Name - Deans Community High School
... 4. A car travels a distance of 2 000 metres in a time of 160 seconds. Calculate the average speed of the car in metres per second. 5. Jane jogs to work every day at an average speed of 4 m/s. Most days it takes her 600 seconds to reach work. Calculate how far she jogs. 6. Describe a method of findin ...
... 4. A car travels a distance of 2 000 metres in a time of 160 seconds. Calculate the average speed of the car in metres per second. 5. Jane jogs to work every day at an average speed of 4 m/s. Most days it takes her 600 seconds to reach work. Calculate how far she jogs. 6. Describe a method of findin ...
Old 105 exam 2 - solutions. doc
... the door. (2) is true. The force of the door prevents you from moving in a straight line. Therefore the answer is (2) A car can go from 0 to 60 mph (26.82 m/s) in 8.11 seconds. If the car has a mass of 1318 kg, with what force is it pushing backwards on the road during this time? (assume no air fric ...
... the door. (2) is true. The force of the door prevents you from moving in a straight line. Therefore the answer is (2) A car can go from 0 to 60 mph (26.82 m/s) in 8.11 seconds. If the car has a mass of 1318 kg, with what force is it pushing backwards on the road during this time? (assume no air fric ...
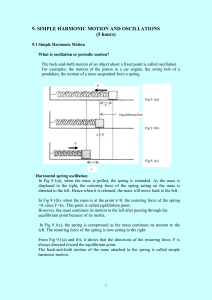
simple harmonic motion and oscilation
... It is oscillation where the amplitudes are decreasing with time until it becomes zero. The mass which oscillates in the water is an example of such oscillation. The critically damped oscillation For a critically damped oscillation, there is a resistance that prevents the system to vibrate. The time ...
... It is oscillation where the amplitudes are decreasing with time until it becomes zero. The mass which oscillates in the water is an example of such oscillation. The critically damped oscillation For a critically damped oscillation, there is a resistance that prevents the system to vibrate. The time ...
File
... State of Physics- Newton and His Laws By now the world knew: • Bodies of different weights fall at the same speed • Bodies in motion did not necessarily come to rest ...
... State of Physics- Newton and His Laws By now the world knew: • Bodies of different weights fall at the same speed • Bodies in motion did not necessarily come to rest ...
Part 2 - Haiku
... the amount of applied force, Fapplied, necessary to overcome static friction, Fstatic and at this moment, they are nearly equal forces, so assume Fapplied = Fstatic . Record the minimum applied force as Fstatic. 3. While the crate is in motion, let go of the slider, observe the change in the force v ...
... the amount of applied force, Fapplied, necessary to overcome static friction, Fstatic and at this moment, they are nearly equal forces, so assume Fapplied = Fstatic . Record the minimum applied force as Fstatic. 3. While the crate is in motion, let go of the slider, observe the change in the force v ...
Physics 513 Name Vaughan Worksheet Newton`s Second Law
... 16. Tammy is pulling Jack up a hill on a sled. Jack and the sled have a mass of 45 kg. The angle of incline is 30 degrees. The tension in the rope is 400 N. The rope makes a 20 degree angle to the incline as shown. a) Find the components of the tension that are parallel and perpendicular to the plan ...
... 16. Tammy is pulling Jack up a hill on a sled. Jack and the sled have a mass of 45 kg. The angle of incline is 30 degrees. The tension in the rope is 400 N. The rope makes a 20 degree angle to the incline as shown. a) Find the components of the tension that are parallel and perpendicular to the plan ...
Chapter 6 - AstroStop
... Simple Examples of Head-On Collisions (Energy and Momentum are Both Conserved) Collision between two objects of the same mass. One mass is at rest. ...
... Simple Examples of Head-On Collisions (Energy and Momentum are Both Conserved) Collision between two objects of the same mass. One mass is at rest. ...
2004_11_03ImpulseMomentum
... Hailstones Versus Raindrops Unlike rain, hail usually does not come to rest after striking a surface. Instead, the hailstones bounce off the roof of the car. If hail fell instead of rain, would the force on the roof be smaller than, equal to, or greater? ...
... Hailstones Versus Raindrops Unlike rain, hail usually does not come to rest after striking a surface. Instead, the hailstones bounce off the roof of the car. If hail fell instead of rain, would the force on the roof be smaller than, equal to, or greater? ...
Ch_5
... Earth is fixed, so it cannot move. Earth can move, but other objects on it prevent it from moving. It moves, but a very small amount that you cannot see. None of the above. ...
... Earth is fixed, so it cannot move. Earth can move, but other objects on it prevent it from moving. It moves, but a very small amount that you cannot see. None of the above. ...
Conservation Laws
... Consider the collision of two balls on the billiards table. The collision occurs in an isolated system as long as friction is small enough that its influence upon the momentum of the billiard balls can be neglected. If so, then the only unbalanced forces acting upon the two balls are the contact for ...
... Consider the collision of two balls on the billiards table. The collision occurs in an isolated system as long as friction is small enough that its influence upon the momentum of the billiard balls can be neglected. If so, then the only unbalanced forces acting upon the two balls are the contact for ...
Momentum
... Momentum Momentum and changing momentum Momentum = mass x velocity (p = mv) Momentum is a vector quantity and is measured in Ns or kgms-1. ...
... Momentum Momentum and changing momentum Momentum = mass x velocity (p = mv) Momentum is a vector quantity and is measured in Ns or kgms-1. ...