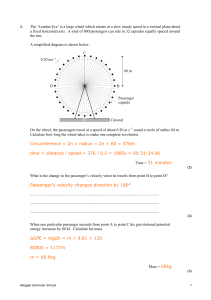
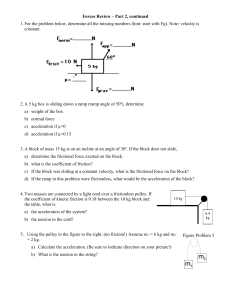
Document
... Solution The pivot point is at the hinges of the door, opposite to where you were pushing the door. The force you used was 50N, at a distance 1.0m from the pivot point. You hit the door perpendicular to its plane, so the angle between the door and the direction of force was 90 degrees. Since = r x ...
... Solution The pivot point is at the hinges of the door, opposite to where you were pushing the door. The force you used was 50N, at a distance 1.0m from the pivot point. You hit the door perpendicular to its plane, so the angle between the door and the direction of force was 90 degrees. Since = r x ...
Chapter 7 - Circular Motion
... force, an object in motion (such as the passenger) continues in motion in a straight line at constant speed. This is Newton's first law of motion. While the car begins to make the turn, the passenger and the seat begin to edge rightward. In a sense, the car is beginning to slide out from under the p ...
... force, an object in motion (such as the passenger) continues in motion in a straight line at constant speed. This is Newton's first law of motion. While the car begins to make the turn, the passenger and the seat begin to edge rightward. In a sense, the car is beginning to slide out from under the p ...
Physics - Circular Motion
... horizontal circles with the same speed. The diameter of one circle is half of the diameter of the other. The force required to keep the object on the smaller circular path is A. the same as The answer is D. The centripetal force needed B. one fourth of to maintain the circular motion of an object is ...
... horizontal circles with the same speed. The diameter of one circle is half of the diameter of the other. The force required to keep the object on the smaller circular path is A. the same as The answer is D. The centripetal force needed B. one fourth of to maintain the circular motion of an object is ...
Chapter 9 Clickers
... mass 3m as each is driven along the same road. Which vehicle, if either, has the largest momentum and what is the difference in their momenta, if any? Express your result as a percentage. a) Since their kinetic energies are the same, their momenta are the same. The difference is zero percent. b) The ...
... mass 3m as each is driven along the same road. Which vehicle, if either, has the largest momentum and what is the difference in their momenta, if any? Express your result as a percentage. a) Since their kinetic energies are the same, their momenta are the same. The difference is zero percent. b) The ...
Lab Instructions
... The timer strikes the tape 60 times per second. Therefore the space between each dot is 1/60 of a second. For simplicity and accuracy we will count every 3rd space and make up an arbitrary time of a tock. Count every three spaces for the ticker tape and measure the displacement of each section and r ...
... The timer strikes the tape 60 times per second. Therefore the space between each dot is 1/60 of a second. For simplicity and accuracy we will count every 3rd space and make up an arbitrary time of a tock. Count every three spaces for the ticker tape and measure the displacement of each section and r ...
Newton`s Scholium on Time, Space, Place and Motion
... intentions is supported by a related passage from his unpublished essay De gravitatione, where he writes: It follows from the Cartesian doctrine that motion can be generated where no force is impressed. If, for the sake of argument, God were to make it happen that the rotation of our vortex were su ...
... intentions is supported by a related passage from his unpublished essay De gravitatione, where he writes: It follows from the Cartesian doctrine that motion can be generated where no force is impressed. If, for the sake of argument, God were to make it happen that the rotation of our vortex were su ...
Rotational Motion
... Solution The pivot point is at the hinges of the door, opposite to where you were pushing the door. The force you used was 50N, at a distance 1.0m from the pivot point. You hit the door perpendicular to its plane, so the angle between the door and the direction of force was 90 degrees. Since = r x ...
... Solution The pivot point is at the hinges of the door, opposite to where you were pushing the door. The force you used was 50N, at a distance 1.0m from the pivot point. You hit the door perpendicular to its plane, so the angle between the door and the direction of force was 90 degrees. Since = r x ...
Force
... much it wants to stay at rest. If an object is moving with constant velocity, the object’s inertia is a measure of how much it wants to maintain its current speed and direction. (Refer to Newton’s Laws for a more complete explanation) ...
... much it wants to stay at rest. If an object is moving with constant velocity, the object’s inertia is a measure of how much it wants to maintain its current speed and direction. (Refer to Newton’s Laws for a more complete explanation) ...
Force, Work, & Simple Machines
... Work problem example: If you lifted an object weighing 200 N through a distance of 0.5 m, how much work would you do? W = F x D W = 200 N x 0.5 m W = 100 J ...
... Work problem example: If you lifted an object weighing 200 N through a distance of 0.5 m, how much work would you do? W = F x D W = 200 N x 0.5 m W = 100 J ...
Newton`s 2nd Law, friction
... Specifically, kinematics is the descriptive branch of mechanics, and dynamics is the causal. Newton's second law relates the net sum of vector forces that are dynamical to the acceleration of an object. In this lab, we verify Newton's second law on an air track. Equipment: air track, masses, photoga ...
... Specifically, kinematics is the descriptive branch of mechanics, and dynamics is the causal. Newton's second law relates the net sum of vector forces that are dynamical to the acceleration of an object. In this lab, we verify Newton's second law on an air track. Equipment: air track, masses, photoga ...
Physics 231 Topic 7: Oscillations Wade Fisher October 5-10 2012
... A h=2m tall, M=80 kg bungee jumper leaps from a H=30m bridge with a bungee cord with spring constant k = 100 N/m attached to his legs. What is the maximum length the cord needs to be if he is to avoid hitting the water below? Define A = extended “amplitude” of the bungee cord Total extension = jumpe ...
... A h=2m tall, M=80 kg bungee jumper leaps from a H=30m bridge with a bungee cord with spring constant k = 100 N/m attached to his legs. What is the maximum length the cord needs to be if he is to avoid hitting the water below? Define A = extended “amplitude” of the bungee cord Total extension = jumpe ...
EOF11 L5 - WordPress.com
... k is the spring constant AKA force constant of a spring. It is measured in N/m x is the distance that a spring is stretched from its relaxed position. ...
... k is the spring constant AKA force constant of a spring. It is measured in N/m x is the distance that a spring is stretched from its relaxed position. ...
Rotational Dynamics and Static Equilibrium
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
AP-Physics-C-10Syllabus-16-17
... Level C exam given in mid–May. This class is oriented toward the serious science student. Heavy emphasis is given on critical thinking, problem solving, research, as well as hands on lab experience. Many of the concepts are introduced by using inquiry based experiences, more formal lab experiments, ...
... Level C exam given in mid–May. This class is oriented toward the serious science student. Heavy emphasis is given on critical thinking, problem solving, research, as well as hands on lab experience. Many of the concepts are introduced by using inquiry based experiences, more formal lab experiments, ...