Lecture 16 - Circular Motion
... bodies (apples) fall 5 m in the first second, and that this acceleration is due to earth’s gravity. He showed that the gravity force is the same as if all earth’s mass were at its center, 4000 mi from the surface. (This required inventing Calculus). He wondered whether the same force attracts the mo ...
... bodies (apples) fall 5 m in the first second, and that this acceleration is due to earth’s gravity. He showed that the gravity force is the same as if all earth’s mass were at its center, 4000 mi from the surface. (This required inventing Calculus). He wondered whether the same force attracts the mo ...
Circular Motion and Gravity Jeopardy
... related to a job of converting speech from one language to another.) ...
... related to a job of converting speech from one language to another.) ...
Name: Sect:______ Date
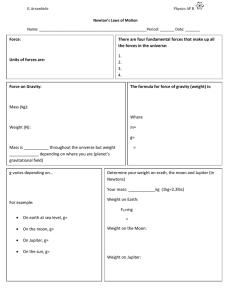
... 6. What is Newton’s 1st Law of Motion? 7. What is Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion? 8. What is Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion? ...
... 6. What is Newton’s 1st Law of Motion? 7. What is Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion? 8. What is Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion? ...
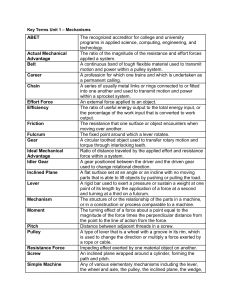
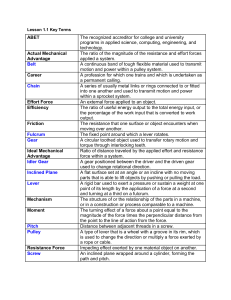
Lesson 1.1 Key Terms ABET The recognized accreditor for college
... The resistance that one surface or object encounters when moving over another. The fixed point around which a lever rotates. A circular toothed object used to transfer rotary motion and torque through interlocking teeth. Ratio of distance traveled by the applied effort and resistance force within a ...
... The resistance that one surface or object encounters when moving over another. The fixed point around which a lever rotates. A circular toothed object used to transfer rotary motion and torque through interlocking teeth. Ratio of distance traveled by the applied effort and resistance force within a ...
Student Learning Goals
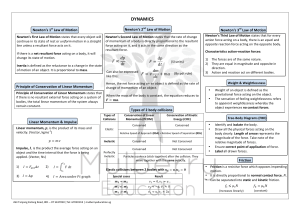
... 4. Force is measured in units of newtons. A one newton net force acting on a one-kilogram object produces an acceleration of 1 m/s2. Therefore, a newton is the same as a kilogrammeter/second2. (N = kgm/s2) 5. Use Newton's 2nd Law to qualitatively describe the relationship between m and a, F and ...
... 4. Force is measured in units of newtons. A one newton net force acting on a one-kilogram object produces an acceleration of 1 m/s2. Therefore, a newton is the same as a kilogrammeter/second2. (N = kgm/s2) 5. Use Newton's 2nd Law to qualitatively describe the relationship between m and a, F and ...
Force and motion
... Motion- a change in position, measured by distance and time. ◦ When motion is changed it is called applied force. ...
... Motion- a change in position, measured by distance and time. ◦ When motion is changed it is called applied force. ...
Grade 10 Force PowerPoint II
... force applied to the object. • a = Fnet / m or Fnet = ma • 1 Newton = the force required to ...
... force applied to the object. • a = Fnet / m or Fnet = ma • 1 Newton = the force required to ...
3 5-1 Kinematics of Uniform Circular Motion
... constant the direction of the velocity is constantly changing Recall that acceleration is the change in velocity over the change in time and is a vector In circular motion, the direction is constantly changing which means an object moving in circular motion is ALWAYS accelerating, even if it’s v ...
... constant the direction of the velocity is constantly changing Recall that acceleration is the change in velocity over the change in time and is a vector In circular motion, the direction is constantly changing which means an object moving in circular motion is ALWAYS accelerating, even if it’s v ...
Newton`s First and Second Laws
... continue moving at a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force Clothes on the floor will stay there unless someone uses a force to pick them up A tennis ball that was hit will continue until a force stops it Gravity and friction are the 2 forces on Earth that often change an object ...
... continue moving at a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force Clothes on the floor will stay there unless someone uses a force to pick them up A tennis ball that was hit will continue until a force stops it Gravity and friction are the 2 forces on Earth that often change an object ...
Chapter 12 Study Guide
... Chapter 12: Force and Newton’s Laws Study Guide Define the following terms: Force Balanced Force Unbalanced Force Net Force Friction Inertia Acceleration Gravity Action and Reaction Weight Mass 1. Write out each of Newton’s three laws and explain an example of each. Newton’s First Law states: ...
... Chapter 12: Force and Newton’s Laws Study Guide Define the following terms: Force Balanced Force Unbalanced Force Net Force Friction Inertia Acceleration Gravity Action and Reaction Weight Mass 1. Write out each of Newton’s three laws and explain an example of each. Newton’s First Law states: ...
Ex. A 650 kg car accelerates at 4.0 m/s2 south. What is the net force
... Inertia is how much an object does not want to ___________ how it is moving. It is the tendency of an object to ____________a change in motion. The greater the mass, the ___________ its inertia. o ...
... Inertia is how much an object does not want to ___________ how it is moving. It is the tendency of an object to ____________a change in motion. The greater the mass, the ___________ its inertia. o ...
Name Class Date Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section
... 1. In science, a push or a pull exerted on an object is known as ...
... 1. In science, a push or a pull exerted on an object is known as ...