Angular Motion Vocabulary
... 3. Angular Momentum- The quantity of rotation of a body, which is the product of its moment of inertia and its angular speed. 4. Angular Speed- Change of angle per unit time, measured in radians 5. Arc Length- The length of a curve, measured in meters (the radius multiplied by Pi). 6. Center of Mass ...
... 3. Angular Momentum- The quantity of rotation of a body, which is the product of its moment of inertia and its angular speed. 4. Angular Speed- Change of angle per unit time, measured in radians 5. Arc Length- The length of a curve, measured in meters (the radius multiplied by Pi). 6. Center of Mass ...
Newton`s First Law
... Net Force: the Sum of the Forces • This car is moving with a constant velocity. • Fforward = road pushing the tires • Fresistance = force caused by friction and air • Forces are balanced ...
... Net Force: the Sum of the Forces • This car is moving with a constant velocity. • Fforward = road pushing the tires • Fresistance = force caused by friction and air • Forces are balanced ...
Unit 5 Review
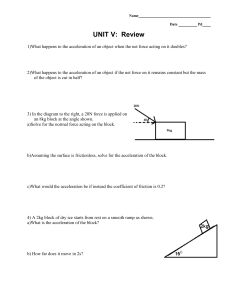
... 3) In the diagram to the right, a 20N force is applied on an 8kg block at the angle shown. a)Solve for the normal force acting on the block. ...
... 3) In the diagram to the right, a 20N force is applied on an 8kg block at the angle shown. a)Solve for the normal force acting on the block. ...
Document
... • A particle originally at rest, or moving in a straight line with a constant velocity, will remain in this state provided the particle is not subjected to an unbalance force. • Static law ...
... • A particle originally at rest, or moving in a straight line with a constant velocity, will remain in this state provided the particle is not subjected to an unbalance force. • Static law ...
Wed Lecture
... Suppose you are driving through a valley whose bottom has a circular shape. If your mass is m, what is the magnitude of the normal force FN exerted on you by the car seat as you drive past the bottom of the hill A. FN < mg a=v2/R ...
... Suppose you are driving through a valley whose bottom has a circular shape. If your mass is m, what is the magnitude of the normal force FN exerted on you by the car seat as you drive past the bottom of the hill A. FN < mg a=v2/R ...
File
... both attracting the man to the earth and keeping him moving in a circular path at approximately 1670 km/h. As a result, the force holding him away from the earth, as measured on a bathroom scale, would be slightly less than that at the pole where there is no centripetal acceleration. Again, a free b ...
... both attracting the man to the earth and keeping him moving in a circular path at approximately 1670 km/h. As a result, the force holding him away from the earth, as measured on a bathroom scale, would be slightly less than that at the pole where there is no centripetal acceleration. Again, a free b ...
for reference Name Period ______ Date ______ Motion Notes from
... Near the surface of Earth all objects are accelerated by gravity at a rate of 9.8 m/s/s .* Weight: the effect of gravity on an object’s mass Momentum: mass x velocity: the product of an object’s mass and its velocity. (Think of momentum as moving inertia.) All moving objects have momentum. To ...
... Near the surface of Earth all objects are accelerated by gravity at a rate of 9.8 m/s/s .* Weight: the effect of gravity on an object’s mass Momentum: mass x velocity: the product of an object’s mass and its velocity. (Think of momentum as moving inertia.) All moving objects have momentum. To ...