(Work together) Consider the child, initially at rest
... TA: Right, unless there's a force. S1: Unless a force acts on it. S3: Unless something else acts on it, yeah. TA: Right, so when you don't have a force, what are the possibilities you could have with Timmy? S2: He can move forever. S1: He could be moving forever, or he could be staying still forever ...
... TA: Right, unless there's a force. S1: Unless a force acts on it. S3: Unless something else acts on it, yeah. TA: Right, so when you don't have a force, what are the possibilities you could have with Timmy? S2: He can move forever. S1: He could be moving forever, or he could be staying still forever ...
Simple Harmonic Motion
... position. But we have to use logic to determine which way the acceleration is pointing. ...
... position. But we have to use logic to determine which way the acceleration is pointing. ...
A force.
... This experimental result is the basis for one of the postulates of general relativity: The Principle of Equivalence: an observer in a closed laboratory cannot distinguish between the effects produced by a gravitational field and those produced by an acceleration of the laboratory. ...
... This experimental result is the basis for one of the postulates of general relativity: The Principle of Equivalence: an observer in a closed laboratory cannot distinguish between the effects produced by a gravitational field and those produced by an acceleration of the laboratory. ...
Extra problems similar to final:
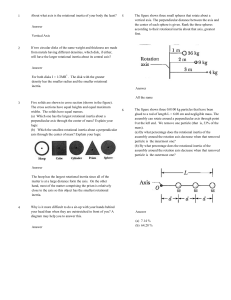
... mass of 200 kg, M1 has a mass of 100 kg, and M 2 has a mass of 150 kg. If the forward ...
... mass of 200 kg, M1 has a mass of 100 kg, and M 2 has a mass of 150 kg. If the forward ...
Chapter 6 Work and Energy
... and over the displacement s, the speed of the car will increase. Newton's 2nd law: acceleration of the car, a = F mCar Starting with velocity v0 , find the final speed. ...
... and over the displacement s, the speed of the car will increase. Newton's 2nd law: acceleration of the car, a = F mCar Starting with velocity v0 , find the final speed. ...
Final Exam Practice questions
... mass of 200 kg, M1 has a mass of 100 kg, and M 2 has a mass of 150 kg. If the forward acceleration is 0.6 m/s 2 , then the horizontal force on the tractor due to the ground is, a) 270 N backward. b) 270 N forward c) 150 N backward. d) 150 N forward e) 90 N forward Ans: b ...
... mass of 200 kg, M1 has a mass of 100 kg, and M 2 has a mass of 150 kg. If the forward acceleration is 0.6 m/s 2 , then the horizontal force on the tractor due to the ground is, a) 270 N backward. b) 270 N forward c) 150 N backward. d) 150 N forward e) 90 N forward Ans: b ...
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS
... Which vector diagram represents the forces, T1, T2,and W, that act on the picture? ...
... Which vector diagram represents the forces, T1, T2,and W, that act on the picture? ...
Document
... Why does a spinning ice skater speed up when she pulls her arms in? Suppose Mr. Stickman is sitting on a stool that swivels holding a pair of dumbbells. His axis of rotation is vertical. With the weights far from that axis, his moment of inertia is large. When he pulls his arms in as he’s spinning, ...
... Why does a spinning ice skater speed up when she pulls her arms in? Suppose Mr. Stickman is sitting on a stool that swivels holding a pair of dumbbells. His axis of rotation is vertical. With the weights far from that axis, his moment of inertia is large. When he pulls his arms in as he’s spinning, ...
Chapter 7, Part I
... difficult to apply, especially to very complicated systems. So, alternate formulations have been developed which are often easier to apply. ...
... difficult to apply, especially to very complicated systems. So, alternate formulations have been developed which are often easier to apply. ...
Acceleration - The Science Queen
... sniffing along at 0.1 m/s. but it hears and starts to scurry for safety. In just 3.7 s it accelerates to 0.9 m/s. Find its acceleration. ...
... sniffing along at 0.1 m/s. but it hears and starts to scurry for safety. In just 3.7 s it accelerates to 0.9 m/s. Find its acceleration. ...