Bio Chap 15 - mlfarrispsych
... produce a detachment from the self. – People with damage to the ACC and the insula may treat their mirror image as a companion, intruder, or stalker. – The insula and inferior parietal cortex appear to distinguish between self as agent and other as agent. • When subjects perceived they were controll ...
... produce a detachment from the self. – People with damage to the ACC and the insula may treat their mirror image as a companion, intruder, or stalker. – The insula and inferior parietal cortex appear to distinguish between self as agent and other as agent. • When subjects perceived they were controll ...
L8-Physiology of Sleep and EEG 2013
... Sleep spindles Spindles are groups of waves that occur during many sleep stages but especially in stage 2. They have frequencies in the upper levels of alpha or lower levels of beta. Lasting for a second or less, they increase in amplitude initially and then decrease slowly. The waveform resemb ...
... Sleep spindles Spindles are groups of waves that occur during many sleep stages but especially in stage 2. They have frequencies in the upper levels of alpha or lower levels of beta. Lasting for a second or less, they increase in amplitude initially and then decrease slowly. The waveform resemb ...
Anatomical and physiological bases of consciousness and sleep
... • Maintenance of consciousness, attention and regulation of wake-sleep cycle • Consciousness–awareness of environment and self = two aspects: 1. content of consciousness- representing cognitive mental functions that reflect the activity of the cerebral cortex 2. arousal and wakefulness –dependent on ...
... • Maintenance of consciousness, attention and regulation of wake-sleep cycle • Consciousness–awareness of environment and self = two aspects: 1. content of consciousness- representing cognitive mental functions that reflect the activity of the cerebral cortex 2. arousal and wakefulness –dependent on ...
SLEEP
... Beta waves, irregular, low amplitude, at 13-30 Hz seen during alert wakefulness and REM sleep Theta activity (3.5-7.5 Hz) in stage 1 sleep (transiting from awake to sleep) Delta waves – high amplitude, low frequency (<3.5 Hz) pattern seen in stage 3 and 4 sleep Sleep spindles – short burst of 12-14 ...
... Beta waves, irregular, low amplitude, at 13-30 Hz seen during alert wakefulness and REM sleep Theta activity (3.5-7.5 Hz) in stage 1 sleep (transiting from awake to sleep) Delta waves – high amplitude, low frequency (<3.5 Hz) pattern seen in stage 3 and 4 sleep Sleep spindles – short burst of 12-14 ...
sensor
... the skin it diffuses into the electrolyte. It reacts with water forming carbonic acid and immediately dissociates by the following equation. The changes in H in the electrolyte imply changes in pH. As the pH in the electrolyte changes, the voltage between the glass electrode and reference electrode ...
... the skin it diffuses into the electrolyte. It reacts with water forming carbonic acid and immediately dissociates by the following equation. The changes in H in the electrolyte imply changes in pH. As the pH in the electrolyte changes, the voltage between the glass electrode and reference electrode ...
Sensors in the field of Sleep
... For the pO2 reading oxygen diffuses to the platinum cathode through the electrodes membrane. A reduction in oxygen occurs as a result of the current generating process.This reduction generates a current which is fed into the pO2 channel and converted to a voltage, digitalized then passed to the micr ...
... For the pO2 reading oxygen diffuses to the platinum cathode through the electrodes membrane. A reduction in oxygen occurs as a result of the current generating process.This reduction generates a current which is fed into the pO2 channel and converted to a voltage, digitalized then passed to the micr ...
Unit 2: Biological Psychology
... What are neural networks and where are they found? What is the peripheral nervous system, and what does it do? What is the central nervous system, and what structures is it comprised of? What are the two components of the peripheral nervous system? What does the somatic nervous system do? What is th ...
... What are neural networks and where are they found? What is the peripheral nervous system, and what does it do? What is the central nervous system, and what structures is it comprised of? What are the two components of the peripheral nervous system? What does the somatic nervous system do? What is th ...
OL Chapter 2
... • Researchers can awaken people during or within 3 minutes of REM sleep for a vivid account of dreams • Dream: a sequence of images, emotions, and thoughts passing through a sleeping ...
... • Researchers can awaken people during or within 3 minutes of REM sleep for a vivid account of dreams • Dream: a sequence of images, emotions, and thoughts passing through a sleeping ...
Sleep Mar 19 2013x - Lakehead University
... The pontine nucleus, via the thalamus, activate different areas of the cortex, elicit images/emotions, and the cortex attempts to synthesize the disparate images into a coherent whole • This process can account for the often bizarre and nonsensical nature of many dreams; since they are triggered by ...
... The pontine nucleus, via the thalamus, activate different areas of the cortex, elicit images/emotions, and the cortex attempts to synthesize the disparate images into a coherent whole • This process can account for the often bizarre and nonsensical nature of many dreams; since they are triggered by ...
Slide 1
... in beats per quarter minute, and body movement (BM) in numbers per minute over 100 minutes of uninterrupted sleep. The interval from 242 to 273 minutes is considered the REM period, although eye movements are not continuous during that interval. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... in beats per quarter minute, and body movement (BM) in numbers per minute over 100 minutes of uninterrupted sleep. The interval from 242 to 273 minutes is considered the REM period, although eye movements are not continuous during that interval. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. ...
Part 2 - Kirkwood Community College
... – Stage 1 – eyes are closed and relaxation begins; the EEG shows alpha waves; one can be easily aroused – Stage 2 – EEG pattern is irregular with sleep spindles (high-voltage wave bursts); arousal is more difficult – Stage 3 – sleep deepens; theta and delta waves appear; vital signs decline; dreamin ...
... – Stage 1 – eyes are closed and relaxation begins; the EEG shows alpha waves; one can be easily aroused – Stage 2 – EEG pattern is irregular with sleep spindles (high-voltage wave bursts); arousal is more difficult – Stage 3 – sleep deepens; theta and delta waves appear; vital signs decline; dreamin ...
Chapter 9 Sleep and Biological Rhythms
... occipital) in addition to EEG activity, muscular paralysis, etc PGO waves are bursts of phasic electrical activity originating in the pons followed by activity in the LGN and visual cortex REM sleep controlled by mechanisms located within the pons: ...
... occipital) in addition to EEG activity, muscular paralysis, etc PGO waves are bursts of phasic electrical activity originating in the pons followed by activity in the LGN and visual cortex REM sleep controlled by mechanisms located within the pons: ...
States of Consciousness Ch. 5
... • 11 times more likely to fall behind in school • 10 times morel likely to drive • 2 times as likely to have unprotected sex ...
... • 11 times more likely to fall behind in school • 10 times morel likely to drive • 2 times as likely to have unprotected sex ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 40.1 Periodic activation in sleep cycles
... quarter minute, and body movement (BM) in numbers per minute over 100 minutes of uninterrupted sleep. The interval from 242 to 273 minutes is considered the REM period, although eye movements are not continuous during that interval. FIGURE 40.2 Behavioral states in humans. Body position changes duri ...
... quarter minute, and body movement (BM) in numbers per minute over 100 minutes of uninterrupted sleep. The interval from 242 to 273 minutes is considered the REM period, although eye movements are not continuous during that interval. FIGURE 40.2 Behavioral states in humans. Body position changes duri ...
rapid eye movement sleep deprivation induces acetylcholinesterase
... cholinolytic activity, co-exists with other transmitter systems and possesses other functions. In the present study, the effects of short-tenn rapid-eye-movement sleep deprivation (REM-SD) on AchE activity in the anterior hypothalamic area have been investigated. Using the flower-pot method, adult m ...
... cholinolytic activity, co-exists with other transmitter systems and possesses other functions. In the present study, the effects of short-tenn rapid-eye-movement sleep deprivation (REM-SD) on AchE activity in the anterior hypothalamic area have been investigated. Using the flower-pot method, adult m ...
Sleep and Biological Rhythms
... in the visual association cortex but low levels in the inferior frontal cortex ...
... in the visual association cortex but low levels in the inferior frontal cortex ...
SLEEP AND EEG
... EEG pattern during REM cycle abruptly gets similar to that of wake, alert person, although person is in sleep, therefore, it is called paradoxical sleep (person sleeping but EEG pattern is like awake person). ...
... EEG pattern during REM cycle abruptly gets similar to that of wake, alert person, although person is in sleep, therefore, it is called paradoxical sleep (person sleeping but EEG pattern is like awake person). ...
Edwards Amy Edwards FYS 11/04/2011 Follow Your Dreams
... usually have fragmented visual memory of what they were experiencing while asleep” (Cohen 2). “Many also experience sudden muscle contractions called hypnic myoclonia, often preceded by a sensation of starting to fall. These sudden movements are similar to the "jump" we make when startled” (NIH 3). ...
... usually have fragmented visual memory of what they were experiencing while asleep” (Cohen 2). “Many also experience sudden muscle contractions called hypnic myoclonia, often preceded by a sensation of starting to fall. These sudden movements are similar to the "jump" we make when startled” (NIH 3). ...
SLEEP AND EEG
... EEG pattern during REM cycle abruptly gets similar to that of wake, alert person, although person is in sleep, therefore, it is called paradoxical sleep (person sleeping but EEG pattern is like awake person). ...
... EEG pattern during REM cycle abruptly gets similar to that of wake, alert person, although person is in sleep, therefore, it is called paradoxical sleep (person sleeping but EEG pattern is like awake person). ...
Sleep Brain Labelling
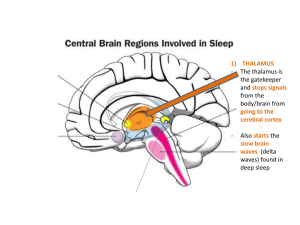
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...
James Robertson
... Sleep homeostatic response not influenced by means of SD Not affected by level of arousal Rather, means of SD affected subsequent arousal CC reduced latency to sleep to control levels Delta power similar to GH SD DNM1-mediated regulation of presynaptic endocytosis and the level of arousa ...
... Sleep homeostatic response not influenced by means of SD Not affected by level of arousal Rather, means of SD affected subsequent arousal CC reduced latency to sleep to control levels Delta power similar to GH SD DNM1-mediated regulation of presynaptic endocytosis and the level of arousa ...
Reticular formation,sleep and wakefulness
... • PASSIVE THEORY OF SLEEP: this earlier theory of sleep said that the RAS became simply fatigued during the day & as a result inactivated during the night; • It was later proved that sleep is caused by an active inhibitory process, once that there seems to be a center located below the midpontile le ...
... • PASSIVE THEORY OF SLEEP: this earlier theory of sleep said that the RAS became simply fatigued during the day & as a result inactivated during the night; • It was later proved that sleep is caused by an active inhibitory process, once that there seems to be a center located below the midpontile le ...
Focus on Vocabulary Chapter 02
... Ditto for religious experience. The word “ditto” means that whatever has just been said about someone or something applies equally to another person or thing. Memory, language, and attention are a function of synchronized activity among distinct brain areas; the same is true (ditto) for religious ex ...
... Ditto for religious experience. The word “ditto” means that whatever has just been said about someone or something applies equally to another person or thing. Memory, language, and attention are a function of synchronized activity among distinct brain areas; the same is true (ditto) for religious ex ...
File
... for growth. – Evidence for – Longer sleep usually occurs after large amounts of physical exercise and growth hormones are released during sleep. ...
... for growth. – Evidence for – Longer sleep usually occurs after large amounts of physical exercise and growth hormones are released during sleep. ...
Sleep and memory
Memory is the cognitive process whereby experiences, learning and recognition are recalled. Memory “formation” is a product of brain plasticity, the structural changes within synapses that create associations between stimuli. Stimuli are encoded within milliseconds, however the long-term maintenance of memories can take additional minutes, days, or even years to fully consolidate and become a stable memory (more resistant to change or interference). Therefore, the formation of a specific memory occurs rapidly, but the evolution of a memory is often an ongoing process.Memory processes have been shown to be stabilized and enhanced (sped up and/or integrated) by nocturnal sleep and even daytime naps. Certain sleep stages are noted to improve an individual’s memory, although this is task specific. Generally, declarative memories are enhanced by slow-wave sleep, while non-declarative memories are enhanced by rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, although there are some inconsistencies among experimental results.