BIOCHEMISTRY 2.1
... and nucleic acids) and their functions in biological systems—CHO focus on glucose polymers including chitin, starch, cellulose, glycogen; Proteins intro enzymes and give common examples including hemoglobin, antibodies, collagen, muscle fibers, hair, nails, and cell fibers actin and myosin; Nucleic ...
... and nucleic acids) and their functions in biological systems—CHO focus on glucose polymers including chitin, starch, cellulose, glycogen; Proteins intro enzymes and give common examples including hemoglobin, antibodies, collagen, muscle fibers, hair, nails, and cell fibers actin and myosin; Nucleic ...
AP Biology Study Guide Part II: Cells Describe the structure and
... Part II: Cells 1. Describe the structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells AND those found only in plant cells or only in animal cells. 2. What is a peroxisome? How is this an example of compartmentalization being crucial to function? 3. Why are membranes selectively permea ...
... Part II: Cells 1. Describe the structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells AND those found only in plant cells or only in animal cells. 2. What is a peroxisome? How is this an example of compartmentalization being crucial to function? 3. Why are membranes selectively permea ...
Major Themes of Biology
... Energy is the capacity to do work. All living organisms are active (living) because of their abilities to link energy reactions to the biochemical reactions that take place within their cells. Example: The energy of sunlight, along with carbon dioxide and water, allows plant cells to make organi ...
... Energy is the capacity to do work. All living organisms are active (living) because of their abilities to link energy reactions to the biochemical reactions that take place within their cells. Example: The energy of sunlight, along with carbon dioxide and water, allows plant cells to make organi ...
Biology Chapter 4
... the process and is used to make water molecules. Water and heat are given off as waste products ...
... the process and is used to make water molecules. Water and heat are given off as waste products ...
SCIENCE 4 – 3rd Term UT1 REVIEWER MODIFIED TRUE OR
... The female part of a flower is the ____________. The filament and anther make up a flower’s male part, the ___________. Flowers containing either the stamen or the pistil are called ____________ flowers, while flowers that contain both the stamen and pistil are called __________ flowers. 5. The two ...
... The female part of a flower is the ____________. The filament and anther make up a flower’s male part, the ___________. Flowers containing either the stamen or the pistil are called ____________ flowers, while flowers that contain both the stamen and pistil are called __________ flowers. 5. The two ...
Microbial Metabolism (Part 2) I. Objectives II. What does a
... Microbial Metabolism (Part 2) The life of a heterotroph Chapter 5: 122-136 ...
... Microbial Metabolism (Part 2) The life of a heterotroph Chapter 5: 122-136 ...
Plant Kingdom PPT
... • Plant cells are eukaryotic. • Plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts. • Plants make their own food in the process of photosynthesis. ...
... • Plant cells are eukaryotic. • Plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts. • Plants make their own food in the process of photosynthesis. ...
The Proton Motive Force
... Two reaction series are linked to energy conservation in chemoorganotrophs: fermentation and respiration (Figure 4.13) Differ in mechanism of ATP synthesis Fermentation: substrate-level phosphorylation; ATP directly synthesized from an energy-rich intermediate Respiration: oxidative phosphorylation; ...
... Two reaction series are linked to energy conservation in chemoorganotrophs: fermentation and respiration (Figure 4.13) Differ in mechanism of ATP synthesis Fermentation: substrate-level phosphorylation; ATP directly synthesized from an energy-rich intermediate Respiration: oxidative phosphorylation; ...
Respiration Eq. for reaction: C6H12O6 + 6O2 ------
... Eq. for reaction: C6H12O6 + 6O2 -------> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP - occurs in the cytoplasm and then the cristae and matrix of the mitochondria - reaction is an oxidation reaction (uses oxygen): aerobic respiration - energy is in the form of ATP (adenosine tri-phosphate) - some is lost as heat (responsible ...
... Eq. for reaction: C6H12O6 + 6O2 -------> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP - occurs in the cytoplasm and then the cristae and matrix of the mitochondria - reaction is an oxidation reaction (uses oxygen): aerobic respiration - energy is in the form of ATP (adenosine tri-phosphate) - some is lost as heat (responsible ...
Kingdom Plantae Review #1 KEY Evolution of Plants Water Rigid
... Kingdom Plantae Review #1 KEY Evolution of Plants 1. Water 2. Rigid xylem provide plants with the support they need to grow up against gravity to out-compete other plants in obtaining sunlight for photosynthesis. 3. Vascular plants transport water and minerals through their Xylem and they transport ...
... Kingdom Plantae Review #1 KEY Evolution of Plants 1. Water 2. Rigid xylem provide plants with the support they need to grow up against gravity to out-compete other plants in obtaining sunlight for photosynthesis. 3. Vascular plants transport water and minerals through their Xylem and they transport ...
Notes Food Web Terms
... How do ocean organisms get their nutrition? Producers Some organisms are photosynthetic. They use energy from the sun to produce their own food through the process of photosynthesis. Since photosynthesis requires light, these organisms live either near the surface or in very shallow water. Photosynt ...
... How do ocean organisms get their nutrition? Producers Some organisms are photosynthetic. They use energy from the sun to produce their own food through the process of photosynthesis. Since photosynthesis requires light, these organisms live either near the surface or in very shallow water. Photosynt ...
UNIT 2: Energy Flow and Cycles
... Greenhouse effect – when heat is trapped in the Earth’s atmosphere by carbon dioxide, methane and other greenhouse gases. A drastic rise in greenhouse gases could increase the greenhouse effect and lead to ...
... Greenhouse effect – when heat is trapped in the Earth’s atmosphere by carbon dioxide, methane and other greenhouse gases. A drastic rise in greenhouse gases could increase the greenhouse effect and lead to ...
Biogeochemical Cycles
... component of the atmosphere, and is taken up by plants in photosynthesis. In the atmosphere, carbon is present as carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbon dioxide is released into the air by volcanic activity, burning of fossil fuels, and by decomposition of organic matter (matter from living organisms) Ani ...
... component of the atmosphere, and is taken up by plants in photosynthesis. In the atmosphere, carbon is present as carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbon dioxide is released into the air by volcanic activity, burning of fossil fuels, and by decomposition of organic matter (matter from living organisms) Ani ...
The Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
... cycle of reactions called the Krebs cycle. The common pathway to completely oxidize fuel molecules which mostly is acetyl CoA ,the product from the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate It enters the cycle and passes ten steps of reactions that yield energy and CO2 These reactions can only occ ...
... cycle of reactions called the Krebs cycle. The common pathway to completely oxidize fuel molecules which mostly is acetyl CoA ,the product from the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate It enters the cycle and passes ten steps of reactions that yield energy and CO2 These reactions can only occ ...
Respiration
... • 6 carbon glucose split into 3 carbon pyruvate • Energy is needed in first steps but released in later steps (net gain of 2 ATP) • Takes place in cytoplasm ...
... • 6 carbon glucose split into 3 carbon pyruvate • Energy is needed in first steps but released in later steps (net gain of 2 ATP) • Takes place in cytoplasm ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... Vascular tissue in plants responsible for transporting water from the roots to the leaves. Vascular tissue in plants responsible for transporting sugars from the leaves to the roots. Plants need sunlight to make food, making them autotrophs, so they have evolved to be able to grow towards a light so ...
... Vascular tissue in plants responsible for transporting water from the roots to the leaves. Vascular tissue in plants responsible for transporting sugars from the leaves to the roots. Plants need sunlight to make food, making them autotrophs, so they have evolved to be able to grow towards a light so ...
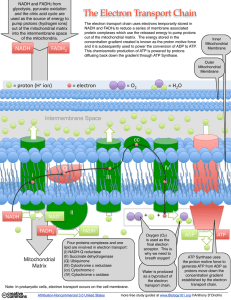
What is the Electron Transport Chain?
... glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation and the citric acid cycle are used as the source of energy to pump protons (hydrogen ions) out of the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space of the mitochondria. ...
... glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation and the citric acid cycle are used as the source of energy to pump protons (hydrogen ions) out of the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space of the mitochondria. ...
Whitter`s Learning Centre Science Quiz Mixed 2
... image this is as a result of ______. A. the refraction of light B. an optical illusion C. the reflection of light D. the rapid movement of light 2. Why is it possible to see clearly through glass? It is ____. A. dull B. opaque C. shiny D. transparent 3. Andrea was able to find her shiny new coin at ...
... image this is as a result of ______. A. the refraction of light B. an optical illusion C. the reflection of light D. the rapid movement of light 2. Why is it possible to see clearly through glass? It is ____. A. dull B. opaque C. shiny D. transparent 3. Andrea was able to find her shiny new coin at ...
UNIDAD EDUCATIVA PARTICULAR ECOMUNDO WORKSHEET
... f – Plants are called __________________ because they can make their own food using photosynthesis. g – Vascular plants that have seeds surrounded by fruit are called ______________ h.– Growth, wilting, and dormancy are examples of plant ________________ 3) Introduction to plants. Complete the foll ...
... f – Plants are called __________________ because they can make their own food using photosynthesis. g – Vascular plants that have seeds surrounded by fruit are called ______________ h.– Growth, wilting, and dormancy are examples of plant ________________ 3) Introduction to plants. Complete the foll ...
BIO 6.3 Carbon - Steinbach Science
... The largest carbs are polysaccharides, polymers composed of many monosaccharide subunits (e.g., starch, glycogen, cellulose) Lipids are organic compounds that have a large portion (much greater than 2 to 1) ...
... The largest carbs are polysaccharides, polymers composed of many monosaccharide subunits (e.g., starch, glycogen, cellulose) Lipids are organic compounds that have a large portion (much greater than 2 to 1) ...
Cell Test 1 – Review Sheet
... a. Nucleus- directs all of the cell’s activities b. Mitochondria – the “powerhouses” of the cell that convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use to carry out its functions c. Cell membrane –the next barrier within the cell wall – all cells have membranes - controls what substances c ...
... a. Nucleus- directs all of the cell’s activities b. Mitochondria – the “powerhouses” of the cell that convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use to carry out its functions c. Cell membrane –the next barrier within the cell wall – all cells have membranes - controls what substances c ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.