Name
... Which force will change? Which force remains the same? If the upwards acceleration is 3 m/s2, then what is the magnitude of each force? ...
... Which force will change? Which force remains the same? If the upwards acceleration is 3 m/s2, then what is the magnitude of each force? ...
File
... If you know the acceleration of an object, you can determine the net force acting on it. ...
... If you know the acceleration of an object, you can determine the net force acting on it. ...
Chapter 5 Work and Energy conclusion
... Chapter 6 is about the COLLISION of TWO masses. To understand the interaction, both masses must be considered. Newton's 3rd Law plays a very important part. Collisions involve two new concepts: Impulse and Momentum. Impulse concept leads to the Momentum definition. Also applied to two (or more) mass ...
... Chapter 6 is about the COLLISION of TWO masses. To understand the interaction, both masses must be considered. Newton's 3rd Law plays a very important part. Collisions involve two new concepts: Impulse and Momentum. Impulse concept leads to the Momentum definition. Also applied to two (or more) mass ...
pompton lakes high school - Pompton Lakes School District
... Standard: 5.2 Physical Science: All students will understand that physical science principles, including fundamental ideas about matter, energy, and motion, are powerful conceptual tools for making sense of phenomena in physical, living and Earth systems science. Strand: D. Energy Transfer: The cons ...
... Standard: 5.2 Physical Science: All students will understand that physical science principles, including fundamental ideas about matter, energy, and motion, are powerful conceptual tools for making sense of phenomena in physical, living and Earth systems science. Strand: D. Energy Transfer: The cons ...
FRICTION
... FRICTION - the force that present whenever two surfaces are in contact and always acts opposite to the direction of motion. Depends on: • Type of materials in contact • Surfaces of materials ...
... FRICTION - the force that present whenever two surfaces are in contact and always acts opposite to the direction of motion. Depends on: • Type of materials in contact • Surfaces of materials ...
AM Class -I - Directorate General of Shipping
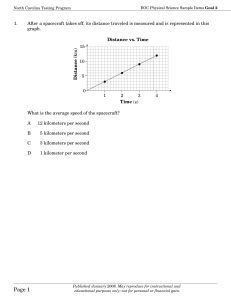
... travelled half the distance at a speed of 30 km/hr and the other half at a speed of 60 km/hr. The other boat covered the entire distance with a constant acceleration. At what instants of time were the speeds of both the boats the same? 4. Two spherical soap bubbles of radius 3.00 cm and 4.00 cm coal ...
... travelled half the distance at a speed of 30 km/hr and the other half at a speed of 60 km/hr. The other boat covered the entire distance with a constant acceleration. At what instants of time were the speeds of both the boats the same? 4. Two spherical soap bubbles of radius 3.00 cm and 4.00 cm coal ...