Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... · Equilibrium is a state of no change. · Objects at rest are said to be in static equilibrium, objects moving at constant speed in a straight-line path are said to be in dynamic equilibrium. ...
... · Equilibrium is a state of no change. · Objects at rest are said to be in static equilibrium, objects moving at constant speed in a straight-line path are said to be in dynamic equilibrium. ...
ch 8
... Here vB2x – vA2x is the velocity of B relative to A after the collision; according to the equation, this relative velocity equals to vA1x, which is the velocity A relative to B, or the negative of the velocity of B relative to A before the collision. The relative velocity has the same magnitude, but ...
... Here vB2x – vA2x is the velocity of B relative to A after the collision; according to the equation, this relative velocity equals to vA1x, which is the velocity A relative to B, or the negative of the velocity of B relative to A before the collision. The relative velocity has the same magnitude, but ...
Tuesday, June 26, 2007 - UTA High Energy Physics page.
... L L1 L2 ...... Ln L i Since the individual angular momentum can change, the total angular momentum of the system can change. Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let ...
... L L1 L2 ...... Ln L i Since the individual angular momentum can change, the total angular momentum of the system can change. Both internal and external forces can provide torque to individual particles. However, the internal forces do not generate net torque due to Newton’s third law. Let ...
Teaching six simple machines to middle school students
... numerical measure of its inertia; a fundamental measure of the amount of matter in the object. Mass can be measured in many different ways and can appear abstract. SI units are recommended to establish comfort. ...
... numerical measure of its inertia; a fundamental measure of the amount of matter in the object. Mass can be measured in many different ways and can appear abstract. SI units are recommended to establish comfort. ...
AP Physics Course Description 2010-2011
... Calculator Policy: The exam consists of 35 multiple-choice problems that must be answered without using a calculator, and three free-response problems on which any kind of calculator may be used (but no QWERTY keyboards are allowed). The student will not be required to erase the calculator’s memory ...
... Calculator Policy: The exam consists of 35 multiple-choice problems that must be answered without using a calculator, and three free-response problems on which any kind of calculator may be used (but no QWERTY keyboards are allowed). The student will not be required to erase the calculator’s memory ...
S2-3-06 - In Motion - Lesson Sequence
... If time discuss as a class what has taken place at each station. Have a student volunteer to draw their explanation on the board and see if other students agree or wish to add something to it. ...
... If time discuss as a class what has taken place at each station. Have a student volunteer to draw their explanation on the board and see if other students agree or wish to add something to it. ...
Motion in Two and Three Dimensions: Vectors
... • In the previous lecture, we analyzed the motion of a particle moving vertically under gravity. • In this lecture and the next, we’ll generalize to the case of a particle moving in two or three dimensions under gravity, like a projectile. • First we must generalize displacement, velocity and accele ...
... • In the previous lecture, we analyzed the motion of a particle moving vertically under gravity. • In this lecture and the next, we’ll generalize to the case of a particle moving in two or three dimensions under gravity, like a projectile. • First we must generalize displacement, velocity and accele ...
Jeopardy Force
... What is the child’s mass in kg? m = Weight/g = 20.4 kg What does the scale read (tension T) when the elevator accelerates upward at 1.00 m/s2? Fy= ma = T - mg T = mg + ma T = m(g + a) = 220 N ...
... What is the child’s mass in kg? m = Weight/g = 20.4 kg What does the scale read (tension T) when the elevator accelerates upward at 1.00 m/s2? Fy= ma = T - mg T = mg + ma T = m(g + a) = 220 N ...
The Law of Conservation of Momentum
... Elastic collisions conserve both momentum and kinetic energy. This is a slight change on the conservation of energy we had in the last section where energy could have different initial and final forms. Even inelastic collisions conserve energy; the energy gets converted into forms other than kinetic ...
... Elastic collisions conserve both momentum and kinetic energy. This is a slight change on the conservation of energy we had in the last section where energy could have different initial and final forms. Even inelastic collisions conserve energy; the energy gets converted into forms other than kinetic ...
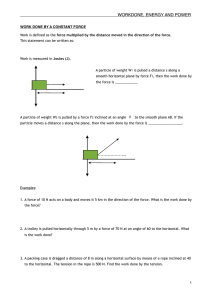
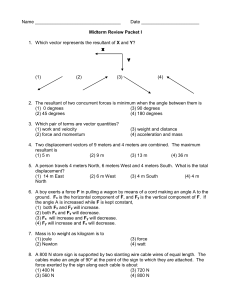
Name
... 19. Which pair of concurrent forces may have a resultant of 20 N? (1) 5.0 N and 10 N (3) 20 N and 50 N (2) 20 N and 20 N (4) 30 N and 5.0 N 20. Three forces act concurrently on an object in equilibrium. These forces are 10 N, 8 N and 6 N. The resultant of the 6 N force and the 8 N force is ...
... 19. Which pair of concurrent forces may have a resultant of 20 N? (1) 5.0 N and 10 N (3) 20 N and 50 N (2) 20 N and 20 N (4) 30 N and 5.0 N 20. Three forces act concurrently on an object in equilibrium. These forces are 10 N, 8 N and 6 N. The resultant of the 6 N force and the 8 N force is ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Physics 121. Lecture 07.
... Measuring G. • The gravitational constant G can be measured using the Cavendish ...
... Measuring G. • The gravitational constant G can be measured using the Cavendish ...