This is Your Brain. This Is How It Works.
... • Importance of depth perception – When you drive, you use depth to assess the distance of an approaching automobile – When you decide to call out to a friend walking down the street, you determine how loudly to call, based on how far away you perceive your friend to ...
... • Importance of depth perception – When you drive, you use depth to assess the distance of an approaching automobile – When you decide to call out to a friend walking down the street, you determine how loudly to call, based on how far away you perceive your friend to ...
REM-off
... the smaller the brain, the quicker the cycle - NREM-REM cycles recur about every 90 minutes in humans, about every 30 minutes in cats and about every 12 minutes in rats) ...
... the smaller the brain, the quicker the cycle - NREM-REM cycles recur about every 90 minutes in humans, about every 30 minutes in cats and about every 12 minutes in rats) ...
Why Do We Sleep - The Dallas Philosophers Forum
... for breakfast a week ago, or what color the car in front of you at the light was. It is important that you remember what you learned for your job or a project. So sleep aids the acquisition of new memories. Many studies have shown that a person can learn new material much better after a good night’s ...
... for breakfast a week ago, or what color the car in front of you at the light was. It is important that you remember what you learned for your job or a project. So sleep aids the acquisition of new memories. Many studies have shown that a person can learn new material much better after a good night’s ...
Chapter 1
... preceded by development of Lewy bodies in medulla • Sleep disturbances may be “soft” sign of these disorders – As disease progresses, Lewy bodies progress up into higher brain areas ...
... preceded by development of Lewy bodies in medulla • Sleep disturbances may be “soft” sign of these disorders – As disease progresses, Lewy bodies progress up into higher brain areas ...
sleep
... • This ability of prefrontal areas to keep track of many bits of information could well explain abilities to prognosticate, do plan for the future, delay action in response to incoming sensory signals, consider the consequences of motor actions even before they are performed, solve complicated mathe ...
... • This ability of prefrontal areas to keep track of many bits of information could well explain abilities to prognosticate, do plan for the future, delay action in response to incoming sensory signals, consider the consequences of motor actions even before they are performed, solve complicated mathe ...
Consciousness
... Brain waves become less frequent as we move through the 3 stages of Non-REM sleep. Then our brain becomes very frequent during REM ...
... Brain waves become less frequent as we move through the 3 stages of Non-REM sleep. Then our brain becomes very frequent during REM ...
neurons
... awake, his brain activity slows down to a large amplitude and slow, regular alpha waves (9-14 cps). A meditating person exhibits an alpha brain ...
... awake, his brain activity slows down to a large amplitude and slow, regular alpha waves (9-14 cps). A meditating person exhibits an alpha brain ...
What is a sleep disorder?
... regular sleep routines, exercise, a good diet, using the bed for sleeping. ...
... regular sleep routines, exercise, a good diet, using the bed for sleeping. ...
Consciousness & Its Variants
... waves w/ some delta waves (slower, larger waves) – Characterized by short bursts of brain activity called sleep spindles • Last about a second or two ...
... waves w/ some delta waves (slower, larger waves) – Characterized by short bursts of brain activity called sleep spindles • Last about a second or two ...
Brain
... – permeable to lipid-soluble materials (alcohol, O2, CO2, nicotine and anesthetics) – circumventricular organs in 3rd & 4th ventricles at breaks in the barrier where blood has direct access • monitoring of glucose, pH, osmolarity & other variations • allows route for HIV virus to invade the brain ...
... – permeable to lipid-soluble materials (alcohol, O2, CO2, nicotine and anesthetics) – circumventricular organs in 3rd & 4th ventricles at breaks in the barrier where blood has direct access • monitoring of glucose, pH, osmolarity & other variations • allows route for HIV virus to invade the brain ...
bs10
... individual--Beta waves over the frontal lobes are commonly seen with active mental concentration. Alpha waves over the occipital and parietal lobes are seen when a person relaxes with closed eyes. ...
... individual--Beta waves over the frontal lobes are commonly seen with active mental concentration. Alpha waves over the occipital and parietal lobes are seen when a person relaxes with closed eyes. ...
8 pages - Science for Monks
... studies have shown that during sleep those neuronal networks, which were predominantly active during waking hours, reactivate. If I learn something or focus too much on one particular subject during my to sleep the same neural network is reactivated. This is the basis of memory consolidation. There ...
... studies have shown that during sleep those neuronal networks, which were predominantly active during waking hours, reactivate. If I learn something or focus too much on one particular subject during my to sleep the same neural network is reactivated. This is the basis of memory consolidation. There ...
States of Consciuosnes
... Breathing becomes rhythmical Some small muscle twitches Brain activity begins to slow down, sleep talking may occur, and the appearances of sleep spindles Quick bursts of brain activity that last for a second or two – creation of memories? ...
... Breathing becomes rhythmical Some small muscle twitches Brain activity begins to slow down, sleep talking may occur, and the appearances of sleep spindles Quick bursts of brain activity that last for a second or two – creation of memories? ...
SLEEP AND EEG
... Infants spent more time in REM sleep. In children, NREM and REM become 50% each. New born sleeps about 16-20 hrs/day. During childhood, child sleeps 10 hrs/day. Adult person needs 7-8 hours of sleep In elderly NREM, Stage IV (deep sleep) and REM sleep decreases. ...
... Infants spent more time in REM sleep. In children, NREM and REM become 50% each. New born sleeps about 16-20 hrs/day. During childhood, child sleeps 10 hrs/day. Adult person needs 7-8 hours of sleep In elderly NREM, Stage IV (deep sleep) and REM sleep decreases. ...
bYTEBoss brain_notes
... • Delta rhythms (6-8 cycles per second) with some activity • Totally out of it – dreams usually not remembered. • Difficult to awake (may try to hit etc.) • Not conscious of surroundings (talk with you, but not aware.) • If disorder or young you may spend too much time in III ...
... • Delta rhythms (6-8 cycles per second) with some activity • Totally out of it – dreams usually not remembered. • Difficult to awake (may try to hit etc.) • Not conscious of surroundings (talk with you, but not aware.) • If disorder or young you may spend too much time in III ...
of sleep
... • Stage 2 sleep: more fully asleep but still could be awakened; “spindles” of activity in brain waves • Stage 3 sleep: a transition to Stage 4 (omitted in some models) • Stage 4 sleep: Such deep sleep that many kids wet the bed, yet you can waken to baby’s cry • REM (rapid eye movement) sleep: recur ...
... • Stage 2 sleep: more fully asleep but still could be awakened; “spindles” of activity in brain waves • Stage 3 sleep: a transition to Stage 4 (omitted in some models) • Stage 4 sleep: Such deep sleep that many kids wet the bed, yet you can waken to baby’s cry • REM (rapid eye movement) sleep: recur ...
Practical Implications of Sleep Neurochemistry
... http://journals.prous.com/journals/dnp/20031608/html/dn160504/images/DeLeccea_f1.jpg ...
... http://journals.prous.com/journals/dnp/20031608/html/dn160504/images/DeLeccea_f1.jpg ...
nervous system part 6 EEG, walkfulness and sleep
... called brain waves Brain waves change with age, sensory stimuli, brain disease, and the chemical state of the body An electroencephalogram (EEG) records this activity EEGs can be used to diagnose and localize brain lesions, tumors, infarcts, infections, abscesses, and epileptic ...
... called brain waves Brain waves change with age, sensory stimuli, brain disease, and the chemical state of the body An electroencephalogram (EEG) records this activity EEGs can be used to diagnose and localize brain lesions, tumors, infarcts, infections, abscesses, and epileptic ...
EEG - pressthebar
... called brain waves Brain waves change with age, sensory stimuli, brain disease, and the chemical state of the body An electroencephalogram (EEG) records this activity EEGs can be used to diagnose and localize brain lesions, tumors, infarcts, infections, abscesses, and epileptic ...
... called brain waves Brain waves change with age, sensory stimuli, brain disease, and the chemical state of the body An electroencephalogram (EEG) records this activity EEGs can be used to diagnose and localize brain lesions, tumors, infarcts, infections, abscesses, and epileptic ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿 - Shandong University
... called brain waves Brain waves change with age, sensory stimuli, brain disease, and the chemical state of the body An electroencephalogram (EEG) records this activity EEGs can be used to diagnose and localize brain lesions, tumors, infarcts, infections, abscesses, and epileptic ...
... called brain waves Brain waves change with age, sensory stimuli, brain disease, and the chemical state of the body An electroencephalogram (EEG) records this activity EEGs can be used to diagnose and localize brain lesions, tumors, infarcts, infections, abscesses, and epileptic ...
Supplementary Figure Legends - Word file (28 KB )
... promoting/sleep-inhibiting neurons (e.g. c309/MBSwitch) are normally most active during the day (diurnal influences are indicated by upward and downward deflections in sinusoids). Antagonistic signals from these two sets of cells are integrated to generate sleep/wake activity cycles. Dashed arrows i ...
... promoting/sleep-inhibiting neurons (e.g. c309/MBSwitch) are normally most active during the day (diurnal influences are indicated by upward and downward deflections in sinusoids). Antagonistic signals from these two sets of cells are integrated to generate sleep/wake activity cycles. Dashed arrows i ...
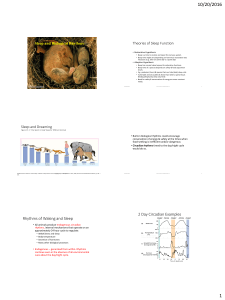
Rhythms of Waking and Sleep 2 Day Circadian Examples
... • During waking, the reticular formation arouses entire cortex. Sleep does not work this way. • GABA & adenosine promote sleep, but in a more “region by region” fashion. So there are situations where part of the brain is asleep but not the entire brain. • Drugs that increase effect of GABA (tranquil ...
... • During waking, the reticular formation arouses entire cortex. Sleep does not work this way. • GABA & adenosine promote sleep, but in a more “region by region” fashion. So there are situations where part of the brain is asleep but not the entire brain. • Drugs that increase effect of GABA (tranquil ...
Sleep and memory
Memory is the cognitive process whereby experiences, learning and recognition are recalled. Memory “formation” is a product of brain plasticity, the structural changes within synapses that create associations between stimuli. Stimuli are encoded within milliseconds, however the long-term maintenance of memories can take additional minutes, days, or even years to fully consolidate and become a stable memory (more resistant to change or interference). Therefore, the formation of a specific memory occurs rapidly, but the evolution of a memory is often an ongoing process.Memory processes have been shown to be stabilized and enhanced (sped up and/or integrated) by nocturnal sleep and even daytime naps. Certain sleep stages are noted to improve an individual’s memory, although this is task specific. Generally, declarative memories are enhanced by slow-wave sleep, while non-declarative memories are enhanced by rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, although there are some inconsistencies among experimental results.