Chemistry - WISE @ UC
... Research in the Dima group focuses on understanding the role of various structural and cellular factors in the mechanical response of biological molecules ranging from small multi-domain proteins to large fibrillar assemblies that play crucial roles in fundamental processes such as the maintenance o ...
... Research in the Dima group focuses on understanding the role of various structural and cellular factors in the mechanical response of biological molecules ranging from small multi-domain proteins to large fibrillar assemblies that play crucial roles in fundamental processes such as the maintenance o ...
Loose Ends on Chapters 3,5,6
... • Dipicolinic acid theoretically may contribute to the stability of the nucleic acids which is a contributory to the spore’s survival- The Ca and the dipicolinic acid may enhance the activity of DNA binding proteins that are vital to the spore’s ability to resist radiation • Calcium contributes to t ...
... • Dipicolinic acid theoretically may contribute to the stability of the nucleic acids which is a contributory to the spore’s survival- The Ca and the dipicolinic acid may enhance the activity of DNA binding proteins that are vital to the spore’s ability to resist radiation • Calcium contributes to t ...
Plasma Membrane
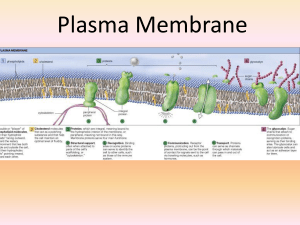
... 2. Enzymes – catalyze chemical reactions; may be on interior or exterior of the cell membrane; often grouped together for a chain reaction (called metabolic pathway) 3. Cell adhesion – proteins hook together to provide temporary or permanent connections; these connections referred to as junctions ...
... 2. Enzymes – catalyze chemical reactions; may be on interior or exterior of the cell membrane; often grouped together for a chain reaction (called metabolic pathway) 3. Cell adhesion – proteins hook together to provide temporary or permanent connections; these connections referred to as junctions ...
Harris presentation
... •Molecular Function — elemental activity or task nuclease, DNA binding, transcription factor •Biological Process — broad objective or goal mitosis, signal transduction, metabolism ...
... •Molecular Function — elemental activity or task nuclease, DNA binding, transcription factor •Biological Process — broad objective or goal mitosis, signal transduction, metabolism ...
Design of Novel Organocatalytic Click Chemistry: Biological and Medicinal Application.
... fluorescence tags has become a major tool in modern biotechnology and cell biology. Encoding fusion proteins with comparatively large fluorescent proteins (FPs) as originally developed by the Chalfie and Tsien groups is currently the most widely applied technique. As synthetic dyes typically offer b ...
... fluorescence tags has become a major tool in modern biotechnology and cell biology. Encoding fusion proteins with comparatively large fluorescent proteins (FPs) as originally developed by the Chalfie and Tsien groups is currently the most widely applied technique. As synthetic dyes typically offer b ...
Genome-wide association studies for microbial genomes
... Molecular function ↔ phenotype • Molecular systems biology – First determine protein functions – … then model how functions lead to phenotype ...
... Molecular function ↔ phenotype • Molecular systems biology – First determine protein functions – … then model how functions lead to phenotype ...
d) Structural Proteins
... c) Input the xxx.pdb file to Pymol (download from www.pymol.org) to see the molecular structure, notice its structural characters. d) Read the major reference paper (from www.pubmed.org) for this protein structure and the corresponding gene, summarize the connection of the structure and the protein ...
... c) Input the xxx.pdb file to Pymol (download from www.pymol.org) to see the molecular structure, notice its structural characters. d) Read the major reference paper (from www.pubmed.org) for this protein structure and the corresponding gene, summarize the connection of the structure and the protein ...
Biological Molecules- You are What You Eat:
... Animals store their energy in _________________________. It is made up of glucose left over from what we eat. It’s generally a short term store. ...
... Animals store their energy in _________________________. It is made up of glucose left over from what we eat. It’s generally a short term store. ...
Unit 3. Basic of Biopolymers (3) Control of Protein Function
... targeted to cellular compartments by signal sequences or by attachment of a lipid tail that inserts into membranes. directed to a complex of interacting proteins by a structural interaction domain Localization is a dynamic process and a given protein may be targeted to different compartments at diff ...
... targeted to cellular compartments by signal sequences or by attachment of a lipid tail that inserts into membranes. directed to a complex of interacting proteins by a structural interaction domain Localization is a dynamic process and a given protein may be targeted to different compartments at diff ...
point mutation - Northwest ISD Moodle
... • Deletion = lose one or more bases AUGCGUGUAUACGCAUGCGAGUGA MetArgValTyrAlaCysGluStop AUGCGUGUAUACGAUGCGAGUGA MetArgValTyrAspAlaSerGA ...
... • Deletion = lose one or more bases AUGCGUGUAUACGCAUGCGAGUGA MetArgValTyrAlaCysGluStop AUGCGUGUAUACGAUGCGAGUGA MetArgValTyrAspAlaSerGA ...
Protein thermodynamics: Are native proteins
... with respect to the fibril structures1. An immediate consequence of their finding is that large kinetic barriers between the folded functional states to aggregation-competent structures must exist (Fig. 1), which prevent transitions to the aggregation-prone structures during the lifetimes of protein ...
... with respect to the fibril structures1. An immediate consequence of their finding is that large kinetic barriers between the folded functional states to aggregation-competent structures must exist (Fig. 1), which prevent transitions to the aggregation-prone structures during the lifetimes of protein ...
Proteins
... amounts of SER in testes, ovaries, and adrenal glands; SER a storage site for calcium in skeletal cells Rough ER – ribosomes attached to ER; protein synthesis, folding, and some posttranslational modifications – addition of carbohydrates (glycosylation), membranebound polypeptides threaded through m ...
... amounts of SER in testes, ovaries, and adrenal glands; SER a storage site for calcium in skeletal cells Rough ER – ribosomes attached to ER; protein synthesis, folding, and some posttranslational modifications – addition of carbohydrates (glycosylation), membranebound polypeptides threaded through m ...
18CellStructsFL
... Animal Cell 7. What part of the cell is the arrow pointing to? A.Golgi B. Endoplasmic Reticulum C. Cell wall D. Cell membrane ...
... Animal Cell 7. What part of the cell is the arrow pointing to? A.Golgi B. Endoplasmic Reticulum C. Cell wall D. Cell membrane ...
EPO a Fc Human
... erythroid differentiation and initiating hemoglobin synthesis. This protein also has neuroprotective activity against a variety of potential brain injuries and antiapoptotic functions in several tissue types. Description: Erythropoietin-alpha Fc-Chimera Human Recombinant is produced in Chinese hamst ...
... erythroid differentiation and initiating hemoglobin synthesis. This protein also has neuroprotective activity against a variety of potential brain injuries and antiapoptotic functions in several tissue types. Description: Erythropoietin-alpha Fc-Chimera Human Recombinant is produced in Chinese hamst ...
Proteome analysis of cell nuclei enriched subcellular fraction of
... information for system biology analysis of complex molecular mechanisms involved in plant development, productivity and response to environmental stimuli. However, proteome of entire plant cell presents high demands on dynamic range and sensitivity of protein and analysis procedures. The problems en ...
... information for system biology analysis of complex molecular mechanisms involved in plant development, productivity and response to environmental stimuli. However, proteome of entire plant cell presents high demands on dynamic range and sensitivity of protein and analysis procedures. The problems en ...
A comprehensive analysis of protein
... 2) Unrecognized interactions have been identified between proteins involved in the same biological process. 3) The screen has provided clues for seeing how individual biological events are integrated into larger cellular process. ...
... 2) Unrecognized interactions have been identified between proteins involved in the same biological process. 3) The screen has provided clues for seeing how individual biological events are integrated into larger cellular process. ...
Διαφάνεια 1 - Aristotle University of Thessaloniki
... In patients with CF the viscous mucus that is produced from the epithelial cells, obstructs the ducts of the pancreas, the gastrointestinal tract, also the bile ducts and some of the salivary glands. So, it is difficult for their products to be secreted. Therefore, there is food maldigestion and ...
... In patients with CF the viscous mucus that is produced from the epithelial cells, obstructs the ducts of the pancreas, the gastrointestinal tract, also the bile ducts and some of the salivary glands. So, it is difficult for their products to be secreted. Therefore, there is food maldigestion and ...
Macromolecules and SPF groups
... to this in the planet; every culture based their food on starch. Cellulose - Beta Glucose are geometric isomers. Humans cannot digest cellulose. Plants use it for their structure like cell walls. ...
... to this in the planet; every culture based their food on starch. Cellulose - Beta Glucose are geometric isomers. Humans cannot digest cellulose. Plants use it for their structure like cell walls. ...
Chapter 2 Notes ch._2_lecture_notes_2005
... in cell signal and recognition factors and acting as molecules of immunity Carbohydrates serve as the major source of energy for most living organisms. When simple sugars combine to form polymers they can function as long term food storage molecules, as protective coverings for cells and organisms, ...
... in cell signal and recognition factors and acting as molecules of immunity Carbohydrates serve as the major source of energy for most living organisms. When simple sugars combine to form polymers they can function as long term food storage molecules, as protective coverings for cells and organisms, ...
Transport of Cytoplasmically Synthesized Proteins into Membranous
... – Target sequence N-X-S and N-X-T (X = P) ...
... – Target sequence N-X-S and N-X-T (X = P) ...
Protein moonlighting

Protein moonlighting (or gene sharing) is a phenomenon by which a protein can perform more than one function. Ancestral moonlighting proteins originally possessed a single function but through evolution, acquired additional functions. Many proteins that moonlight are enzymes; others are receptors, ion channels or chaperones. The most common primary function of moonlighting proteins is enzymatic catalysis, but these enzymes have acquired secondary non-enzymatic roles. Some examples of functions of moonlighting proteins secondary to catalysis include signal transduction, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, motility, and structural.Protein moonlighting may occur widely in nature. Protein moonlighting through gene sharing differs from the use of a single gene to generate different proteins by alternative RNA splicing, DNA rearrangement, or post-translational processing. It is also different from multifunctionality of the protein, in which the protein has multiple domains, each serving a different function. Protein moonlighting by gene sharing means that a gene may acquire and maintain a second function without gene duplication and without loss of the primary function. Such genes are under two or more entirely different selective constraints.Various techniques have been used to reveal moonlighting functions in proteins. The detection of a protein in unexpected locations within cells, cell types, or tissues may suggest that a protein has a moonlighting function. Furthermore, sequence or structure homology of a protein may be used to infer both primary function as well as secondary moonlighting functions of a protein.The most well-studied examples of gene sharing are crystallins. These proteins, when expressed at low levels in many tissues function as enzymes, but when expressed at high levels in eye tissue, become densely packed and thus form lenses. While the recognition of gene sharing is relatively recent—the term was coined in 1988, after crystallins in chickens and ducks were found to be identical to separately identified enzymes—recent studies have found many examples throughout the living world. Joram Piatigorsky has suggested that many or all proteins exhibit gene sharing to some extent, and that gene sharing is a key aspect of molecular evolution. The genes encoding crystallins must maintain sequences for catalytic function and transparency maintenance function.Inappropriate moonlighting is a contributing factor in some genetic diseases, and moonlighting provides a possible mechanism by which bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.