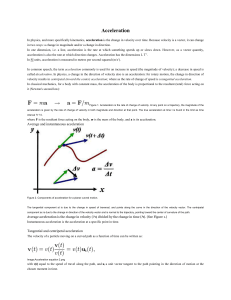
force and acceleration
... Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. As already mentioned, mass depends on the number and kinds of atoms in the object. Weight, however, depends on gravity. You would weigh less on the Moon, for example, than you do on Earth. Why? The Moon's gravity is weaker than Earth's, so you ...
... Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. As already mentioned, mass depends on the number and kinds of atoms in the object. Weight, however, depends on gravity. You would weigh less on the Moon, for example, than you do on Earth. Why? The Moon's gravity is weaker than Earth's, so you ...
Word
... the spring balance will read close to zero. On a flat surface we need just enough force to oppose frictional forces To pull a trolley up a ramp at constant speed we need to apply a constant force of mgsin so that the net force is zero. N balances the component of mg perpendicular to N, which is mgc ...
... the spring balance will read close to zero. On a flat surface we need just enough force to oppose frictional forces To pull a trolley up a ramp at constant speed we need to apply a constant force of mgsin so that the net force is zero. N balances the component of mg perpendicular to N, which is mgc ...
Lecture 2c - Newton`s Laws & Applications
... Newton’s first law is valid. This excludes rotating and accelerating frames. How can we tell if we are in an inertial reference frame? By checking to see if Newton’s first law holds! ...
... Newton’s first law is valid. This excludes rotating and accelerating frames. How can we tell if we are in an inertial reference frame? By checking to see if Newton’s first law holds! ...
+ m 2 v 2
... glides together with the ball across the ice. • The momentum of the medicine ball is 80 kg∙m/s before the collision. The momentum of the clown is 0 kg∙m/s before the collision. The total momentum of the system before the collision is ______________ 80 kg∙m/s. • Therefore, the total momentum of the s ...
... glides together with the ball across the ice. • The momentum of the medicine ball is 80 kg∙m/s before the collision. The momentum of the clown is 0 kg∙m/s before the collision. The total momentum of the system before the collision is ______________ 80 kg∙m/s. • Therefore, the total momentum of the s ...
2 What Is a Force? - Mr. Krohn 8th grade science
... player kicks the ball, the kick is an unbalanced force. It sends the ball in a new direction with a new speed. An object can continue to move when the unbalanced forces are removed. For example, when it is kicked, a soccer ball receives an unbalanced force. The ball continues to roll on the ground a ...
... player kicks the ball, the kick is an unbalanced force. It sends the ball in a new direction with a new speed. An object can continue to move when the unbalanced forces are removed. For example, when it is kicked, a soccer ball receives an unbalanced force. The ball continues to roll on the ground a ...
Motion in One Dimension
... • Motion is relative • When we say an object is moving, we mean it is moving relative to something ...
... • Motion is relative • When we say an object is moving, we mean it is moving relative to something ...
PHYSICS UNIT 3 Motion
... Weight is the gravitational force that the Earth exerts on all masses. Close to the Earth, the size of the force on an object can be calculated by multiplying its mass by (the acceleration due to gravity), that is :W = mg, where g =9.8 Newton/kg or m/s2. It also acceptable to approximate this to 10 ...
... Weight is the gravitational force that the Earth exerts on all masses. Close to the Earth, the size of the force on an object can be calculated by multiplying its mass by (the acceleration due to gravity), that is :W = mg, where g =9.8 Newton/kg or m/s2. It also acceptable to approximate this to 10 ...
Chapter 7 - Circular Motion
... force, an object in motion (such as the passenger) continues in motion in a straight line at constant speed. This is Newton's first law of motion. While the car begins to make the turn, the passenger and the seat begin to edge rightward. In a sense, the car is beginning to slide out from under the p ...
... force, an object in motion (such as the passenger) continues in motion in a straight line at constant speed. This is Newton's first law of motion. While the car begins to make the turn, the passenger and the seat begin to edge rightward. In a sense, the car is beginning to slide out from under the p ...
Student Class ______ Date ______ MULTIPLE
... 14. This is a tricky question. Remember that the block is being pulled up the incline plane, not moving by itself. This means that we cannot say that the mechanical energy of the system is conserved. (If you like to use a formula, you could say that: W=ET, which means that work that you do, equals ...
... 14. This is a tricky question. Remember that the block is being pulled up the incline plane, not moving by itself. This means that we cannot say that the mechanical energy of the system is conserved. (If you like to use a formula, you could say that: W=ET, which means that work that you do, equals ...
Document
... Solution The pivot point is at the hinges of the door, opposite to where you were pushing the door. The force you used was 50N, at a distance 1.0m from the pivot point. You hit the door perpendicular to its plane, so the angle between the door and the direction of force was 90 degrees. Since = r x ...
... Solution The pivot point is at the hinges of the door, opposite to where you were pushing the door. The force you used was 50N, at a distance 1.0m from the pivot point. You hit the door perpendicular to its plane, so the angle between the door and the direction of force was 90 degrees. Since = r x ...