Document
... Static and Dynamic Equilibrium Equilibrium implies the object is at rest (static) or its center of mass moves with a constant velocity (dynamic) 106 deals only with the special case in which linear and angular velocities are equal to zero, called “static equilibrium” : vCM = 0 and w = ...
... Static and Dynamic Equilibrium Equilibrium implies the object is at rest (static) or its center of mass moves with a constant velocity (dynamic) 106 deals only with the special case in which linear and angular velocities are equal to zero, called “static equilibrium” : vCM = 0 and w = ...
List of AP Physics 1 Labs
... Based on the motion of Jupiter’s moons Europa, Ganymede, Io and Callisto, what is the mass of ...
... Based on the motion of Jupiter’s moons Europa, Ganymede, Io and Callisto, what is the mass of ...
Document
... 4-2 Newton’s First Law of Motion Newton’s first law is often called the law of inertia. Every object continues in its state of rest, or of uniform velocity in a straight line, as long as no net force acts on it. ...
... 4-2 Newton’s First Law of Motion Newton’s first law is often called the law of inertia. Every object continues in its state of rest, or of uniform velocity in a straight line, as long as no net force acts on it. ...
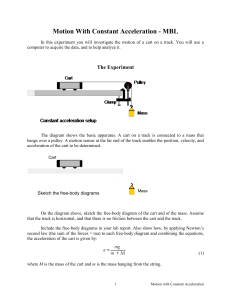
Motion With Constant Acceleration
... . You should wait 3 or 4 seconds after the cart stops moving before hitting ...
... . You should wait 3 or 4 seconds after the cart stops moving before hitting ...
Chapter11
... b) The friction force acts at the center of mass of the cylinder and is directed down the plane. c) The friction force acts at the point of contact between the cylinder and the plane and is directed up the plane. d) The friction force acts at the point of contact between the cylinder and the plane a ...
... b) The friction force acts at the center of mass of the cylinder and is directed down the plane. c) The friction force acts at the point of contact between the cylinder and the plane and is directed up the plane. d) The friction force acts at the point of contact between the cylinder and the plane a ...
Principle of Impulse and momentum
... P has been applied. The initial velocity is v1 = 1 m/s down the plane, and mk = 0.3. ...
... P has been applied. The initial velocity is v1 = 1 m/s down the plane, and mk = 0.3. ...
ch11_stp_as - Doral Academy Preparatory
... The friction between two surfaces before they move is called static friction. After the two surfaces begin moving against each other, the frictional force lessens; the force is then called kinetic friction. Once a runner’s foot begins to slip, the frictional force decreases, as does the force exerte ...
... The friction between two surfaces before they move is called static friction. After the two surfaces begin moving against each other, the frictional force lessens; the force is then called kinetic friction. Once a runner’s foot begins to slip, the frictional force decreases, as does the force exerte ...
Work,energy and power
... 2 Find the work done against gravity when a person of mass 90kg climbs a vertical distance of 32m. 3 A box of mass 12kg is pulled a distance of 25m across a horizontal surface against resistances totaling 50N. If the body moves with uniform velocity, find the work done against the resistances. 4 A h ...
... 2 Find the work done against gravity when a person of mass 90kg climbs a vertical distance of 32m. 3 A box of mass 12kg is pulled a distance of 25m across a horizontal surface against resistances totaling 50N. If the body moves with uniform velocity, find the work done against the resistances. 4 A h ...
Work Energy - Red Hook Central Schools
... Energy Transformations What are the energy transformations in the following situations? • Tossing a ball into the air and catching it. • Bouncing a ball on the floor. ...
... Energy Transformations What are the energy transformations in the following situations? • Tossing a ball into the air and catching it. • Bouncing a ball on the floor. ...
Topic 1: Math and Measurement Review
... a- Does not depend upon the direction traveled by the object b- Measured in meters or kilometers 2- Displacement- the total length between the starting point and the ending point a- Depends on the direction traveled by the object b- Measured in meters or kilometers 3- Speed- how fast an object trave ...
... a- Does not depend upon the direction traveled by the object b- Measured in meters or kilometers 2- Displacement- the total length between the starting point and the ending point a- Depends on the direction traveled by the object b- Measured in meters or kilometers 3- Speed- how fast an object trave ...
2015-16 Newton`s Laws and Model Rocketry
... – In rocketry, the principal of action and reaction is very important. – Newton's third law explains the generation of thrust by a rocket engine. In a rocket engine, hot exhaust gas is produced through the combustion of a fuel with an oxidizer. The hot exhaust gas flows through the rocket nozzle and ...
... – In rocketry, the principal of action and reaction is very important. – Newton's third law explains the generation of thrust by a rocket engine. In a rocket engine, hot exhaust gas is produced through the combustion of a fuel with an oxidizer. The hot exhaust gas flows through the rocket nozzle and ...
Dynamics 1
... Recognize the significance of Newton’s second law of motion and use it to solve motion ...
... Recognize the significance of Newton’s second law of motion and use it to solve motion ...