Introduction to mechanical engineering lecture notes
... existence of at least one frame of reference called a Newtonian or inertial reference frame, relative to which the motion of a particle not subject to forces is a straight line at a constant speed. ...
... existence of at least one frame of reference called a Newtonian or inertial reference frame, relative to which the motion of a particle not subject to forces is a straight line at a constant speed. ...
Forces - Cloudfront.net
... 2. Suppose you push two people and they both accelerate at the same rate. However, one person has much more mass than the other. Which one required more force to accelerate? 3. Suppose you push two people with the same amount of force. However, one person has more mass than the other. Which person w ...
... 2. Suppose you push two people and they both accelerate at the same rate. However, one person has much more mass than the other. Which one required more force to accelerate? 3. Suppose you push two people with the same amount of force. However, one person has more mass than the other. Which person w ...
Section 3 Friction: A Force That Opposes Motion Chapter 19
... due to their masses. Gravity can change the motion of an object by changing its speed, direction, or both. • All matter has mass, and gravity is a result of mass. Therefore, all matter is affected by gravity and all objects experience an attraction toward all other objects. • The mass of most object ...
... due to their masses. Gravity can change the motion of an object by changing its speed, direction, or both. • All matter has mass, and gravity is a result of mass. Therefore, all matter is affected by gravity and all objects experience an attraction toward all other objects. • The mass of most object ...
AP Physics This and Samples
... a force constant k, it oscillates with a period T. If the spring is cut to one third of its original length and the same mass is attached to it, the new period of oscillation will be A) less than T. B) equal to T. C) greater than T. D) It could be greater or less than T, depending on how you cut the ...
... a force constant k, it oscillates with a period T. If the spring is cut to one third of its original length and the same mass is attached to it, the new period of oscillation will be A) less than T. B) equal to T. C) greater than T. D) It could be greater or less than T, depending on how you cut the ...
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 18: equilibrium & revision
... ac=v2/r directed to the center of the circular motion Also v=r, so ac=2r Fto center=mac=mv2/r This acceleration is caused by ‘known’ force (gravitation, friction, tension…) Make sure you understand how to use Kepler’s 3rd law and the general definition of gravitational PE. PHY 231 ...
... ac=v2/r directed to the center of the circular motion Also v=r, so ac=2r Fto center=mac=mv2/r This acceleration is caused by ‘known’ force (gravitation, friction, tension…) Make sure you understand how to use Kepler’s 3rd law and the general definition of gravitational PE. PHY 231 ...
Thursday, Oct. 9, 2014 - UTA HEP WWW Home Page
... Impulse and Linear Momentum Net force causes change of momentum Newton’s second law By integrating the above equation in a time interval ti to tf, one can obtain impulse I. Effect of the force F acting on an object over the time So what do you interval Δt=tf-ti is equal to the change of the momen ...
... Impulse and Linear Momentum Net force causes change of momentum Newton’s second law By integrating the above equation in a time interval ti to tf, one can obtain impulse I. Effect of the force F acting on an object over the time So what do you interval Δt=tf-ti is equal to the change of the momen ...
Momentum and impulse
... divided by the elapsed time Δt equals the constant net force Fnet acting on the object If a constant force acts on a object. The impulse I delivered to the object over a time interval Δt is given by: I = F Δt SI unit: kg m/s (ex 6.2/163) ...
... divided by the elapsed time Δt equals the constant net force Fnet acting on the object If a constant force acts on a object. The impulse I delivered to the object over a time interval Δt is given by: I = F Δt SI unit: kg m/s (ex 6.2/163) ...
GRADE 10F: Physics 2
... acting while the objects are moving at constant velocity and guide them through the following argument. When the velocity is constant, there is no acceleration. Hence there can be no overall force acting. If there is a force acting in one direction (e.g. gravity in the case of falling objects) then ...
... acting while the objects are moving at constant velocity and guide them through the following argument. When the velocity is constant, there is no acceleration. Hence there can be no overall force acting. If there is a force acting in one direction (e.g. gravity in the case of falling objects) then ...
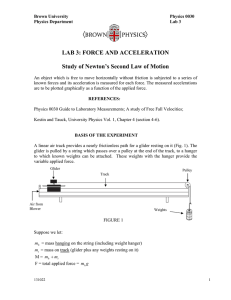
LAB 3: FORCE AND ACCELERATION Study of Newton`s Second
... techniques required. Practice releasing the glider from rest (starting at the backstop position and letting go without imparting any initial velocity). Pick a U photocell position near to the rest position, and an L position near the pulley, note the measured transit time from U to L and repeat seve ...
... techniques required. Practice releasing the glider from rest (starting at the backstop position and letting go without imparting any initial velocity). Pick a U photocell position near to the rest position, and an L position near the pulley, note the measured transit time from U to L and repeat seve ...
Document
... Static and Dynamic Equilibrium Equilibrium implies the object is at rest (static) or its center of mass moves with a constant velocity (dynamic) 106 deals only with the special case in which linear and angular velocities are equal to zero, called “static equilibrium” : vCM = 0 and w = ...
... Static and Dynamic Equilibrium Equilibrium implies the object is at rest (static) or its center of mass moves with a constant velocity (dynamic) 106 deals only with the special case in which linear and angular velocities are equal to zero, called “static equilibrium” : vCM = 0 and w = ...