A baseball is thrown vertically upward
... A baseball is thrown vertically upward. It then goes upward until it reaches its highest point and then comes back down to the thrower. 1) Make a system schema for the situation above. ...
... A baseball is thrown vertically upward. It then goes upward until it reaches its highest point and then comes back down to the thrower. 1) Make a system schema for the situation above. ...
Application of Newton`s Laws Circular Motion Answers
... 5) At the top of the loop the forces acting on the rider are gravity and the normal force. These forces need to be equal to the centripetal force. ...
... 5) At the top of the loop the forces acting on the rider are gravity and the normal force. These forces need to be equal to the centripetal force. ...
FMALiveForcesMotionPC
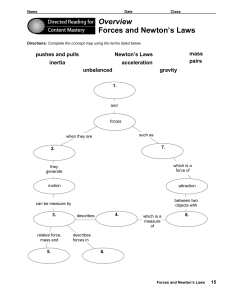
... Force = Mass times acceleration (F=Ma) For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. And sometimes, they all happen at once! ...
... Force = Mass times acceleration (F=Ma) For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. And sometimes, they all happen at once! ...
M - Otterbein University
... • If we know which force is acting on an object of known mass we can calculate (predict) its motion • Qualitatively: – objects subject to a constant force will speed up (slow down) in that direction – Objects subject to a force perpendicular to their motion (velocity!) will not speed up, but change ...
... • If we know which force is acting on an object of known mass we can calculate (predict) its motion • Qualitatively: – objects subject to a constant force will speed up (slow down) in that direction – Objects subject to a force perpendicular to their motion (velocity!) will not speed up, but change ...
File
... motion, and is directed towards the center of the circle. Example of centripetal force: the moon being held in orbit by gravity. Centrifugal Force: an imaginary force that seems to pull away from the center of the circle which is caused by inertia. Example of centrifugal force: carnival rides. ...
... motion, and is directed towards the center of the circle. Example of centripetal force: the moon being held in orbit by gravity. Centrifugal Force: an imaginary force that seems to pull away from the center of the circle which is caused by inertia. Example of centrifugal force: carnival rides. ...
Forces and Energy Summary Sheet File
... Braking distance is affected by things which influence the forces of friction e.g. condition of the brakes, wetness of the road surface. Road safety has been improved by the introduction of speed limits and road side speed cameras in order to slow down traffic. Passenger safety has been improved by ...
... Braking distance is affected by things which influence the forces of friction e.g. condition of the brakes, wetness of the road surface. Road safety has been improved by the introduction of speed limits and road side speed cameras in order to slow down traffic. Passenger safety has been improved by ...
Study Notes
... system is in an elevator accelerating upward at 9.8 m/s2 (i.e. ay = g). The student who immediately writes down 98 N downward is only correct if they know that the system is not accelerating!! (Note: The system can be moving and still have no acceleration.) ...
... system is in an elevator accelerating upward at 9.8 m/s2 (i.e. ay = g). The student who immediately writes down 98 N downward is only correct if they know that the system is not accelerating!! (Note: The system can be moving and still have no acceleration.) ...
File
... “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.” More Scientific Version When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second exerts a force on the first that is equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction. ...
... “For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.” More Scientific Version When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second exerts a force on the first that is equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction. ...
Forces and Motion PP
... Law of Conservation of Momentum: the total momentum of objects that interact does not change, unless acted on by an outside force (eg. Friction) ...
... Law of Conservation of Momentum: the total momentum of objects that interact does not change, unless acted on by an outside force (eg. Friction) ...