* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Uniform Circular Motion
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
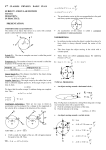
Uniform Circular Motion Acceleration When an object moves at a constant speed in a circular path, it is constantly changing direction – accelerating Centripetal Acceleration Δv always points to the center of the circle Since a = Δv/t, a must also be pointed to the center of the circle Centripetal Acceleration – center seeking acceleration Also called Radial Acceleration – directed along the radius Symbol - ar Equation a r = v2 / r v is the velocity and r the radius Greater v, faster direction changes, greater the ar Greater r, less rapidly changing direction, lower the ar v and a are always perpendicular to one another at any given point on a circle v a Frequency and Period Circular motion is often described in terms of frequency (f) and period (T) Frequency – revolutions per sec – unit Hz Period – time for one revolution – unit sec The velocity is the distance traveled per time Distance is the circumference of the circle which is 2π r v = 2π r / T Example 1 A 150 g ball at the end of a string is revolving in a horizontal circle of radius .600 m. The ball makes 2.00 revolutions in a second. What is the centripetal acceleration? Example 2 The moon’s nearly circular orbit about the earth has a radius of about 384000 km and a period of 27.3 days. Determine the acceleration of the moon toward the earth. Force Objects accelerating must have a force acting on them therefore there must be a force keeping an object in a circular path This force is called Centripetal Force (Fr) Fr = mar = mv2 / r Since ar is directed into the center of the circle, so is Fr This force is always applied by other objects Fictious Force There is no force pulling objects out from the center of a circle There is an illusion of an outward force caused by inertia This fictious force is called centrifugal force Example 3 What force must a person exert on a string attached to a .150 kg ball in order to keep it revolving in a horizontal circle of radius .600 m ? The ball makes 2.00 revolutions per second. Example 4 In a tetherball game a .85 kg ball is hit in a horizontal circle around a pole. The rope makes an angle of 35° with the pole and is holding the ball with a tension of 12.5 N. The radius of its circular path is 1.25 m. Find the centripetal acceleration, centripetal force, the velocity, and period.