Why Plants Need Phosphorus (Missouri)
... phosphate for signaling events is ATP (adeno- plants by phosphorylation or dephosphorylasine triphosphate). Besides this role, ATP is tion is of critical importance in many plant also the major energy currency in the cell. processes. Several proteins have unique strucThis molecule contains high ener ...
... phosphate for signaling events is ATP (adeno- plants by phosphorylation or dephosphorylasine triphosphate). Besides this role, ATP is tion is of critical importance in many plant also the major energy currency in the cell. processes. Several proteins have unique strucThis molecule contains high ener ...
ppt - Coastalzone
... Biogeochemical cycles • All materials flow through the environment over time- materials cycle through the environment ...
... Biogeochemical cycles • All materials flow through the environment over time- materials cycle through the environment ...
A stable, mature community that undergoes little or no change in
... A water biome where fresh water empties into a salt water body creating a biome where organisms must be able to tolerate both. Portion of the shorline that lies between high and low tides. ...
... A water biome where fresh water empties into a salt water body creating a biome where organisms must be able to tolerate both. Portion of the shorline that lies between high and low tides. ...
Photosynthesis & Respiration
... When O2 is scarce, human muscle switches from aerobic respiration to LAF. Lactate accumulates, but is eventually taken to the liver and converted back to pyruvic acid ...
... When O2 is scarce, human muscle switches from aerobic respiration to LAF. Lactate accumulates, but is eventually taken to the liver and converted back to pyruvic acid ...
Protists
... PROTISTS- Chapter 28 “More about what they are not… than what they are” CHARACTERISTICS EUKARYOTES that AREN’T animals, plants, or fungi Primarily unicellular (Paramecium, Euglena); Some colonial (Volvox); some multicellular (Seaweed) Cilia or flagella at some time in life cycle Kingdom is POLYPHYLE ...
... PROTISTS- Chapter 28 “More about what they are not… than what they are” CHARACTERISTICS EUKARYOTES that AREN’T animals, plants, or fungi Primarily unicellular (Paramecium, Euglena); Some colonial (Volvox); some multicellular (Seaweed) Cilia or flagella at some time in life cycle Kingdom is POLYPHYLE ...
BIOL 303 Cell Biology Test preparation questionnaire # 1
... 106. What is the name of the enzyme that phosphorylates ADP into ATP? 107. Describe the loop that constitutes the direct photophosphorylation cycle found in plant chloroplasts. 108. Where do the reactions of the Calvin-Benson cycle take place? 109. Name the main intermediate in the dark reactions of ...
... 106. What is the name of the enzyme that phosphorylates ADP into ATP? 107. Describe the loop that constitutes the direct photophosphorylation cycle found in plant chloroplasts. 108. Where do the reactions of the Calvin-Benson cycle take place? 109. Name the main intermediate in the dark reactions of ...
Plants, Transpiration, Photosynthesis and Respiration
... Transpiration(water loss through stomata) regulated by the guard cells through their opining/closing Leaves have epidermis with cuticles and stomata to prevent water loss; guard cells control the opening of the stomata In plants, chlorophyll (found in chloroplasts) captures energy from the sun in or ...
... Transpiration(water loss through stomata) regulated by the guard cells through their opining/closing Leaves have epidermis with cuticles and stomata to prevent water loss; guard cells control the opening of the stomata In plants, chlorophyll (found in chloroplasts) captures energy from the sun in or ...
External sources of energy → biologically energy : ATP
... C6H12O6 + 2NAD+ + 2ADP3- + 2Pi2- 2 C3H4O3 + 2NADH + 2 ATP4• Citric acid cycle • In mitochondrion • Pyruvate CO2 + NADH + FADH2 • Electron transport chain • High energy electrons from NADH and FADH2 O2 • Convert energy released into a proton motive force (H+ gradient) ...
... C6H12O6 + 2NAD+ + 2ADP3- + 2Pi2- 2 C3H4O3 + 2NADH + 2 ATP4• Citric acid cycle • In mitochondrion • Pyruvate CO2 + NADH + FADH2 • Electron transport chain • High energy electrons from NADH and FADH2 O2 • Convert energy released into a proton motive force (H+ gradient) ...
What makes a Plant a Plant?
... Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll Chlorophyll absorbs energy from the sun Plants use the energy to make food - glucose (sugar) Process is called Photosynthesis ...
... Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll Chlorophyll absorbs energy from the sun Plants use the energy to make food - glucose (sugar) Process is called Photosynthesis ...
Carbon-Silicate Cycle
... • Defined as the geochemical cycle that is naturally occurring reversible chemical reaction with summary equation CaSiO3+CO2<=>CaCO3+SiO2. • reaction is generally shifted in the favor of carbonate formation under near surface temperature and pressure conditions, but shifts to silicate formation at t ...
... • Defined as the geochemical cycle that is naturally occurring reversible chemical reaction with summary equation CaSiO3+CO2<=>CaCO3+SiO2. • reaction is generally shifted in the favor of carbonate formation under near surface temperature and pressure conditions, but shifts to silicate formation at t ...
Chapter 36
... • When a disturbance damages an existing community but leaves the soil intact, the change that follows is called secondary succession. – Fires – Land cleared for farming, then abandoned. ...
... • When a disturbance damages an existing community but leaves the soil intact, the change that follows is called secondary succession. – Fires – Land cleared for farming, then abandoned. ...
Ecology Exam 1 True / False: Only hermit crabs hypoosmotic to their
... 2. A group of individuals of the same species occupying a given area is referred to as a(n) ______________________ ...
... 2. A group of individuals of the same species occupying a given area is referred to as a(n) ______________________ ...
Standard B-2
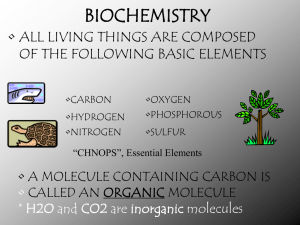
... Enzymatic proteins accelerate the speed of chemical reactions such as digestive enzymes Carbohydrates: sugars and starches; composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; main source of energy for the cell and used to store energy for short periods of time; caloric value of carbs depend on the number o ...
... Enzymatic proteins accelerate the speed of chemical reactions such as digestive enzymes Carbohydrates: sugars and starches; composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; main source of energy for the cell and used to store energy for short periods of time; caloric value of carbs depend on the number o ...
student notes - Science and Plants for Schools
... absence of light. The mitochondrion is using up sugar from the cytoplasm and oxygen from the air spaces in the leaf. It is producing carbon dioxide and water, which diffuse through the cytoplasm to the air space surrounding the cell. The process taking place in the mitochondrion is respiration. A si ...
... absence of light. The mitochondrion is using up sugar from the cytoplasm and oxygen from the air spaces in the leaf. It is producing carbon dioxide and water, which diffuse through the cytoplasm to the air space surrounding the cell. The process taking place in the mitochondrion is respiration. A si ...
Systems in Plants
... 4. What do chloroplasts do? 5. Why are leaves wide and green? 6. What is the function of the root system? 7. What is the function of the shoot system? 8. What does a stomata do? 9. Research three ways that plants use to have their pollen fertilize the female plant’s eggs. 10. Research: What strategi ...
... 4. What do chloroplasts do? 5. Why are leaves wide and green? 6. What is the function of the root system? 7. What is the function of the shoot system? 8. What does a stomata do? 9. Research three ways that plants use to have their pollen fertilize the female plant’s eggs. 10. Research: What strategi ...
What are reactions? - UTLNET Secure Site
... If they are formed in a reaction you will see __________. This can be a sign that a chemical __________ has happened. 2. Other signs of a chemical reaction might be an increase in temperature if _____ is released or a change in ________. 3. Physical changes like _________ do not make new materials a ...
... If they are formed in a reaction you will see __________. This can be a sign that a chemical __________ has happened. 2. Other signs of a chemical reaction might be an increase in temperature if _____ is released or a change in ________. 3. Physical changes like _________ do not make new materials a ...
What are reactions?
... If they are formed in a reaction you will see __________. This can be a sign that a chemical __________ has happened. 2. Other signs of a chemical reaction might be an increase in temperature if _____ is released or a change in ________. 3. Physical changes like _________ do not make new materials a ...
... If they are formed in a reaction you will see __________. This can be a sign that a chemical __________ has happened. 2. Other signs of a chemical reaction might be an increase in temperature if _____ is released or a change in ________. 3. Physical changes like _________ do not make new materials a ...
photosynthesis - Northwest ISD Moodle
... using sun’s energy to make ATP using CO2 & water to make sugar in chloroplasts (leaf) allows plants to grow makes a waste product ...
... using sun’s energy to make ATP using CO2 & water to make sugar in chloroplasts (leaf) allows plants to grow makes a waste product ...
Plant Homeostasis
... leaves through the stem to all parts of the plant, mainly the roots (storage) ...
... leaves through the stem to all parts of the plant, mainly the roots (storage) ...
Matthew Mekari
... A. The main way that organisms break down organic molecules is cellular respiration, the oxygen dependent process by which cells extract energy from food molecules. B. Most eukaryotes cells (and many prokaryotic cells ) are aerobic, that is, they depend on oxygen for life. C. Many prokaryotes and a ...
... A. The main way that organisms break down organic molecules is cellular respiration, the oxygen dependent process by which cells extract energy from food molecules. B. Most eukaryotes cells (and many prokaryotic cells ) are aerobic, that is, they depend on oxygen for life. C. Many prokaryotes and a ...
Basics of Biology Chapter 4
... Aerobic respiration- releases the most, and needs oxygen. Anaerobic- does not release as much energy, no oxygen required. -organisms that live in sediments or in the guts of fishes. ...
... Aerobic respiration- releases the most, and needs oxygen. Anaerobic- does not release as much energy, no oxygen required. -organisms that live in sediments or in the guts of fishes. ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.