4. Weighty Arguments - The University of Arizona – The Atlas Project
... absolute space, which I have demonstratively confuted by the principle of the want of a sufficient reason of things. It is quite right that, in the context of Galilean relativity, the acceleration of all the matter of the universe in tandem would be strictly unobservable, so Leibniz has a valid poin ...
... absolute space, which I have demonstratively confuted by the principle of the want of a sufficient reason of things. It is quite right that, in the context of Galilean relativity, the acceleration of all the matter of the universe in tandem would be strictly unobservable, so Leibniz has a valid poin ...
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 13: Keeping momentum
... A friend claims that it is safe to go on a car trip with your child without a child seat since he can hold onto your 12kg child even if the car makes a frontal collision (lasting 0.05s and causing the vehicle to stop completely) at v=50 km/h (about 30 miles/h). Is he to be trusted? F=p/t force=imp ...
... A friend claims that it is safe to go on a car trip with your child without a child seat since he can hold onto your 12kg child even if the car makes a frontal collision (lasting 0.05s and causing the vehicle to stop completely) at v=50 km/h (about 30 miles/h). Is he to be trusted? F=p/t force=imp ...
Key Learning(s) - East Pennsboro Area School District
... Lesson Essential Questions: How is the concept of Rotational Kinetic Energy related to the Law of Conservation of Energy? Competencies: Use information from the various representations of rotational motion to solve for unknown motion quantities of objects in rotational motion. ...
... Lesson Essential Questions: How is the concept of Rotational Kinetic Energy related to the Law of Conservation of Energy? Competencies: Use information from the various representations of rotational motion to solve for unknown motion quantities of objects in rotational motion. ...
massachusetts institute of technology
... collision to find the final height in terms of the initial y-component of the velocity of acrobat A and the initial height of clown B, ...
... collision to find the final height in terms of the initial y-component of the velocity of acrobat A and the initial height of clown B, ...
ap physics b
... not talking about a new kind of force, but a new kind of situation in which the same old forces such as, the gravitational force, frictional force, normal force, the tension in a string, or a combination thereof constrain the object to follow a curved path. The centripetal force does NO work on an o ...
... not talking about a new kind of force, but a new kind of situation in which the same old forces such as, the gravitational force, frictional force, normal force, the tension in a string, or a combination thereof constrain the object to follow a curved path. The centripetal force does NO work on an o ...
Document
... constant over a wide range of low speeds, and in the standard model of friction the frictional force is described by the relationship below. The coefficient is typically less than the coefficient of static Friction friction, reflecting the common experience that it is easier to keep something in mot ...
... constant over a wide range of low speeds, and in the standard model of friction the frictional force is described by the relationship below. The coefficient is typically less than the coefficient of static Friction friction, reflecting the common experience that it is easier to keep something in mot ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... 2. Suppose several more horses were hitched up to the same cart. How would this affect the speed of the cart? __________________________________________________________ Although these questions may seem simple, they form the basis of Newton’s second law of motion. The Fan Cart Physics Gizmo™ can be ...
... 2. Suppose several more horses were hitched up to the same cart. How would this affect the speed of the cart? __________________________________________________________ Although these questions may seem simple, they form the basis of Newton’s second law of motion. The Fan Cart Physics Gizmo™ can be ...
P221_2009_week4
... any force acting parallel to the surfaces. • The statement is false because without friction we wouldn't be able to walk--(motion). • The force of friction always acts opposite to any real or “virtual” RELATIVE motion of the two surfaces in contact. In so doing, it can generate motion (e.g walking). ...
... any force acting parallel to the surfaces. • The statement is false because without friction we wouldn't be able to walk--(motion). • The force of friction always acts opposite to any real or “virtual” RELATIVE motion of the two surfaces in contact. In so doing, it can generate motion (e.g walking). ...
net_forces_10-12_physics_ph5
... The amount by which the forces acting on an object are unbalanced is called the net force. When the forces acting on an object are unbalanced, the object will accelerate. Because acceleration is a change in velocity, and velocity includes both speed and direction, a net force will change the speed a ...
... The amount by which the forces acting on an object are unbalanced is called the net force. When the forces acting on an object are unbalanced, the object will accelerate. Because acceleration is a change in velocity, and velocity includes both speed and direction, a net force will change the speed a ...
AP Physics B/C
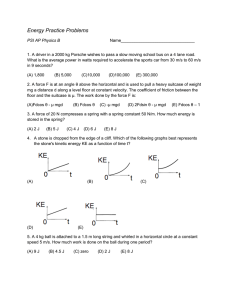
... 19. Two projectiles A and B are launched from the ground with velocities of 50 m/s at 60 ̊and 50 m/s at 30 ̊ with respect to the horizontal. Assuming there is no air resistance involved, which projectile has greater kinetic energy when it reaches the highest point? (A) projectile A ...
... 19. Two projectiles A and B are launched from the ground with velocities of 50 m/s at 60 ̊and 50 m/s at 30 ̊ with respect to the horizontal. Assuming there is no air resistance involved, which projectile has greater kinetic energy when it reaches the highest point? (A) projectile A ...