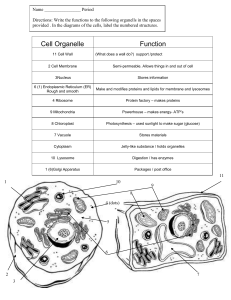
Cell Organelle
... Directions: Write the functions to the following organells in the spaces provided . In the diagrams of the cells, label the numbered structures. ...
... Directions: Write the functions to the following organells in the spaces provided . In the diagrams of the cells, label the numbered structures. ...
Stellingen behorende bij het proefschrift Liprin
... Liprin-alpha proteins regulate neuronal development and synapse function 1. All liprin proteins are not created equal. 2. Connecting cell adhesion molecules to the neuronal cytoskeleton is critical for axon growth and branching. 3. Some proteins function by disappearing rather than arriving. 4. Alth ...
... Liprin-alpha proteins regulate neuronal development and synapse function 1. All liprin proteins are not created equal. 2. Connecting cell adhesion molecules to the neuronal cytoskeleton is critical for axon growth and branching. 3. Some proteins function by disappearing rather than arriving. 4. Alth ...
Homework Exercise 6 1(a). Name the “building blocks” of a protein
... Cell Biology Homework – Key Area: Proteins and Enzymes ...
... Cell Biology Homework – Key Area: Proteins and Enzymes ...
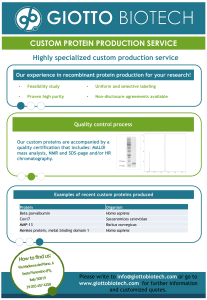
custom protein production service
... CUSTOM PROTEIN PRODUCTION SERVICE Highly specialized custom production service Our experience in recombinant protein production for your research! ...
... CUSTOM PROTEIN PRODUCTION SERVICE Highly specialized custom production service Our experience in recombinant protein production for your research! ...
Ch 4 Reading Guide
... 2. Give three reasons it is important to know the primary sequence of a protein. 3. Give a chemical explanation of why a peptide bond is planar. 4. Why are almost all peptide bonds in proteins trans rather than cis. 5. Regular, folded segments of amino acids near one another in linear sequence is ca ...
... 2. Give three reasons it is important to know the primary sequence of a protein. 3. Give a chemical explanation of why a peptide bond is planar. 4. Why are almost all peptide bonds in proteins trans rather than cis. 5. Regular, folded segments of amino acids near one another in linear sequence is ca ...
Key Points Folding
... Key Points Prions and Protein Folding • Protein structure (primary, secondary, tertiary) • Proteins have many possible conformations (ways to fold up into a 3D structure) • Proteins can spontaneously fold into the correct (biologically functional) 3D structure demonstrated by Christian Anfinsen in t ...
... Key Points Prions and Protein Folding • Protein structure (primary, secondary, tertiary) • Proteins have many possible conformations (ways to fold up into a 3D structure) • Proteins can spontaneously fold into the correct (biologically functional) 3D structure demonstrated by Christian Anfinsen in t ...
Chapter9.2a
... Beadle and Tatum • George Beadle and Edward Tatum, 1941 • Exposed spores of Neurospora crassa (a bread mold) to X-rays or UV radiation and studied the resulting mutations • Each mutant has specific nutrition needs • Discovered that each mutant strain differed by only one gene • Beadle and Tatum wer ...
... Beadle and Tatum • George Beadle and Edward Tatum, 1941 • Exposed spores of Neurospora crassa (a bread mold) to X-rays or UV radiation and studied the resulting mutations • Each mutant has specific nutrition needs • Discovered that each mutant strain differed by only one gene • Beadle and Tatum wer ...
Protein
... Protein Foods high in protein are Animal products, nuts, lentils, soy, dairy, cheese ...
... Protein Foods high in protein are Animal products, nuts, lentils, soy, dairy, cheese ...
Elise Young: Animal & Range Sciences
... Elise Young: Animal & Range Sciences Mentor: David Sands -- Plant Sciences & Plant Pathology Linking common factors in the phenomenon of protein clumping observed in several diseases Proteins perform many important functions at the cellular level. However, if proteins do not fold properly, they are ...
... Elise Young: Animal & Range Sciences Mentor: David Sands -- Plant Sciences & Plant Pathology Linking common factors in the phenomenon of protein clumping observed in several diseases Proteins perform many important functions at the cellular level. However, if proteins do not fold properly, they are ...
20150819105285
... R groups of a few of the amino acids that are in the active site catalyze the conversion of substrate to product, then product leaves. One enzyme typically acts on about a thousand substrate molecules per second! ...
... R groups of a few of the amino acids that are in the active site catalyze the conversion of substrate to product, then product leaves. One enzyme typically acts on about a thousand substrate molecules per second! ...
Proteins - Wesleyan College Faculty
... http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/dna/transcribe/ ...
... http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/dna/transcribe/ ...
Document
... b.) in the introns? Generally speaking…No. BUT! There are those CRITICAL consensus splice junction sequences at the exon-intron boundary that are necessary for proper splicing! So, the book says Yes. c.) in the promoter? Ask yourself—What acts at the promoter?! RNA Polymerase…Okay, there are some cr ...
... b.) in the introns? Generally speaking…No. BUT! There are those CRITICAL consensus splice junction sequences at the exon-intron boundary that are necessary for proper splicing! So, the book says Yes. c.) in the promoter? Ask yourself—What acts at the promoter?! RNA Polymerase…Okay, there are some cr ...
For complex multicellular organisms to function, individual
... Michael Hinczewski, Case Western Reserve University ...
... Michael Hinczewski, Case Western Reserve University ...
The human kinome and all its associated signaling proteins
... kinases involved largely in cell cycle control in fungi, mammals and other eukaryotes. hNek5 is a new member of the human Nek family of yet unknown function. Analysis of RT-PCR products showed that hNek5 mRNA was expressed in asynchronous HeLa cells, but, the expression was strongly regulated during ...
... kinases involved largely in cell cycle control in fungi, mammals and other eukaryotes. hNek5 is a new member of the human Nek family of yet unknown function. Analysis of RT-PCR products showed that hNek5 mRNA was expressed in asynchronous HeLa cells, but, the expression was strongly regulated during ...
asdfgfghrted * *** *** * ts
... Reminder - protein structure • The primary structure of a protein is its sequence of amino acids, e.g. Glu-Asp-Gly-Leu-Asp---• The secondary structure is how the chain of AAs coils up into helices, loops and sheets • The tertiary structure is the 3-dimensional folding of the secondary structures • ...
... Reminder - protein structure • The primary structure of a protein is its sequence of amino acids, e.g. Glu-Asp-Gly-Leu-Asp---• The secondary structure is how the chain of AAs coils up into helices, loops and sheets • The tertiary structure is the 3-dimensional folding of the secondary structures • ...
Clp proteins in photosynthetic organisms: An essential family of
... Molecular chaperones and proteases are vital for regulating the function and structure of most proteins within a cell. They are found in all organisms and are separated into many different families. One such family is Clp, which in photosynthetic organisms plays an essential role for cell function a ...
... Molecular chaperones and proteases are vital for regulating the function and structure of most proteins within a cell. They are found in all organisms and are separated into many different families. One such family is Clp, which in photosynthetic organisms plays an essential role for cell function a ...
" Exploring the Unique Dual Function and the Evolutionary
... Instituto Mercedes y Martín Ferreyra, Argentina Endocytosis and lysosomal protein trafficking is essential in pathogenic parasites since it is directly linked to vital parasite-specific processes, e.g. host cell invasion, nutrition, and cell differentiation into resistant stages, as in the case of G ...
... Instituto Mercedes y Martín Ferreyra, Argentina Endocytosis and lysosomal protein trafficking is essential in pathogenic parasites since it is directly linked to vital parasite-specific processes, e.g. host cell invasion, nutrition, and cell differentiation into resistant stages, as in the case of G ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... Example: lac operon in E. coli, control genes that code for proteins that break down lactose for food • Lac operons are turned on by lactose and turned ...
... Example: lac operon in E. coli, control genes that code for proteins that break down lactose for food • Lac operons are turned on by lactose and turned ...
Name: Date: Class Period: Video questions: Video 1: Gene
... What is a regulatory gene? What is an example of a regulatory sequence? What is lactose? What does it mean when a gene is expressed? What is the function of the TATA box? What is the function of an operator sequence? Why would bacteria want to make enzymes (proteins) that break down lactose only whe ...
... What is a regulatory gene? What is an example of a regulatory sequence? What is lactose? What does it mean when a gene is expressed? What is the function of the TATA box? What is the function of an operator sequence? Why would bacteria want to make enzymes (proteins) that break down lactose only whe ...
14-3-3 Sigma (S7323) - Datasheet - Sigma
... protein 1, HME1, SFN Product Description The 14-3-3 proteins are a multifunctional protein family composed of seven mammalian isoforms, which interact with over 200 different intracellular molecules including kinases, phosphatases, transcription factors, scaffold proteins, and DNA. 14-3-3 proteins a ...
... protein 1, HME1, SFN Product Description The 14-3-3 proteins are a multifunctional protein family composed of seven mammalian isoforms, which interact with over 200 different intracellular molecules including kinases, phosphatases, transcription factors, scaffold proteins, and DNA. 14-3-3 proteins a ...
Life’s molecular diversity is based on the properties of carbon 8/25/2011 1
... • Defensive proteins: The antibodies of the immune system • Signal proteins: Such as hormones that coordinate body activity ...
... • Defensive proteins: The antibodies of the immune system • Signal proteins: Such as hormones that coordinate body activity ...
7.2.A1 The promoter as an example of non
... operator. RNA polymerase binds to the _____________ allowing the genes that produce proteins involved in lactose metabolism ___________ be transcribed. ...
... operator. RNA polymerase binds to the _____________ allowing the genes that produce proteins involved in lactose metabolism ___________ be transcribed. ...
Heller’s-ring-test
... aromatic amino acids. It can be obtained by treating the proteins with other acids like HCl and H2SO4. ...
... aromatic amino acids. It can be obtained by treating the proteins with other acids like HCl and H2SO4. ...
Protein moonlighting

Protein moonlighting (or gene sharing) is a phenomenon by which a protein can perform more than one function. Ancestral moonlighting proteins originally possessed a single function but through evolution, acquired additional functions. Many proteins that moonlight are enzymes; others are receptors, ion channels or chaperones. The most common primary function of moonlighting proteins is enzymatic catalysis, but these enzymes have acquired secondary non-enzymatic roles. Some examples of functions of moonlighting proteins secondary to catalysis include signal transduction, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, motility, and structural.Protein moonlighting may occur widely in nature. Protein moonlighting through gene sharing differs from the use of a single gene to generate different proteins by alternative RNA splicing, DNA rearrangement, or post-translational processing. It is also different from multifunctionality of the protein, in which the protein has multiple domains, each serving a different function. Protein moonlighting by gene sharing means that a gene may acquire and maintain a second function without gene duplication and without loss of the primary function. Such genes are under two or more entirely different selective constraints.Various techniques have been used to reveal moonlighting functions in proteins. The detection of a protein in unexpected locations within cells, cell types, or tissues may suggest that a protein has a moonlighting function. Furthermore, sequence or structure homology of a protein may be used to infer both primary function as well as secondary moonlighting functions of a protein.The most well-studied examples of gene sharing are crystallins. These proteins, when expressed at low levels in many tissues function as enzymes, but when expressed at high levels in eye tissue, become densely packed and thus form lenses. While the recognition of gene sharing is relatively recent—the term was coined in 1988, after crystallins in chickens and ducks were found to be identical to separately identified enzymes—recent studies have found many examples throughout the living world. Joram Piatigorsky has suggested that many or all proteins exhibit gene sharing to some extent, and that gene sharing is a key aspect of molecular evolution. The genes encoding crystallins must maintain sequences for catalytic function and transparency maintenance function.Inappropriate moonlighting is a contributing factor in some genetic diseases, and moonlighting provides a possible mechanism by which bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.