Chapter 06 Test B
... The forces are acting on different objects and do not cancel one another. The force has a larger effect on the mower because Brianna has a larger mass, which is more difficult to accelerate, so the mower is accelerated in the direction that Brianna is pushing. ...
... The forces are acting on different objects and do not cancel one another. The force has a larger effect on the mower because Brianna has a larger mass, which is more difficult to accelerate, so the mower is accelerated in the direction that Brianna is pushing. ...
Default Normal Template
... Q10. A 16 – pound weight stretches a spring 2 feet. Initially the weight starts from rest 2 feet below the equilibrium position. Determine the differential equation and the initial conditions of the motion, if the surrounding medium offers a damping force numerically equal to the instantaneous veloc ...
... Q10. A 16 – pound weight stretches a spring 2 feet. Initially the weight starts from rest 2 feet below the equilibrium position. Determine the differential equation and the initial conditions of the motion, if the surrounding medium offers a damping force numerically equal to the instantaneous veloc ...
pompton lakes high school - Pompton Lakes School District
... Unit Summary: In this unit students will become familiar with the way scientists describe forces and motion in the physical sense. They will become accustomed to performing mathematical equations to find the information necessary to answer questions related to physics. Primary interdisciplinary conn ...
... Unit Summary: In this unit students will become familiar with the way scientists describe forces and motion in the physical sense. They will become accustomed to performing mathematical equations to find the information necessary to answer questions related to physics. Primary interdisciplinary conn ...
The Law of Force and Acceleration
... meters. When it reaches the ground, it is rolling at a speed of 1.95 m/sec. How much energy in the bowling ball was lost to the surroundings as a result of friction? ...
... meters. When it reaches the ground, it is rolling at a speed of 1.95 m/sec. How much energy in the bowling ball was lost to the surroundings as a result of friction? ...
1. Introductory Concepts
... b. To what extent does the buoyancy of the surrounding air affect the weight measurement? (Hint: estimate it using Archimedes Principle. Assume the air density to be ρair = 0.0768 lbm/ft3). 1-7 You may recall from Physics that the heat capacity, C, of a substance is the energy gained for a given te ...
... b. To what extent does the buoyancy of the surrounding air affect the weight measurement? (Hint: estimate it using Archimedes Principle. Assume the air density to be ρair = 0.0768 lbm/ft3). 1-7 You may recall from Physics that the heat capacity, C, of a substance is the energy gained for a given te ...
Name: Period: Points: /28pts. Study Guide/Take home test: Density
... 2. What is the upward force on a swimmer that balances the downward force of gravity and keeps the swimmer from sinking? ______________ 1 pt. 3. What is Archimedes’ Principle? 2pts. 4. What does density depend on? _____________ and _______________ 2pts. 5. How do you know if an object will float in ...
... 2. What is the upward force on a swimmer that balances the downward force of gravity and keeps the swimmer from sinking? ______________ 1 pt. 3. What is Archimedes’ Principle? 2pts. 4. What does density depend on? _____________ and _______________ 2pts. 5. How do you know if an object will float in ...
Review
... Bottom string breaks because block has lots of inertia and resists acceleration. Pulling force doesn’t reach top string. ...
... Bottom string breaks because block has lots of inertia and resists acceleration. Pulling force doesn’t reach top string. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Physics 121, Lecture 12.
... shape of the objects were are studying. • Objects that are not point-like appear to carry out more complicated motions than pointlike objects (e.g. the object may be rotating during its motion). • We will find that we can use whatever we have learned about motion of point-like objects if we consider ...
... shape of the objects were are studying. • Objects that are not point-like appear to carry out more complicated motions than pointlike objects (e.g. the object may be rotating during its motion). • We will find that we can use whatever we have learned about motion of point-like objects if we consider ...
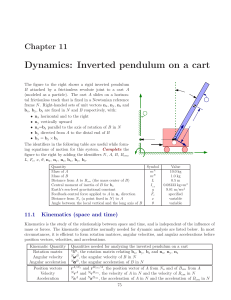
Dynamics: Inverted pendulum on a cart
... • Use the right-hand rule to determine the sign of λ . In other words, point the four fingers of your right hand in the direction of n⊥ , and then curl them in the direction of b⊥ . If you thumb points in the direction of λ , the sign of λ is positive, otherwise it is negative. ...
... • Use the right-hand rule to determine the sign of λ . In other words, point the four fingers of your right hand in the direction of n⊥ , and then curl them in the direction of b⊥ . If you thumb points in the direction of λ , the sign of λ is positive, otherwise it is negative. ...
Tutorial 4
... (iv) At time t = 0 s, the only resistive force acting is (static) friction. When time increases to 30s, the cycle and the cyclist picks up speed (i.e. accelerates due to the resultant force acting on them). This causes the air resistance acting them to increase, since magnitude of air resistance inc ...
... (iv) At time t = 0 s, the only resistive force acting is (static) friction. When time increases to 30s, the cycle and the cyclist picks up speed (i.e. accelerates due to the resultant force acting on them). This causes the air resistance acting them to increase, since magnitude of air resistance inc ...
Physics 201 Fall, 2010 Solved Problems: Examples for Mid
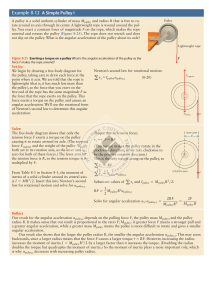
... x-direction: - TL cos (30o ) + TR cos (45o ) = 0 z-direction: + TL sin (30o) + TR sin (45o ) = (20.0 kg) (9.80) These two equations have solutions: TL = 144 newton, TR = 176 newton. 7. Two objects are connected by a frictionless pulley. The M1 = (10.0 kg) mass hangs vertically. The M2 = (15.0 kg) ma ...
... x-direction: - TL cos (30o ) + TR cos (45o ) = 0 z-direction: + TL sin (30o) + TR sin (45o ) = (20.0 kg) (9.80) These two equations have solutions: TL = 144 newton, TR = 176 newton. 7. Two objects are connected by a frictionless pulley. The M1 = (10.0 kg) mass hangs vertically. The M2 = (15.0 kg) ma ...