B4 revision ppt
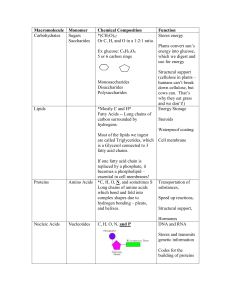
... walls. Both are polymers of glucose Glucose can also be built up into fats, proteins and chlorophyll Glucose molecules are broken down by respiration, releasing energy to power chemical reactions in cells ...
... walls. Both are polymers of glucose Glucose can also be built up into fats, proteins and chlorophyll Glucose molecules are broken down by respiration, releasing energy to power chemical reactions in cells ...
Enzymes
... Changes in pH changes protein shape (most human proteins sit at a pH of 6-8) Denaturing=extreme temperature and pH can change enzyme shape, rendering it useless! ...
... Changes in pH changes protein shape (most human proteins sit at a pH of 6-8) Denaturing=extreme temperature and pH can change enzyme shape, rendering it useless! ...
Metabolic Processes Jeopardy Review
... (1) Save a duplicate of this template. (2) Enter all answers and questions in the normal view. (view/normal) (3) Change the category headings in the normal view (view/normal) (4) View as a slideshow. (5) Use the home red button after each question. ...
... (1) Save a duplicate of this template. (2) Enter all answers and questions in the normal view. (view/normal) (3) Change the category headings in the normal view (view/normal) (4) View as a slideshow. (5) Use the home red button after each question. ...
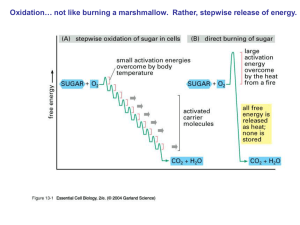
Cellular Respiration NOTES
... Cellular respiration converts the energy stored in the bonds of the glucose into energy in ATP. Why is it important? – all living organisms need to convert the energy in the food they eat (or in the case of plants in the food they produce through photosynthesis) into a form of energy that is easy to ...
... Cellular respiration converts the energy stored in the bonds of the glucose into energy in ATP. Why is it important? – all living organisms need to convert the energy in the food they eat (or in the case of plants in the food they produce through photosynthesis) into a form of energy that is easy to ...
KEY
... Thin walled allows for quick gas exchange, moist which facilitates diffusion, numerous which increase surface area, stretch receptors in their walls signal medulla oblongata to stop inhalation 10) What does reduced hemoglobin carry? Hydrogen ions 11) Where does oxyhemoglobin become deoxyhemoglobin? ...
... Thin walled allows for quick gas exchange, moist which facilitates diffusion, numerous which increase surface area, stretch receptors in their walls signal medulla oblongata to stop inhalation 10) What does reduced hemoglobin carry? Hydrogen ions 11) Where does oxyhemoglobin become deoxyhemoglobin? ...
Producers - Humble ISD
... → Most of the oxygen in the atmosphere comes from plants. Living, breathing organisms must have oxygen. → Photosynthesis provides energy for living organisms. Living organisms must have energy. ...
... → Most of the oxygen in the atmosphere comes from plants. Living, breathing organisms must have oxygen. → Photosynthesis provides energy for living organisms. Living organisms must have energy. ...
Chapter 10: Cycles and Patterns in the Biosphere
... 1. sun is the basic energy source on which nearly all life ultimately depends a. ~ 0.1% of solar energy that reaches Earth is fixed in photosynthesis b. > ½ of that total is used immediately in the plant’s own respiration c. remainder is temporarily stored, eventually entering the food chain 2. Phot ...
... 1. sun is the basic energy source on which nearly all life ultimately depends a. ~ 0.1% of solar energy that reaches Earth is fixed in photosynthesis b. > ½ of that total is used immediately in the plant’s own respiration c. remainder is temporarily stored, eventually entering the food chain 2. Phot ...
Cycles and Patterns in the Biosphere
... 1. sun is the basic energy source on which nearly all life ultimately depends a. ~ 0.1% of solar energy that reaches Earth is fixed in photosynthesis b. > ½ of that total is used immediately in the plant’s own respiration c. remainder is temporarily stored, eventually entering the food chain 2. Phot ...
... 1. sun is the basic energy source on which nearly all life ultimately depends a. ~ 0.1% of solar energy that reaches Earth is fixed in photosynthesis b. > ½ of that total is used immediately in the plant’s own respiration c. remainder is temporarily stored, eventually entering the food chain 2. Phot ...
Plant Production PPT
... occurs on new growth and on some it occurs on old growth. Most fruit trees require this bud tissue to undergo a cold period before it will burst. The basic sturucture of the flower has developed inside the bud and then bursts out (blossums). Most horticultural crops are insect pollinated. The except ...
... occurs on new growth and on some it occurs on old growth. Most fruit trees require this bud tissue to undergo a cold period before it will burst. The basic sturucture of the flower has developed inside the bud and then bursts out (blossums). Most horticultural crops are insect pollinated. The except ...
Nitrogen Cycle Presenter: ___ Nitrogen Fixation: ___ Atmosphere
... ___ Carbon makes up Life, organic/biotic matter ___ Atmosphere – contains Carbon Dioxide, CO2 ___ Plants’ leaves take in/absorbs CO2 ___ Plants perform Photosynthesis ___ Photosynthesis – plants take in water and CO2 use the sun’s energy to convert to carbohydrates/glucose and release Oxygen, O2 ___ ...
... ___ Carbon makes up Life, organic/biotic matter ___ Atmosphere – contains Carbon Dioxide, CO2 ___ Plants’ leaves take in/absorbs CO2 ___ Plants perform Photosynthesis ___ Photosynthesis – plants take in water and CO2 use the sun’s energy to convert to carbohydrates/glucose and release Oxygen, O2 ___ ...
Objective: How can we describe the basic characteristics of plants
... Where do they occur in the cell? Respiration occurs in the mitochondria of ALL cells. PS occurs in the chloroplasts of SOME leaf cells. Resp. = C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + energy PS = CO2 + H2O + light ...
... Where do they occur in the cell? Respiration occurs in the mitochondria of ALL cells. PS occurs in the chloroplasts of SOME leaf cells. Resp. = C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + energy PS = CO2 + H2O + light ...
chapter 8 section 3 notes
... During the light-independent reactions, commonly referred to as the Calvin cycle, plants use the energy that ATP and NADPH contains to build stable high-energy carbohydrate compounds that can be stored for a long time. ...
... During the light-independent reactions, commonly referred to as the Calvin cycle, plants use the energy that ATP and NADPH contains to build stable high-energy carbohydrate compounds that can be stored for a long time. ...
Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Notes
... • Photosynthesis, CO2 and Plants • The Energy of life (ATP) • Structure of chloroplast + Photosynthesis overview ...
... • Photosynthesis, CO2 and Plants • The Energy of life (ATP) • Structure of chloroplast + Photosynthesis overview ...
Lecture 27
... Exciton transfer (resonance energy transfer)-electronic energy is directly transferred to nearby unexcited molecules with similar electronic properties Funnels the light to photosynthetic reaction centers Photooxidation-light-excited donor molecule is oxidized by transferring an electron to an accep ...
... Exciton transfer (resonance energy transfer)-electronic energy is directly transferred to nearby unexcited molecules with similar electronic properties Funnels the light to photosynthetic reaction centers Photooxidation-light-excited donor molecule is oxidized by transferring an electron to an accep ...
Chapter 10. Photosynthesis: The Calvin Cycle Life
... Need to produce all organic molecules necessary for growth carbohydrates, lipids proteins, nucleic acids ...
... Need to produce all organic molecules necessary for growth carbohydrates, lipids proteins, nucleic acids ...
Living things are energy rich complex chemical structures
... IT? endergonic reactions- bonds are formed and energy absorbed. exergonic reactions – bonds are broken and energy is released. ...
... IT? endergonic reactions- bonds are formed and energy absorbed. exergonic reactions – bonds are broken and energy is released. ...
Ch. 6and7_Notes
... – Involves a group of molecules built into the inner membrane of the mitochondrion – Electrons pulled off of food by Glycolysis and Krebs are passed between these molecules. • This will ultimately result in the production of ATP ...
... – Involves a group of molecules built into the inner membrane of the mitochondrion – Electrons pulled off of food by Glycolysis and Krebs are passed between these molecules. • This will ultimately result in the production of ATP ...
Carbon dioxide - cloudfront.net
... • Autotrophic organisms: allows absorption of CO₂ into cells. • Add water and energy from the sun. • Organisms use photosynthesis to chemically convert the CO2 to carbonbased sugar molecules. • Sugar, through metabolism, produce complex compounds (proteins, cellulose, and amino acids). ...
... • Autotrophic organisms: allows absorption of CO₂ into cells. • Add water and energy from the sun. • Organisms use photosynthesis to chemically convert the CO2 to carbonbased sugar molecules. • Sugar, through metabolism, produce complex compounds (proteins, cellulose, and amino acids). ...
Lecture 2
... Mimimimum of three limitation gives actual A and J rates. Farquhar et al. Planta 1980; Long and Bernacchi J Ex Bot. 2003 ...
... Mimimimum of three limitation gives actual A and J rates. Farquhar et al. Planta 1980; Long and Bernacchi J Ex Bot. 2003 ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.