Document
... SB1. Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. ...
... SB1. Students will analyze the nature of the relationships between structures and functions in living cells. ...
chapter 1: the lungs and respiratory system
... has two lobes lymph – the fluid that circulates through the lymphatic vessels; made up of excess tissue fluid, proteins, and cells of the immune system lymphatics/lymphatic vessels – thin walled structures that carry lymph fluid throughout the body mediastinum – the area in the center of the chest b ...
... has two lobes lymph – the fluid that circulates through the lymphatic vessels; made up of excess tissue fluid, proteins, and cells of the immune system lymphatics/lymphatic vessels – thin walled structures that carry lymph fluid throughout the body mediastinum – the area in the center of the chest b ...
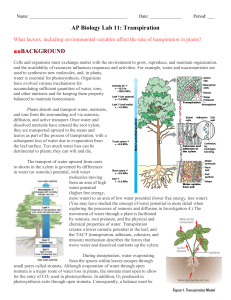
AP Biology Lab 11: Transpiration
... c. What predictions and/or hypotheses can you make about the number of stomata per mm2 and the rate of transpiration? d. Is the leaf surface area directly related to the rate of transpiration? e. What predictions can you make about the rate of transpiration in plants with smaller or fewer leaves? f ...
... c. What predictions and/or hypotheses can you make about the number of stomata per mm2 and the rate of transpiration? d. Is the leaf surface area directly related to the rate of transpiration? e. What predictions can you make about the rate of transpiration in plants with smaller or fewer leaves? f ...
Cellular Respiration
... Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration – cellular process that requires oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide – Often involves complete breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and water Oxidation ...
... Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration – cellular process that requires oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide – Often involves complete breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and water Oxidation ...
LEC 7 respiration
... • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration • Each NADH (the reduce ...
... • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration • Each NADH (the reduce ...
Ecosystem Dynamics
... 94. That’s right – plants. Plants are found nearly every place on earth. 95. Most plants don’t eat other things for energy 96. You Decide! How do plants get their energy? 97. Plants produce energy via the process of photosynthesis. 98. In the process of photosynthesis, plants produce energy from the ...
... 94. That’s right – plants. Plants are found nearly every place on earth. 95. Most plants don’t eat other things for energy 96. You Decide! How do plants get their energy? 97. Plants produce energy via the process of photosynthesis. 98. In the process of photosynthesis, plants produce energy from the ...
Student Book (Unit 1 Module 4) - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... • Activation of chemicals – glucose is phosphorylated at the beginning of respiration so that it is more unstable and can be broken down to release energy. Some of the energy from catabolic reactions is released in the form of heat. This is useful as metabolic reactions are controlled by enzymes, ...
... • Activation of chemicals – glucose is phosphorylated at the beginning of respiration so that it is more unstable and can be broken down to release energy. Some of the energy from catabolic reactions is released in the form of heat. This is useful as metabolic reactions are controlled by enzymes, ...
A. Introduction
... Populations composed of long lived, slow to mature individuals have an increases probability of long tern survival. However, they are slow to recuperate their numbers when population size is reduced. II. COMMUITY INTERACTION A community is composed of all of the populations of organisms inhabiting a ...
... Populations composed of long lived, slow to mature individuals have an increases probability of long tern survival. However, they are slow to recuperate their numbers when population size is reduced. II. COMMUITY INTERACTION A community is composed of all of the populations of organisms inhabiting a ...
userfiles/153/my files/09_lecture_presentation 2015?id=1069
... -Aerobic respiration consumes organic molecules and O2 and yields ATP -Anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration but consumes compounds other than O2 Cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration – Although carboh ...
... -Aerobic respiration consumes organic molecules and O2 and yields ATP -Anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration but consumes compounds other than O2 Cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration – Although carboh ...
Cellular Respiration - Esperanza High School
... requiring process that uses energy extracted from macromolecules (glucose) to produce energy (ATP) and water (H2O). C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy glucose ...
... requiring process that uses energy extracted from macromolecules (glucose) to produce energy (ATP) and water (H2O). C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy glucose ...
oxygen - our most important health supplement
... Oxygen is natures most important nutrient, it is critical to the life processes of all living creatures. Oxygen combines with glucose to produce energy & functions as the major - & most efficient – detoxifying element in the body, ridding the body of the toxic byproducts of metabolism & destroying f ...
... Oxygen is natures most important nutrient, it is critical to the life processes of all living creatures. Oxygen combines with glucose to produce energy & functions as the major - & most efficient – detoxifying element in the body, ridding the body of the toxic byproducts of metabolism & destroying f ...
10th Biology: Life processes solved Questions
... organic compounds, which help in building up the cells. Plants take simple raw materials like CO2 from air, water and minerals from the soil to make their own carbon based compounds like proteins, carbohydrates and fats etc. Sunlight is used as energy source. Animals and other organisms including hu ...
... organic compounds, which help in building up the cells. Plants take simple raw materials like CO2 from air, water and minerals from the soil to make their own carbon based compounds like proteins, carbohydrates and fats etc. Sunlight is used as energy source. Animals and other organisms including hu ...
biology - Textbooks Online
... importance was given to either natural or phylogenetic relationships among different groups of plants. Natural system In this system of classification, plants are classified based on their natural affinities. More number of characters are taken into consideration in this system. It is mainly based o ...
... importance was given to either natural or phylogenetic relationships among different groups of plants. Natural system In this system of classification, plants are classified based on their natural affinities. More number of characters are taken into consideration in this system. It is mainly based o ...
Fatty acid catabolism leture2-3
... The four steps of β -oxidation are repeated to get FA completely converted to acetylCoA. For example for a 16 carbon fatty acid, Palmityl-CoA, it will take 7 cycle of β -oxidation to generate 8 acetyl-CoA. Thus there will be production of ...
... The four steps of β -oxidation are repeated to get FA completely converted to acetylCoA. For example for a 16 carbon fatty acid, Palmityl-CoA, it will take 7 cycle of β -oxidation to generate 8 acetyl-CoA. Thus there will be production of ...
Gas Exchange
... During intense exercise, your cells start to do a different type of respiration, anaerobic respiration (respiration without oxygen). Anaerobic respiration releases less energy and make a chemical called lactic acid. This can cause cramp. It is not just during exercise that your cells do not get enou ...
... During intense exercise, your cells start to do a different type of respiration, anaerobic respiration (respiration without oxygen). Anaerobic respiration releases less energy and make a chemical called lactic acid. This can cause cramp. It is not just during exercise that your cells do not get enou ...
Cellular Respiration
... mitochondrial matrix; pyruvate into carbon dioxide • 3.Electron Transport Chain: inner membrane of mitochondrion; electrons passed to oxygen ...
... mitochondrial matrix; pyruvate into carbon dioxide • 3.Electron Transport Chain: inner membrane of mitochondrion; electrons passed to oxygen ...
Chloroplasts at work during plant innate immunity
... The chloroplast is a vital component of photosynthetic cells in cyanobacteria, algae, and higher plants, since it is the organelle in which photosynthesis takes place. Chloroplasts are large plant cell organelles bounded by a double-celled composite membrane with an intermembrane space, called the c ...
... The chloroplast is a vital component of photosynthetic cells in cyanobacteria, algae, and higher plants, since it is the organelle in which photosynthesis takes place. Chloroplasts are large plant cell organelles bounded by a double-celled composite membrane with an intermembrane space, called the c ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.