* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final exam review1
Coherence (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Shear wave splitting wikipedia , lookup
Speed of sound wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Stokes wave wikipedia , lookup
Wave packet wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
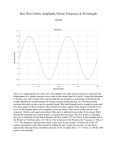
Trivia teams Hawks Songha Ian Taylor 7 Cavaliers Zachary Marquis Timothy 5 Warriors Cameron P Mitchell Erin 8 Rockets Trey Chase Cameron W Nathan 6 Huskies Amir Chloe Breanna Hawks Jay Hunter Bayleigh 13 Cavaliers Johnathan Sam Sydney Trace 13 Warriors Austin Conner C. J. Reco 11 Hawks Albert Kerston Alexis Gaige 14 Cavaliers Alexandria Jessica John Amanda 16 Rockets Malik Magan Joshua Nora 3 A scalar is a quantity that has a. direction. b. magnitude. c. time. d. color. A 15-N force and a 32-N force act on an object toward the right. A 18-N force acts on the same object toward the left. What is the magnitude and direction of the net force on the object? The following graph shows how the velocity of a car changes over time. What is the displacement of the car from t = 0.2 h to t = 0.7 h? a. – 60 km b. 0 km c. 10.5 km d. 21 km e. 60 km Use g = 9.8 m/s2: A 0.250-kg ball sits on a vertical spring with a spring constant of 540 N/m. The ball is pushed downward, compressing the spring 0.10 m. When released, the ball leaves the spring and travels upward. How high does it rise above the point of release? (Neglect friction.) A. 1.1 m B. 2.2 m C. 11 m D. 130 m Which of the following is NOT a form of mechanical energy? A. Translational kinetic energy B. Rotational kinetic energy C. Internal energy D. Gravitational potential energy E. Spring potential energy A rock is kicked horizontally at a speed of 10 m/s from the edge of a cliff. The rock strikes the ground 55 m from the foot of the cliff of height H as suggested in the figure. Neglect air resistance. (Diagram not drawn to scale.) a. How long is the rock in the air? b. What is the approximate value of H, the height of the cliff? After walking 11 km due north from camp, a hiker then walks 21 km due east. What is the magnitude of her displacement from the starting point? Two point masses m and M are separated by a distance d. If the distance between the masses is increased to 3d, how does the gravitational force between them change? a. The force will be one-third as great. b. The force will be one-ninth as great. c. The force will be three times as great. d. The force will be nine times as great. e. It is impossible to determine without knowing the numerical values of m, M, and d. The earth exerts the necessary centripetal force on an orbiting satellite to keep it moving in a circle at constant speed. Which statement best explains why the speed of the satellite does not change even though there is a net force exerted on it? a. The satellite is in equilibrium. b. The acceleration of the satellite is 0 m/s2. c. The centripetal force has magnitude mv2/r. d. The centripetal force is canceled by the reaction force. e. The centripetal force is always perpendicular to the velocity. A 1680-kg car moving at 23 m/s strikes a 2005-kg car at rest. If the two cars stick together, with what speed do they move after the collision? F1 = F2 = F3. Is the net torque about point B clockwise, counterclockwise, or zero? If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of A. B. 1 2 1 2 C. 1 D. E. 2 2 A block attached to the lower end of a vertical spring oscillates up and down. If the spring obeys Hooke's law, the period of oscillation depends on which of the following? I. Mass of the block II. Amplitude of the oscillation III. Force constant of the spring A. B. C. D. E. I only II only III only I and II I and III As a pendulum swings back and forth a. kinetic energy is transformed into potential energy. b. at the end points of its swing, its energy is all potential. c. potential energy is transformed into kinetic energy. d. at the lowest part of its swing, its energy is all kinetic. e. all of the above Use g = 9.8 m/s2: Three resistors having values of 4.0, 6.0 and 10.0 , are connected in parallel. What is their equivalent resistance? If the size of the charge value is tripled for both of two point charges maintained at a constant separation, the mutual force between them will be changed by what factor? A. 9.0 B. 3.0 C. 0.33 D. 1/9 Two wave pulses, each of wavelength , are traveling toward each other along a rope as shown above. When both pulses are in the region between points X and Y. which are a distance apart, the shape of the rope will be which of the following? From the top of a high cliff, a ball is thrown horizontally with initial speed v0. Which of the following graphs best represents the ball's kinetic energy K as a function of time t? Three resistors having values of 4.0, 6.0 and 8.0 Ω, are connected in series with a 6.0-V battery. What is the voltage across the 6.0-Ω resistor? Consider the following decay reaction: 209 85 At ? He A z 4 2 What is the value of A? What is the value of Z? What chemical symbol does What type of decay is this? ? stand for? How long will take a sample of polonium-210 (half-life = 140 days) to decay to onesixteenth of its original strength? Complete the following reaction equations and indicate if they are fission or fusion: A) B) 2 1H + 21H → 32He + ___ For each reaction, indicate if the total mass of the particles is the SAME after the reaction, GREATER after the reaction or LESS after the reaction. A B 2 1H + 21H → 32He + 10n When a 4-N weight is hung from a spring, the spring stretches 0.03 m. How much does the spring stretch when an 8-N weight is hung from it? A. 0.02 m B. 0.03 m C. 0.12 m D. 0.06 m E. 0.24 m If a 100 W light bulb operates at a voltage of 120 V, what is the resistance of the bulb? A standing wave on a string takes the form shown above. The string is 5 m long. The speed on waves in the string is 1,000 m/s What is the frequency of the standing wave? What is the lowest possible frequency possible for this string? The following graph show how the velocity of a car changes over time. 5. During which time interval was the car stopped? a. 0 – 0.2 h b. 0.2 – 0.4 h c. 0.4 – 0.7 h d. 0.7 – 0.8 h e. 0.8 – 1.0 h A ball is thrown into the air. At the ball’s maximum altitude where its velocity is zero, its acceleration is A. zero B. changing from upward to downward C. changing from downward to upward D. directed upward E. directed downward In which part of the graph is the object’s velocity zero? a. AB b. BC c. CD d. DE e. Two are correct. The average velocity of the object from t = 0 s to t = 2 s is a. b. c. d. e. 0 m/s 2 m/s 5 m/s 10 m/s 20 m/s The displacement of the object from t = 2 s to t = 6 s is a. - 40 m b. - 10 m c. 10 m d. 40 m e. 70 m A boat accelerates from 23 m/s to 5.0 m/s in 13.4 s. What is its acceleration? An automobile with an initial velocity of 25 m/s accelerates uniformly at -2.25 m/s2. What is its final velocity after 4.0 s? By dragging his toe, a roller skater can slow from 16 m/s to rest in 2.5 s. How many meters away from a wall must the roller skater start dragging his toe in order to stop before hitting the wall? A car accelerates from rest at a rate of 2.3 m/s2. What is its velocity after traveling 25 m? A cat falls off a ledge that’s 3.0 m tall. How long will it take to hit the ground? A ball is thrown straight up with a speed of 22 m/s. What is the maximum height the ball reaches? A mass on a compressed spring stores 5 J of potential energy. The spring is released, causing the mass to leave the spring and travel straight upward. What is the mass’s gravitational potential energy at the peak of its flight? (Ignore air resistance.) A. Greater than 5 J B. Less than 5 J C. Equal to 5 J What is the weight of a 108-kg football player? As a ball falls, the action force is the pull of the Earth on the ball. What is the reaction to this force? A. The pull of the ball on the Earth B. Air resistance acting against the ball C. The acceleration of the ball D. Nonexistent in this case E. none of the above A 75-kg astronaut weighs 285 N on the surface of Mars. What is the acceleration of gravity on Mars? After a cannonball is fired into frictionless space, the amount of force needed to keep it going equals A. zero, since no force is necessary to keep it moving. B. twice the force with which it was fired. C. one half the force with which it was fired. D. the same amount of force with which it was fired. E. one quarter the force with which it was fired. Betty uses a pulley and a rope to pull a bucket up out of a well. The bucket has a mass of 6.0 kg and accelerates upward at 1.5 m/s2. With what force does Betty pull on the rope? 17 m/s 21° A hummingbird flies at 17 m/s at an angle of 21° to the horizontal, as shown above. What are the x and y components of its velocity? A soccer ball is kicked with an initial speed of 18.6 m/s reaches a maximum height of 14.9 m. At what angle was the ball kicked? A racecar is traveling at constant speed around a circular track. What happens to the centripetal acceleration of the car if the speed is doubled? a. It remains the same. b. It increases by a factor of 2. c. It increases by a factor of 4. d. It is decreased by a factor of one-half. e. It is decreased by a factor of one-fourth. The mass of the planet Mars is 6.4 x 1023 kg and its average distance from the sun is 2.3 x 1011 meters. The sun has a mass of 2.0 x 1030 kg. What is the magnitude of the force of gravitational attraction between the sun and Mars? The driver of a 2,500-kg SUV is traveling at 29 m/s while texting on her phone. She looks up to find she is headed straight for a cornfield. If the force of friction between the corn and the SUV is 1,300 N, how long does it take her to stop? (Ignore other sources of friction.) A bullet traveling at 710 m/s has 1880 J of kinetic energy. What is its mass? If an object is vibrating with a frequency of 25 Hz, what is its period of vibration? a. 25 s b. 0.25 s c. 0.040 s d. 40 s e. None When two or more waves are at the same place at the same time, the resulting effect is called a Doppler wave. b. a shock wave. c. interference. d. a period. a. Brianna is standing still and listening to a siren. She begins running toward the sound. The frequency of the sound she hears will a. increase. b. decrease. c. remain the same. What is the frequency of a sound wave with a speed of 343 m/s and a wavelength of 3.00 m? A repelling force must occur between two charged objects under which of the following conditions? A. charges are of unlike signs B. charges are of like signs C. charges are of equal magnitude D. charges are of unequal magnitude In a thundercloud there is an electric charge of +40 C near the top of the cloud and -40 C near the bottom of the cloud. These charges are separated by 2.0 km. What is the electric force between these two sets of charges? A negatively charged rod is brought near one end of an uncharged metal bar that is supported by an insulator. The end of the metal bar farthest from the charged rod will be which of the following? A. positive B. negative C. neutral D. attracted A wire carries a steady current of 0.1 A over a period of 20 s. What total charge passes through the wire in this time interval? Complete the following statement: When a glass rod is rubbed with silk cloth, the rod becomes positively charged as A. positive charges are transferred from the rod to the silk. positive charges are created on the surface of the rod. C. negative charges are transferred from the silk to the rod. D. negative charges are transferred from the rod to the silk. E. positive charges are transferred from the silk to the rod. B. What charge exists on a test charge that experiences a force of 2.6 x 10-5 N at a point where the electric field intensity is 550 N/C? By using only two resistors, R1 and R2, a student is able to obtain resistances of 3 Ω, 4 Ω, 12 Ω, and 16 Ω. The values of R1 and R2 (in ohms) are: A. 3, 4 B. 2, 12 C. 3, 16 D. 4, 12 E. 4, 16 A battery is connected across a parallel combination of two identical resistors. If the potential difference across the terminals is V and the current in the battery is I, then: A. the potential difference across each resistor is V and B. C. D. E. the current in each resistor is I the potential difference across each resistor is V/2 and the current in each resistor is I/2 he potential difference across each resistor is V and the current in each resistor is I/2 the potential difference across each resistor is V/2 and the current in each resistor is I none of the above are true What is the potential difference across a 5-Ω resistor that carries a current of 5 A? What’s the word? The time needed for a wave to make one complete cycle. What’s the word? The distance between successive identical parts of a wave. What’s the word? A unit of frequency equal to one cycle per second. A man is standing on the shore of a beach, up to his knees in water. Every 2 seconds a wave breaks on him. What is the period of the wave? A man is standing on the shore of a beach, up to his knees in water. Every 2 seconds a wave breaks on him. What is the frequency of the wave? A wave created by shaking a rope up and down is called a A. transverse wave. B. Doppler wave. C. standing wave. D. longitudinal wave. E. constructive wave. Where can you touch a standing wave on a rope without disturbing the wave? A. At a node B. At any place along the wave C. At an antinode Sound waves are A. transverse waves. B. longitudinal waves. C. circular waves. D. polarized waves. When two or more waves are at the same place at the same time, the resulting effect is called A. a Doppler wave. B. a shock wave. C. a period. D. interference. What’s the word? A wave that appears to stay in one place, caused by the superposition of identical waves that travel in opposite directions. Water waves A. transport water but not energy. B. transport energy but not water. C. transport energy and water. D. are not mechanical waves. What’s the word? When the frequency of forced vibrations on an object matches the object’s natural frequency, and a dramatic increase in amplitude occurs. When a sound source moves towards you, what happens to the wave speed? A. It stays the same. B. It decreases. C. It increases. Brianna is standing still and listening to a siren sounding an alarm. She begins running toward the sound. The frequency of the sound she hears will A. increase. B. remain the same. C. decrease. A sound wave that has a higher frequency has a wavelength that is A. longer. B. shorter. Sound waves in air are a series of A. high- and low-pressure regions. B. periodic disturbances. C. periodic compressions and rarefactions. D. all of the above E. none of the above Sound waves A. can travel in a vacuum. B. require a medium. C. are not mechanical waves. D. are unrelated to vibrations. The frequency of a sound wave determines A. how fast the sound travels. B. the magnitude of the compression. C. the pitch of the sound. D. how loud the sound is. Constructive interference occurs when A. two waves of the same color overlap. B. the crests of two waves overlap. C. the crest of one wave meets the trough of another wave. D. all of the above E. none of the above The intensity of a sound depends on A. the medium. B. the amplitude of the waves. C. the wavelength of the sound. D. the pitch of the sound. The speed of a sound wave is determined by the A. source of the wave. B. medium of the wave. C. frequency of the wave. D. amplitude of the wave. Noise-canceling earphones are an example of A. beats. B. resonance. C. destructive interference. D. constructive interference. What is the speed of a wave that is 0.5 m long and has a frequency of 658 Hz? A sound wave has a wavelength of 8 m. If its speed is 340 m/s, what is its frequency?