1 ENZYME LABS Introduction: Without enzymes chemical reactions
... and protein molecules in a watery solution. As we discussed in class, proteins are large organic molecules that are built as a chain (or polymer) of amino acids. The behavior and function of the protein is caused by the specific amino acids that are linked together in the chain. These amino acids re ...
... and protein molecules in a watery solution. As we discussed in class, proteins are large organic molecules that are built as a chain (or polymer) of amino acids. The behavior and function of the protein is caused by the specific amino acids that are linked together in the chain. These amino acids re ...
Chpt19_TxnlRegEuk.doc
... a. Recall from Part One of the course that most genes in eukaryotes are not expressed in any given tissue. Of the approximately 30,000 genes in humans, any particular tissue will express a few at high abundance (these are frequently tissue specific, e.g. globin genes in red cells) and up to a few th ...
... a. Recall from Part One of the course that most genes in eukaryotes are not expressed in any given tissue. Of the approximately 30,000 genes in humans, any particular tissue will express a few at high abundance (these are frequently tissue specific, e.g. globin genes in red cells) and up to a few th ...
RiceRBP: a resource for experimentally identified RNA
... RiceRBP (found at http://www.bioinformatics2.wsu.edu/RiceRBP or bioinformatics1.smb.wsu.edu/RiceRBP), a publicly accessible database for use by the scientific community (Morris et al., 2011). RiceRBP is the only database to our knowledge containing data and analysis tools dedicated to the study of ex ...
... RiceRBP (found at http://www.bioinformatics2.wsu.edu/RiceRBP or bioinformatics1.smb.wsu.edu/RiceRBP), a publicly accessible database for use by the scientific community (Morris et al., 2011). RiceRBP is the only database to our knowledge containing data and analysis tools dedicated to the study of ex ...
Golgi Apparatus
... Figure 3.24 Microtubules and microfilaments function in cell motility by interacting with motor molecules powered by ATP. ...
... Figure 3.24 Microtubules and microfilaments function in cell motility by interacting with motor molecules powered by ATP. ...
Bioinformatics: Network Analysis Comparative Network Analysis Luay Nakhleh, Rice University
... The second is based on empirical runs on randomized data. The randomized data are produced by random shuffling of the input interaction graphs of the two species, preserving their degree sequences, as well as random shuffling of the orthology relations, preserving the number of orthologs associated ...
... The second is based on empirical runs on randomized data. The randomized data are produced by random shuffling of the input interaction graphs of the two species, preserving their degree sequences, as well as random shuffling of the orthology relations, preserving the number of orthologs associated ...
Early cleavage stages
... What is the Evidence for Early Polarity • Anterior half and posterior half of embryo have different potentials shortly after fertilization – ligation experiments • Cut in half gives ends but no middles ...
... What is the Evidence for Early Polarity • Anterior half and posterior half of embryo have different potentials shortly after fertilization – ligation experiments • Cut in half gives ends but no middles ...
RNA-protein interaction
... synthesis on the ribosome) in the cell forms an important theme within the structural biology and biophysics group. ...
... synthesis on the ribosome) in the cell forms an important theme within the structural biology and biophysics group. ...
Chromatin, DNA methylation and neuron gene regulation — the
... Molecular links between DNA methylation and chromatin remodelling Activation or repression of gene transcription is correlated with the acetylation status of nucleosomal histone proteins, especially those in the vicinity of gene promoters. The enzymes that perform histone acetylation (histone acetyl ...
... Molecular links between DNA methylation and chromatin remodelling Activation or repression of gene transcription is correlated with the acetylation status of nucleosomal histone proteins, especially those in the vicinity of gene promoters. The enzymes that perform histone acetylation (histone acetyl ...
File
... The three enzymes involved in the metabolism of lactose are transcribed and expressed cAMP binds to CAP regulatory protein, causing it to bind to the promoter of the lac operon The enzymes needed for lactose metabolism must be transcribed when lactose is present cAMP levels increase because glucose ...
... The three enzymes involved in the metabolism of lactose are transcribed and expressed cAMP binds to CAP regulatory protein, causing it to bind to the promoter of the lac operon The enzymes needed for lactose metabolism must be transcribed when lactose is present cAMP levels increase because glucose ...
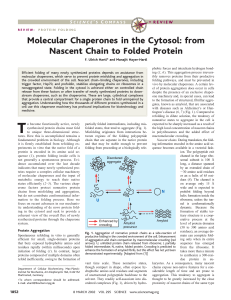
Molecular Chaperones in the Cytosol: from Nascent Chain to Folded
... trigger factor; N, native protein. Nascent chains probably interact generally with TF, and most small proteins (⬃65 to 80% of total) fold rapidly upon synthesis without further assistance. Longer chains (10 to 20% of total) interact subsequently with DnaK and DnaJ and fold upon one or several cycles ...
... trigger factor; N, native protein. Nascent chains probably interact generally with TF, and most small proteins (⬃65 to 80% of total) fold rapidly upon synthesis without further assistance. Longer chains (10 to 20% of total) interact subsequently with DnaK and DnaJ and fold upon one or several cycles ...
Yeast as a navigational aid in genome analysis
... et al., 1994) was found to contain similar ‘GC waves’, the centromere region again being AT-rich and the period of the oscillations being the same as that found for chromosome I11 (100 kb for a complete cycle). Most yeast chromosomes exhibit a similar variation in base composition which is found to ...
... et al., 1994) was found to contain similar ‘GC waves’, the centromere region again being AT-rich and the period of the oscillations being the same as that found for chromosome I11 (100 kb for a complete cycle). Most yeast chromosomes exhibit a similar variation in base composition which is found to ...
Phosphoproteomic analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana Hanna Klang Årstrand
... identified 249 ribosomal protein genes that encode 32 small subunit (S) proteins and 48 large subunit (L) proteins, in total 80 ribosomal proteins (Barakat et al. 2001). The genes are organized into multigene families with two and up to seven members with an average of three family members. Many fam ...
... identified 249 ribosomal protein genes that encode 32 small subunit (S) proteins and 48 large subunit (L) proteins, in total 80 ribosomal proteins (Barakat et al. 2001). The genes are organized into multigene families with two and up to seven members with an average of three family members. Many fam ...
as a PDF
... harmonin. The scaffold protein harmonin can bind directly to F-actin via its PST domain [5], a site present in harmonin b splice variants. Harmonin can also bind to actin indirectly via its PDZ1 domain by interaction with actin associated proteins (e.g., the molecular motor myosin VIIa) [13]. Since ...
... harmonin. The scaffold protein harmonin can bind directly to F-actin via its PST domain [5], a site present in harmonin b splice variants. Harmonin can also bind to actin indirectly via its PDZ1 domain by interaction with actin associated proteins (e.g., the molecular motor myosin VIIa) [13]. Since ...
FIBROUS PROTEINS
... • Collagen provides strength and structure. • Typical collagen molecule is a long, rigid structure in which three polypeptides (referred to as α-chains) are wound around one another in a rope like triple helix • The three polypeptide α-chains are held together by hydrogen bonds • Amino acid sequence ...
... • Collagen provides strength and structure. • Typical collagen molecule is a long, rigid structure in which three polypeptides (referred to as α-chains) are wound around one another in a rope like triple helix • The three polypeptide α-chains are held together by hydrogen bonds • Amino acid sequence ...
Biomolecular Structures and Modeling
... b. *Players: Name the key molecule(s) (proteins, nucleic acid, etc.) performing the function(s) listed above? Are there any other molecules mentioned in the article that interact with the molecule being studied – either facilitating or regulating the discussed function? Name the molecule(s). The alp ...
... b. *Players: Name the key molecule(s) (proteins, nucleic acid, etc.) performing the function(s) listed above? Are there any other molecules mentioned in the article that interact with the molecule being studied – either facilitating or regulating the discussed function? Name the molecule(s). The alp ...
Misfolding and Aggregation ofNewly Synthesized Proteins in the
... cytopathic effects on the folding of glycoproteins in the ER. We observed for p62 that the spontaneous aggregation after 6 h of transfection was highly temperature dependent : no aggregates were found at 32 ° C, whereas up to 50% of the proteins misfolded and aggregated at 37°C when expressed at a s ...
... cytopathic effects on the folding of glycoproteins in the ER. We observed for p62 that the spontaneous aggregation after 6 h of transfection was highly temperature dependent : no aggregates were found at 32 ° C, whereas up to 50% of the proteins misfolded and aggregated at 37°C when expressed at a s ...
Signaling by Serine/Threonine Kinase Receptors
... Receptors with intrinsic serine/threonine kinase activity ...
... Receptors with intrinsic serine/threonine kinase activity ...
Chemical genetics to chemical genomics: small
... further reading and involvement. The field will be described in general terms and then illustrated in detail in five important areas of biology. Genetics has been used widely to study biology by manipulating the biological system at the level of the gene. A gene commonly is defined as the ‘‘nucleic ...
... further reading and involvement. The field will be described in general terms and then illustrated in detail in five important areas of biology. Genetics has been used widely to study biology by manipulating the biological system at the level of the gene. A gene commonly is defined as the ‘‘nucleic ...
Structure and assembly of the spliceosomal small nuclear
... used to investigate pairwise interactions of the Sm proteins [33•,34•]. Kambach et al. [32••] have been able to arrange all seven Sm proteins within a seven-membered ring (Figure 1d) in a manner that is consistent with all the known pairwise interactions [33•,34•]. The heptameric ring is the only co ...
... used to investigate pairwise interactions of the Sm proteins [33•,34•]. Kambach et al. [32••] have been able to arrange all seven Sm proteins within a seven-membered ring (Figure 1d) in a manner that is consistent with all the known pairwise interactions [33•,34•]. The heptameric ring is the only co ...
Prokaryotic Gene Regulation
... "When I was warning about the danger ahead on Wall Street months ago because of the lack of oversight, Senator McCain was telling the Wall Street Journal -- and I quote -- 'I'm always for less regulation.' " – Sen. Barack Obama “Senator Obama was silent on the regulation of Fannie Mae and Freddie Ma ...
... "When I was warning about the danger ahead on Wall Street months ago because of the lack of oversight, Senator McCain was telling the Wall Street Journal -- and I quote -- 'I'm always for less regulation.' " – Sen. Barack Obama “Senator Obama was silent on the regulation of Fannie Mae and Freddie Ma ...
A 2 - Computer Science
... • the elementary unit of information • one of the most commonly used format • LOCUS: locus name/the length of the sequence/the molecule type/ GenBank division code/the date • DEFINITION:summarize the biology of the record genus species/product name/…. ACCESSION:An accession number is label that used ...
... • the elementary unit of information • one of the most commonly used format • LOCUS: locus name/the length of the sequence/the molecule type/ GenBank division code/the date • DEFINITION:summarize the biology of the record genus species/product name/…. ACCESSION:An accession number is label that used ...
Bioreactors and transgenic animals
... gives us the hypothetical ability to do things never contemplated before". Team of 20 top scientists, led by the H. Smith has constructed a synthetic chromosome based on the bacterium Mycoplasma genitalium, that is 381 genes long and contains 580,000 base pairs of genetic code. The synthetically rec ...
... gives us the hypothetical ability to do things never contemplated before". Team of 20 top scientists, led by the H. Smith has constructed a synthetic chromosome based on the bacterium Mycoplasma genitalium, that is 381 genes long and contains 580,000 base pairs of genetic code. The synthetically rec ...
The Proteasomes
... Yet in spite of these remarkable similarities, there are important differences. First, the two structures are not evolutionarily related. The amino acid sequences, along with the tertiary structure, of proteasome and chaperone subunits are quite different. Secondly, the functions are different. Wher ...
... Yet in spite of these remarkable similarities, there are important differences. First, the two structures are not evolutionarily related. The amino acid sequences, along with the tertiary structure, of proteasome and chaperone subunits are quite different. Secondly, the functions are different. Wher ...
Protein moonlighting

Protein moonlighting (or gene sharing) is a phenomenon by which a protein can perform more than one function. Ancestral moonlighting proteins originally possessed a single function but through evolution, acquired additional functions. Many proteins that moonlight are enzymes; others are receptors, ion channels or chaperones. The most common primary function of moonlighting proteins is enzymatic catalysis, but these enzymes have acquired secondary non-enzymatic roles. Some examples of functions of moonlighting proteins secondary to catalysis include signal transduction, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, motility, and structural.Protein moonlighting may occur widely in nature. Protein moonlighting through gene sharing differs from the use of a single gene to generate different proteins by alternative RNA splicing, DNA rearrangement, or post-translational processing. It is also different from multifunctionality of the protein, in which the protein has multiple domains, each serving a different function. Protein moonlighting by gene sharing means that a gene may acquire and maintain a second function without gene duplication and without loss of the primary function. Such genes are under two or more entirely different selective constraints.Various techniques have been used to reveal moonlighting functions in proteins. The detection of a protein in unexpected locations within cells, cell types, or tissues may suggest that a protein has a moonlighting function. Furthermore, sequence or structure homology of a protein may be used to infer both primary function as well as secondary moonlighting functions of a protein.The most well-studied examples of gene sharing are crystallins. These proteins, when expressed at low levels in many tissues function as enzymes, but when expressed at high levels in eye tissue, become densely packed and thus form lenses. While the recognition of gene sharing is relatively recent—the term was coined in 1988, after crystallins in chickens and ducks were found to be identical to separately identified enzymes—recent studies have found many examples throughout the living world. Joram Piatigorsky has suggested that many or all proteins exhibit gene sharing to some extent, and that gene sharing is a key aspect of molecular evolution. The genes encoding crystallins must maintain sequences for catalytic function and transparency maintenance function.Inappropriate moonlighting is a contributing factor in some genetic diseases, and moonlighting provides a possible mechanism by which bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.