∑ = −
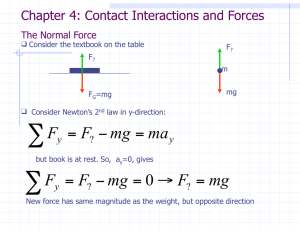
... New force is a result of the contact between the book and the table New force is called the Normal Force, n, N or FN In general it is not equal to mg, - we must usually solve for FN ``Normal’’ means ``perpendicular’’ (to the surface of contact) Now, apply an additional force, FA to the book ...
... New force is a result of the contact between the book and the table New force is called the Normal Force, n, N or FN In general it is not equal to mg, - we must usually solve for FN ``Normal’’ means ``perpendicular’’ (to the surface of contact) Now, apply an additional force, FA to the book ...
Chapter 18 Test Review
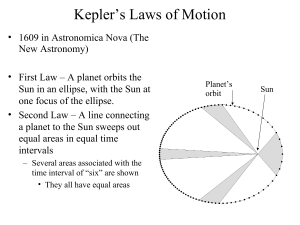
... • Velocity: distance and direction traveled over time. • Law of Universal Gravitation: idea that all objects in the universe attract each other through gravitational force. ...
... • Velocity: distance and direction traveled over time. • Law of Universal Gravitation: idea that all objects in the universe attract each other through gravitational force. ...
FORCES
... It can make something move It can speed something up It can slow something down It can make something stop moving hand twisting a door knob wind pushing on a sail girl pushing a rock a stone being pulled towards the earth by the force of gravity ...
... It can make something move It can speed something up It can slow something down It can make something stop moving hand twisting a door knob wind pushing on a sail girl pushing a rock a stone being pulled towards the earth by the force of gravity ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Newton’s First Law On Earth, gravity and friction are unbalanced forces that often change an object’s motion. The greater the mass of an object is, the greater its inertia, and the greater the force required to change its motion. Example: The tennis ball thrown in the air will continue until ...
... Newton’s First Law On Earth, gravity and friction are unbalanced forces that often change an object’s motion. The greater the mass of an object is, the greater its inertia, and the greater the force required to change its motion. Example: The tennis ball thrown in the air will continue until ...
You get to explore the possible energy transitions for Hydrogen
... body, the second body exerts an equal and opposite force on the first body. • Don’t need a rocket launch pad! • The Bug and the Windshield – who is having the worse day? ...
... body, the second body exerts an equal and opposite force on the first body. • Don’t need a rocket launch pad! • The Bug and the Windshield – who is having the worse day? ...
Circular Motion
... If an object moves in a circle it is accelerating and there has to be an unbalanced force acting on it. A force that causes circular motion is always toward the center. Acceleration is always in the same direction as the force (so centripetal acceleration is toward the center). If, for instance, you ...
... If an object moves in a circle it is accelerating and there has to be an unbalanced force acting on it. A force that causes circular motion is always toward the center. Acceleration is always in the same direction as the force (so centripetal acceleration is toward the center). If, for instance, you ...
Motion and Forces Review Sheet
... 22. Sally is riding her bike down the street. She notices that the harder she pushes on the pedals, the quicker the bike will start to go. Why is that? a. motion b. A=F/M c. The bike feels like it 23. How can you increase friction? ...
... 22. Sally is riding her bike down the street. She notices that the harder she pushes on the pedals, the quicker the bike will start to go. Why is that? a. motion b. A=F/M c. The bike feels like it 23. How can you increase friction? ...
Review: Newton`s second Law
... (2)Sketch forces acting on object – indentify all the external forces acting on an object. (3) Choose coordinate system (x &y) (4) Resolve into components Apply 2nd law to each components. In components Fy ma y Fx ma x ...
... (2)Sketch forces acting on object – indentify all the external forces acting on an object. (3) Choose coordinate system (x &y) (4) Resolve into components Apply 2nd law to each components. In components Fy ma y Fx ma x ...
L10_rotation
... a. Identify and describe at least one characteristic they share. b. Identify and describe at least two differences between them. ...
... a. Identify and describe at least one characteristic they share. b. Identify and describe at least two differences between them. ...
vocabulary
... contact with each other that resists motion of the objects or substances relative to each other; a resistance encountered when one body moves relative to another body with which it is in contact. ...
... contact with each other that resists motion of the objects or substances relative to each other; a resistance encountered when one body moves relative to another body with which it is in contact. ...