flowering plants - VCE
... Adapted to live in either partially or fully submerged in water. Thin cuticle Stomata mainly on upper surface particularly if water lilly… Large air spaces in spongy mesophyll allow storage of gases and make leaf lighter. ...
... Adapted to live in either partially or fully submerged in water. Thin cuticle Stomata mainly on upper surface particularly if water lilly… Large air spaces in spongy mesophyll allow storage of gases and make leaf lighter. ...
Sc 8 Unit 2 Topic 1 Notes WD
... 1. Energy: Animals get their energy from their food. What structures do different animals have to gather and use food? Most plants use the energy of the Sun to make their own food. What structures do plants have to make food? 2. Environment: Plants need light to make food, so they will bend toward a ...
... 1. Energy: Animals get their energy from their food. What structures do different animals have to gather and use food? Most plants use the energy of the Sun to make their own food. What structures do plants have to make food? 2. Environment: Plants need light to make food, so they will bend toward a ...
B2a specification checklist file
... To understand the structures of different types of cells are related to their functions To understand that to get into or out of cells, dissolved substances have to cross the cell membranes. To know the nucleus controls the activities of the cell To know the cytoplasm is where most of the chemical r ...
... To understand the structures of different types of cells are related to their functions To understand that to get into or out of cells, dissolved substances have to cross the cell membranes. To know the nucleus controls the activities of the cell To know the cytoplasm is where most of the chemical r ...
IB Biology Chapter - Fredericksburg City Schools
... energy they hold-ready to be released by burning • Coal must be extracted from below ground to be used for energy-mining • Found in seams, where layers of sediments were deposited, covered, and then transformed and other twisted/deformed by geological forces over millions of years Which is the trans ...
... energy they hold-ready to be released by burning • Coal must be extracted from below ground to be used for energy-mining • Found in seams, where layers of sediments were deposited, covered, and then transformed and other twisted/deformed by geological forces over millions of years Which is the trans ...
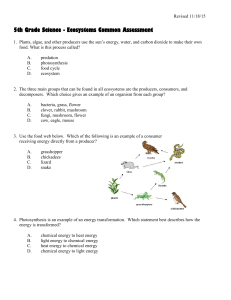
Ecosystems Common Assessment
... 5th Grade Science - Ecosystems Common Assessment 1. Plants, algae, and other producers use the sun’s energy, water, and carbon dioxide to make their own food. What is this process called? A. B. C. D. ...
... 5th Grade Science - Ecosystems Common Assessment 1. Plants, algae, and other producers use the sun’s energy, water, and carbon dioxide to make their own food. What is this process called? A. B. C. D. ...
Hold Back the Water - Supercomputing Challenge
... Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the synthesis of sugar from light and water, with oxygen as a waste product. Without photosynthesis we would not be here on this earth today. Photosynthesis is the creation of oxygen that nearly all life depends on. It occurs in higher plants, algae, some bacteria, a ...
... Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the synthesis of sugar from light and water, with oxygen as a waste product. Without photosynthesis we would not be here on this earth today. Photosynthesis is the creation of oxygen that nearly all life depends on. It occurs in higher plants, algae, some bacteria, a ...
electron transport chain
... The cells of all eukaryotes (all animals, plants, fungi, algae – in other words, all living things except bacteria and archaea) contain intracellular organelles called mitochondria that produce ATP. Energy sources such as glucose are initially metabolized in the cytoplasm. The products are imported ...
... The cells of all eukaryotes (all animals, plants, fungi, algae – in other words, all living things except bacteria and archaea) contain intracellular organelles called mitochondria that produce ATP. Energy sources such as glucose are initially metabolized in the cytoplasm. The products are imported ...
Introduction to Plants
... Vascular Plants These plants are also known as tracheophytes. ▶ Vascular plants have vascular tissues that make it possible to move fluids through their bodies against the force of gravity. • Tracheids are hollow tubelike water-conducting cells with thick cell walls strengthened by lignin. Tracheids ...
... Vascular Plants These plants are also known as tracheophytes. ▶ Vascular plants have vascular tissues that make it possible to move fluids through their bodies against the force of gravity. • Tracheids are hollow tubelike water-conducting cells with thick cell walls strengthened by lignin. Tracheids ...
Enzyme
... 1. O2 and food are used 2. CO2 and H2O are produced 3. Energy in food may be temporarily store in ATP or lost as heat 4. ATP is produced by oxidation of food (oxidative phosphorylation) 5. Hydrogen is transferred from food to NAD or NADP to form NADH or NADPH 6. ATP and NADH or NADPH are available t ...
... 1. O2 and food are used 2. CO2 and H2O are produced 3. Energy in food may be temporarily store in ATP or lost as heat 4. ATP is produced by oxidation of food (oxidative phosphorylation) 5. Hydrogen is transferred from food to NAD or NADP to form NADH or NADPH 6. ATP and NADH or NADPH are available t ...
What are algae? What are algae?
... 1.Bacteria- cyanobacteria (blue green algae) 2.Archae 1. Alveolates- dinoflagellates, coccolithophore 3.Eukaryotes ...
... 1.Bacteria- cyanobacteria (blue green algae) 2.Archae 1. Alveolates- dinoflagellates, coccolithophore 3.Eukaryotes ...
Matter Energy and Life
... Nitrogen is needed to make proteins and nucleic acids such as DNA. Plants take up inorganic nitrogen from the environment and build protein molecules which are later eaten by consumers. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria change nitrogen to a more useful form by combining it with hydrogen to make ammonia. Ot ...
... Nitrogen is needed to make proteins and nucleic acids such as DNA. Plants take up inorganic nitrogen from the environment and build protein molecules which are later eaten by consumers. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria change nitrogen to a more useful form by combining it with hydrogen to make ammonia. Ot ...
Unit 2 Notes: Ecology
... Bacteria in the nodules can take nitrogen gas from the atmosphere and turn it into a form that can be used by the plant; in return, the plant protects the bacteria from harmful oxygen and the bacteria get food from the plant. ...
... Bacteria in the nodules can take nitrogen gas from the atmosphere and turn it into a form that can be used by the plant; in return, the plant protects the bacteria from harmful oxygen and the bacteria get food from the plant. ...
13 - Joe Griffin Media Ministries
... energy to build complex molecules from simple molecules. The others are catabolic7 reactions, which make chemical energy available in the course of breaking down complex molecules into simpler molecules. All the energy used by living organisms derives ultimately from the Sun. Photosynthetic plants u ...
... energy to build complex molecules from simple molecules. The others are catabolic7 reactions, which make chemical energy available in the course of breaking down complex molecules into simpler molecules. All the energy used by living organisms derives ultimately from the Sun. Photosynthetic plants u ...
Ecosystems PowerPoint
... ecosystem, whereas food chains are simple and only show the interaction of a couple organisms. ...
... ecosystem, whereas food chains are simple and only show the interaction of a couple organisms. ...
How do Angelfish Breathe?
... Our lungs have numerous tiny balloon-like sacs that are full of capillaries. The capillaries absorb oxygen into the blood stream and give release carbon dioxide. Then the oxygen-rich blood returns to the left side of the heart to be pumped through our arteries to deliver oxygen to the cells in all p ...
... Our lungs have numerous tiny balloon-like sacs that are full of capillaries. The capillaries absorb oxygen into the blood stream and give release carbon dioxide. Then the oxygen-rich blood returns to the left side of the heart to be pumped through our arteries to deliver oxygen to the cells in all p ...
How Do Angelfish Breathe?
... Our lungs have numerous tiny balloon-like sacs that are full of capillaries. The capillaries absorb oxygen into the blood stream and give release carbon dioxide. Then the oxygen-rich blood returns to the left side of the heart to be pumped through our arteries to deliver oxygen to the cells in all p ...
... Our lungs have numerous tiny balloon-like sacs that are full of capillaries. The capillaries absorb oxygen into the blood stream and give release carbon dioxide. Then the oxygen-rich blood returns to the left side of the heart to be pumped through our arteries to deliver oxygen to the cells in all p ...
Worksheet! - Evolution of the Respiratory System
... a) Small blood vessels that extract Oxygen from the water and release carbon dioxide b) Water c) The Pearl d) Food that is used for the oyster to complete its gas exchange 20) How many hearts and gills do squid have? a) Two gills and three hearts b) One Gill and four hearts c) Three gills and two he ...
... a) Small blood vessels that extract Oxygen from the water and release carbon dioxide b) Water c) The Pearl d) Food that is used for the oyster to complete its gas exchange 20) How many hearts and gills do squid have? a) Two gills and three hearts b) One Gill and four hearts c) Three gills and two he ...
www.ourpgs.com
... publisher will be pleased to make amends at the earliest possible opportunity. University of Cambridge International Examinations is part of the University of Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate (UCLES), which is itself a department of the University of Cambridge. ...
... publisher will be pleased to make amends at the earliest possible opportunity. University of Cambridge International Examinations is part of the University of Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate (UCLES), which is itself a department of the University of Cambridge. ...
History of Fermentation Processes and Their Fundamental
... (47/686) X 100 = 6.9 percent of the total energy that can be set free from glucose This does NOT mean anaerobic glycolysis is wasteful, but only incomplete to this point of metabolism! ...
... (47/686) X 100 = 6.9 percent of the total energy that can be set free from glucose This does NOT mean anaerobic glycolysis is wasteful, but only incomplete to this point of metabolism! ...
Chemistry UIL Topics
... Defining the rate of a reaction. Units for rxn rates. Writing the reaction rate law equation. The specific rate constant and its units. Reaction order. Using tabulated data and using the Method of Initial Rates to determine the rate law for a reaction. The integrated rate laws for zero, first, and s ...
... Defining the rate of a reaction. Units for rxn rates. Writing the reaction rate law equation. The specific rate constant and its units. Reaction order. Using tabulated data and using the Method of Initial Rates to determine the rate law for a reaction. The integrated rate laws for zero, first, and s ...
Chapter 8: Cellular Energy
... light energy is absorbed and then converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. In phase two, the light-independent reactions, the ATP and NADPH that were formed in phase one are used to make glucose. Once glucose is produced, it can be joined to other simple sugars to form larger mol ...
... light energy is absorbed and then converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. In phase two, the light-independent reactions, the ATP and NADPH that were formed in phase one are used to make glucose. Once glucose is produced, it can be joined to other simple sugars to form larger mol ...
Unit 1 Notes
... The chemical reactions in a cell involve either breaking down (degrading) large molecules or building up (synthesising) large molecules. Breakdown reactions convert large molecules into small molecules. For example the carbohydrate starch is a very large molecule which cannot pass through the membra ...
... The chemical reactions in a cell involve either breaking down (degrading) large molecules or building up (synthesising) large molecules. Breakdown reactions convert large molecules into small molecules. For example the carbohydrate starch is a very large molecule which cannot pass through the membra ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.