File - Ms. Thresher
... behavior was guided by consequences. He thought behavior was objective and could be chosen by the individual. He also thought rewarding someone when they acted in a favorable manner that was close to the desired act could shape behavior. A way to achieve this is through positive reinforcers and puni ...
... behavior was guided by consequences. He thought behavior was objective and could be chosen by the individual. He also thought rewarding someone when they acted in a favorable manner that was close to the desired act could shape behavior. A way to achieve this is through positive reinforcers and puni ...
Animal behavior Unit
... 3. Operant Conditioning (Trial and Error Learning): Learning in which an animal receives a reward for a particular response; motivation commands quicker learning. First described by B.F. Skinner, American psychologist; Invented the “Skinner Box” around 1930. ...
... 3. Operant Conditioning (Trial and Error Learning): Learning in which an animal receives a reward for a particular response; motivation commands quicker learning. First described by B.F. Skinner, American psychologist; Invented the “Skinner Box” around 1930. ...
Learning
... Variable-ratio: after random number of responses Fixed-interval: Fixed interval: after a set time interval Variable-interval: after random time intervals ...
... Variable-ratio: after random number of responses Fixed-interval: Fixed interval: after a set time interval Variable-interval: after random time intervals ...
Animal Behavior - Ms. Canga`s page
... How Do Animals Learn? Animals do not have a sense of morals. Owners often project what they think on to the animals behavior. Most animals learn in a similar manner, through associative learning. Respondent Conditioning (Also called classical or Pavlovian conditioning.) Operant Conditio ...
... How Do Animals Learn? Animals do not have a sense of morals. Owners often project what they think on to the animals behavior. Most animals learn in a similar manner, through associative learning. Respondent Conditioning (Also called classical or Pavlovian conditioning.) Operant Conditio ...
Everyone has come across a situation where they want to be able to
... Everyone has come across a situation where they want to be able to change the behavior of a person or animal they are dealing with. Teaching children and pets new things can be difficult at times, such as children learning to count or dogs doing tricks. Children and pets often do things that annoy t ...
... Everyone has come across a situation where they want to be able to change the behavior of a person or animal they are dealing with. Teaching children and pets new things can be difficult at times, such as children learning to count or dogs doing tricks. Children and pets often do things that annoy t ...
Behaviorist Theory
... Founder John B. Watson. He believed psychology should only concern itself with the study of behavior and one's documented behaviors. Watson's work was based on the experiments of Ivan Pavlov's model of classical conditioning based off one's personality and characteristics. (Schunk, 2012, p. 72) ...
... Founder John B. Watson. He believed psychology should only concern itself with the study of behavior and one's documented behaviors. Watson's work was based on the experiments of Ivan Pavlov's model of classical conditioning based off one's personality and characteristics. (Schunk, 2012, p. 72) ...
Chapter 5: Managerial Ethics & Corporate Social Responsibility
... How to Effectively Shape Behavior with Reinforcement ...
... How to Effectively Shape Behavior with Reinforcement ...
Learning Red
... 6 – During extinction, the _________ (UCS, UCR, CS, or CR) must be omitted. 7 – Bill once had a blue car that was in the shop more than it was out. Since then he will not even consider owning blur or green cars. Bill’s aversion to green cars is an example of ___________. 8 – In Garcia and Koelling’s ...
... 6 – During extinction, the _________ (UCS, UCR, CS, or CR) must be omitted. 7 – Bill once had a blue car that was in the shop more than it was out. Since then he will not even consider owning blur or green cars. Bill’s aversion to green cars is an example of ___________. 8 – In Garcia and Koelling’s ...
Name two scientists famous for their studies of classical conditioning 2
... 4 – In Pavlov’s original experiment with dogs, the meat served as the (UCS, UCR, CS or CR)? 5 – During extinction, the _________ (UCS, UCR, CS, or CR) must be omitted. 6 – Bill once had a blue car that was in the shop more than it was out. Since then he will not even consider owning blur or green ca ...
... 4 – In Pavlov’s original experiment with dogs, the meat served as the (UCS, UCR, CS or CR)? 5 – During extinction, the _________ (UCS, UCR, CS, or CR) must be omitted. 6 – Bill once had a blue car that was in the shop more than it was out. Since then he will not even consider owning blur or green ca ...
Applied Behavior Analysis Vocabulary Antecedent stimulus
... functional relationship between a voluntary behavior & its consequences Positive Reinforcement – the contingent presentation of a stimulus immediately following a response, which increases the future rate and/or probability of the response Punisher – a consequent stimulus that decreases the future r ...
... functional relationship between a voluntary behavior & its consequences Positive Reinforcement – the contingent presentation of a stimulus immediately following a response, which increases the future rate and/or probability of the response Punisher – a consequent stimulus that decreases the future r ...
X-Period/Learning Test
... Studied the power of observational learning Experiments on children watching violent TV and then playing more violently ...
... Studied the power of observational learning Experiments on children watching violent TV and then playing more violently ...
Operant Conditioning
... is not set (ex: slot machines – must put money in; fishing – worm, lure in the water—never know when you will win, or catch a fish) 3) Fixed-interval schedule: a set amount of time must pass for you to be rewarded, even if you have not done something (ex: payday every Friday) 4) Variable-interval sc ...
... is not set (ex: slot machines – must put money in; fishing – worm, lure in the water—never know when you will win, or catch a fish) 3) Fixed-interval schedule: a set amount of time must pass for you to be rewarded, even if you have not done something (ex: payday every Friday) 4) Variable-interval sc ...
REDUCTIONISM - School of Psychology
... “…any explanation of an observed fact which appeals to events taking place somewhere else, at some other level of observation, described in different terms, and measured, if at all, in different dimensions.” ...
... “…any explanation of an observed fact which appeals to events taking place somewhere else, at some other level of observation, described in different terms, and measured, if at all, in different dimensions.” ...
SI: September 19, 2011 Chapter 7: Part 2 Part I: Warm
... a. He will learn from his father, and not beat his wife and kids. b. He will not beat his children, because he knows how bad it hurts. c. He will likely beat his wife and children. d. We cannot predict Matt’s future. It is all destiny. Part V: Fill in the Blank Fill in the blanks with the correct wo ...
... a. He will learn from his father, and not beat his wife and kids. b. He will not beat his children, because he knows how bad it hurts. c. He will likely beat his wife and children. d. We cannot predict Matt’s future. It is all destiny. Part V: Fill in the Blank Fill in the blanks with the correct wo ...
Theory of Reasoned Action and Theory of Planned Behavior
... or not a person intends to perform a health behavior should correlate with whether or not they actually DO the behavior ...
... or not a person intends to perform a health behavior should correlate with whether or not they actually DO the behavior ...
Operant Conditioning
... In classical conditioning, one associates different stimuli that it does not control. Through operant conditioning, one associates their behavior with consequences. ...
... In classical conditioning, one associates different stimuli that it does not control. Through operant conditioning, one associates their behavior with consequences. ...
Albert Bandura - Personal Web Pages
... 4. environmental enhancement (children will fight more if they observe parents fighting). ...
... 4. environmental enhancement (children will fight more if they observe parents fighting). ...
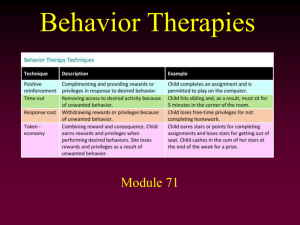
Module 71 - Behavioral Therapy
... • Eventually bladder tension (CR) causes the child to awaken (CR). • It is effective in about 75 percent of school-age children who have difficulties with bedwetting. ...
... • Eventually bladder tension (CR) causes the child to awaken (CR). • It is effective in about 75 percent of school-age children who have difficulties with bedwetting. ...
Motor Mechanisms and Behavior
... Smooth muscle – walls of hollow organs like blood vessels and digestive tract ...
... Smooth muscle – walls of hollow organs like blood vessels and digestive tract ...
Name Crash Course-Psychology #11
... Directions: As you view/listen to the crash course video, listen for information to complete each of the following statements. 1) For scholars of psychology, we can define _______________________________ as the process of acquiring, through experience, new and relatively enduring information or beha ...
... Directions: As you view/listen to the crash course video, listen for information to complete each of the following statements. 1) For scholars of psychology, we can define _______________________________ as the process of acquiring, through experience, new and relatively enduring information or beha ...