Most LGI ...
... Membrane proteins make up about 25% of all proteins encoded by the human genome and are considered major drug targets. One type of membrane protein, the family of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs), mediates crucial functions in the nervous system and has been implicated a numerous diseases. Most LGI ...
Unit2Day2
... cave fish populations is caused by independently derived mutations that prevents the Oca2 gene from producing a functional protein (LOF mutations) ...
... cave fish populations is caused by independently derived mutations that prevents the Oca2 gene from producing a functional protein (LOF mutations) ...
FROM TRAIT TO PROTEIN - CLASSROOM
... Part I Proteins are large, complex macromolecules that play critical roles in the body. Proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids that can be combined to make a prot ...
... Part I Proteins are large, complex macromolecules that play critical roles in the body. Proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids that can be combined to make a prot ...
proteins——Echo,Jason,Philip
... B)immune(means use antibodies to prevent something bad for us) C)genetic D)regulation Genetic effect comes from the nucleic acid rather than proteins. ...
... B)immune(means use antibodies to prevent something bad for us) C)genetic D)regulation Genetic effect comes from the nucleic acid rather than proteins. ...
Proteins and Nucleic Acids Proteins (pp.46-48) Monomer
... Outline of Information to pull out of pp. 46-50 in Text book ...
... Outline of Information to pull out of pp. 46-50 in Text book ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
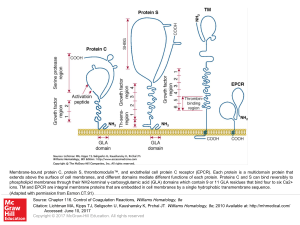
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
Rational Drug Design
... General drug design How to shut down a particular enzyme Antibacterials- penicillin ...
... General drug design How to shut down a particular enzyme Antibacterials- penicillin ...
Cell Structure Differences
... Cellular Structures and Functions There is an intricate network of membrane-bounded organelles in eukaryotic cells, each with a specific function. Organelles keep related biochemicals and structures close together to help them function more efficiently. This handout outlines the major animal cell or ...
... Cellular Structures and Functions There is an intricate network of membrane-bounded organelles in eukaryotic cells, each with a specific function. Organelles keep related biochemicals and structures close together to help them function more efficiently. This handout outlines the major animal cell or ...
Protein moonlighting

Protein moonlighting (or gene sharing) is a phenomenon by which a protein can perform more than one function. Ancestral moonlighting proteins originally possessed a single function but through evolution, acquired additional functions. Many proteins that moonlight are enzymes; others are receptors, ion channels or chaperones. The most common primary function of moonlighting proteins is enzymatic catalysis, but these enzymes have acquired secondary non-enzymatic roles. Some examples of functions of moonlighting proteins secondary to catalysis include signal transduction, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, motility, and structural.Protein moonlighting may occur widely in nature. Protein moonlighting through gene sharing differs from the use of a single gene to generate different proteins by alternative RNA splicing, DNA rearrangement, or post-translational processing. It is also different from multifunctionality of the protein, in which the protein has multiple domains, each serving a different function. Protein moonlighting by gene sharing means that a gene may acquire and maintain a second function without gene duplication and without loss of the primary function. Such genes are under two or more entirely different selective constraints.Various techniques have been used to reveal moonlighting functions in proteins. The detection of a protein in unexpected locations within cells, cell types, or tissues may suggest that a protein has a moonlighting function. Furthermore, sequence or structure homology of a protein may be used to infer both primary function as well as secondary moonlighting functions of a protein.The most well-studied examples of gene sharing are crystallins. These proteins, when expressed at low levels in many tissues function as enzymes, but when expressed at high levels in eye tissue, become densely packed and thus form lenses. While the recognition of gene sharing is relatively recent—the term was coined in 1988, after crystallins in chickens and ducks were found to be identical to separately identified enzymes—recent studies have found many examples throughout the living world. Joram Piatigorsky has suggested that many or all proteins exhibit gene sharing to some extent, and that gene sharing is a key aspect of molecular evolution. The genes encoding crystallins must maintain sequences for catalytic function and transparency maintenance function.Inappropriate moonlighting is a contributing factor in some genetic diseases, and moonlighting provides a possible mechanism by which bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.