To remember Sir Hans Krebs: Nobelist, Friend, and Adviser
... with William A. Johnson, a graduate student, the mechanism for the synthesis of citric acid from oxaloacetic acid and pyruvic acid, one of the major steps in ceU metabolism. 2 While much was known about cell metabolism before this work, Hans supplied much missing information and was able to organize ...
... with William A. Johnson, a graduate student, the mechanism for the synthesis of citric acid from oxaloacetic acid and pyruvic acid, one of the major steps in ceU metabolism. 2 While much was known about cell metabolism before this work, Hans supplied much missing information and was able to organize ...
Fatty acids: Review
... catalyzing a series of reactions that sequentially adds C2 units to a growing fatty acid chain covalently attached to the enzyme complex. The mechanism involves the linking malonyl-CoA to an acyl carrier protein, followed by a decarboxylation and condensation reaction that extends the hydrocarbon ch ...
... catalyzing a series of reactions that sequentially adds C2 units to a growing fatty acid chain covalently attached to the enzyme complex. The mechanism involves the linking malonyl-CoA to an acyl carrier protein, followed by a decarboxylation and condensation reaction that extends the hydrocarbon ch ...
Triacylglycerol Metabolism Gone Bad: A major cause of disease
... – Increase synthesis of muscle and liver genes involved in fatty acid uptake and oxidation. ...
... – Increase synthesis of muscle and liver genes involved in fatty acid uptake and oxidation. ...
Cell Respiration Review 1
... Fats that are broken down between meals or during exercise as alternatives to glucose Used between meals when free glucose supply dwindles; enters glycolysis after conversion Its breakdown yields much more ATP than glucose Absorbed in large amounts immediately following a meal Represents only 1 perc ...
... Fats that are broken down between meals or during exercise as alternatives to glucose Used between meals when free glucose supply dwindles; enters glycolysis after conversion Its breakdown yields much more ATP than glucose Absorbed in large amounts immediately following a meal Represents only 1 perc ...
The Aerobic Fate of Pyruvate
... anaerobic conditions, animals convert glucose into 2 molecules of lactate. Much of the potential energy of the glucose molecule remains untapped. Under Aerobic conditions a much more dynamic pyruvate metabolism occurs. The 2 moles of NADH produced by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase are oxid ...
... anaerobic conditions, animals convert glucose into 2 molecules of lactate. Much of the potential energy of the glucose molecule remains untapped. Under Aerobic conditions a much more dynamic pyruvate metabolism occurs. The 2 moles of NADH produced by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase are oxid ...
Cellular Respiration Oxidation of Pyruvate Krebs Cycle
... releases 2 CO2 (count the carbons!) reduces 2 NAD 2 NADH (moves e ) produces 2 acetyl CoA ...
... releases 2 CO2 (count the carbons!) reduces 2 NAD 2 NADH (moves e ) produces 2 acetyl CoA ...
Jeopardy - Student Resources Home Page
... loses a hydrogen atom. gains one or more electrons. loses a hydrogen atom and gains one or more electrons. ANSWER BACK TO GAME ...
... loses a hydrogen atom. gains one or more electrons. loses a hydrogen atom and gains one or more electrons. ANSWER BACK TO GAME ...
Studies on the Physiological Significance of the Lack
... reached 0.48 mg dry wt/ml (about 16 h). The cells were harvested by centrifugation (10000 g; 20 min, 4 "C) and washed twice in 10 ml of a 60 mM solution of the homologous non-radioactive compound and once in distilled water. The pellet was resuspended in distilled water (I ml) and transferred to gla ...
... reached 0.48 mg dry wt/ml (about 16 h). The cells were harvested by centrifugation (10000 g; 20 min, 4 "C) and washed twice in 10 ml of a 60 mM solution of the homologous non-radioactive compound and once in distilled water. The pellet was resuspended in distilled water (I ml) and transferred to gla ...
6 Energy
... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism. It is one of the end products of phosphorylation and cellular respiration and used in man ...
... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism. It is one of the end products of phosphorylation and cellular respiration and used in man ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... decarboxylation reactions. Isocitrate (C6) is split into succinate (C4) and glyoxylate (C2), preserving the two carbon atoms. Glyoxylate (C2)then reacts with acetyl CoA (C2) to form malate (C4) and subsequently oxaloacetate which can move on to glucose, leaving succinate to provide the carbon skelet ...
... decarboxylation reactions. Isocitrate (C6) is split into succinate (C4) and glyoxylate (C2), preserving the two carbon atoms. Glyoxylate (C2)then reacts with acetyl CoA (C2) to form malate (C4) and subsequently oxaloacetate which can move on to glucose, leaving succinate to provide the carbon skelet ...
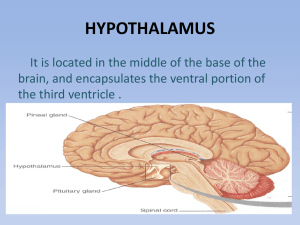
HYPOTHALAMUS
... From controlling the temperature of the body to producing thyroid hormones, the hypothalamus certainly plays a very important role to ensure normal functioning of the body. The hypothalamus also regulates other important mechanisms of the body such as thirst, hunger and sleep. So, one can imagine ho ...
... From controlling the temperature of the body to producing thyroid hormones, the hypothalamus certainly plays a very important role to ensure normal functioning of the body. The hypothalamus also regulates other important mechanisms of the body such as thirst, hunger and sleep. So, one can imagine ho ...
Third Generation Biofuels via Direct Cellulose Fermentation
... hydrogenase-containing organisms could be used to supply affordable and renewable H2 to be used as an energy fuel. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) targeting 16S rDNA and known hydrogenase nucleotide sequences has been used to confirm the presence of clostridial species within anaerobic biohydrogen f ...
... hydrogenase-containing organisms could be used to supply affordable and renewable H2 to be used as an energy fuel. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) targeting 16S rDNA and known hydrogenase nucleotide sequences has been used to confirm the presence of clostridial species within anaerobic biohydrogen f ...
CHAPTER 25
... a) All three statements are true. b) Two of the three statements are true. c) Only one of the statements is true. d) None of the statements is true. 25.40 c - TFF Statements: (1) The number of acetyl CoA molecules produced in the fatty acid spiral is equal to half the number of carbon atoms in the f ...
... a) All three statements are true. b) Two of the three statements are true. c) Only one of the statements is true. d) None of the statements is true. 25.40 c - TFF Statements: (1) The number of acetyl CoA molecules produced in the fatty acid spiral is equal to half the number of carbon atoms in the f ...
Cellular Respiration
... - AP Level: Why does ATP production vary between 36 and 38 ATP per Glucose? Hint: What factors inside the cell that varies could affect ATP production? - Where you paying attention? What are the majority of the ETC proteins ...
... - AP Level: Why does ATP production vary between 36 and 38 ATP per Glucose? Hint: What factors inside the cell that varies could affect ATP production? - Where you paying attention? What are the majority of the ETC proteins ...
Enzymes Activation and Deactivation
... Makes the substrate more active in solution. So? More chances of substrate colliding with active site. Makes the enzyme more flexible. Puts strain on weaker bonds. Pass a certain point enzymes denature. What does it mean to denature? active site changes What ...
... Makes the substrate more active in solution. So? More chances of substrate colliding with active site. Makes the enzyme more flexible. Puts strain on weaker bonds. Pass a certain point enzymes denature. What does it mean to denature? active site changes What ...
video slide - Knappology
... Can produce ATP with or without oxygen, in aerobic or anaerobic conditions It is the ETC that requires oxygen (without it the e- are not pulled down the series of proteins and chemiosmosis fails) Glycolysis can couple with fermentation to produce ATP ...
... Can produce ATP with or without oxygen, in aerobic or anaerobic conditions It is the ETC that requires oxygen (without it the e- are not pulled down the series of proteins and chemiosmosis fails) Glycolysis can couple with fermentation to produce ATP ...
Fundamentals of Human Energy Transfer
... Involves transferring electrons from NADH and FADH2 to molecular oxygen, which release and transfer chemical energy to combine ATP from ADP plus a phosphate ion. During aerobic ATP resynthesis, oxygen combines with hydrogen to form water. More than 90% of ATP synthesis takes place in the respiratory ...
... Involves transferring electrons from NADH and FADH2 to molecular oxygen, which release and transfer chemical energy to combine ATP from ADP plus a phosphate ion. During aerobic ATP resynthesis, oxygen combines with hydrogen to form water. More than 90% of ATP synthesis takes place in the respiratory ...
Chapter 6 Notes
... Cellular Respiration • Plant and animal cells perform cellular respiration, a chemical process that – primarily occurs in mitochondria, – harvests energy stored in organic molecules, – uses oxygen, and – generates ATP. ...
... Cellular Respiration • Plant and animal cells perform cellular respiration, a chemical process that – primarily occurs in mitochondria, – harvests energy stored in organic molecules, – uses oxygen, and – generates ATP. ...
Factors affecting human decomposition
... decompose the corpse. The microorganisms will also die faster once there are insufficient carbon sources to sustain them. Air content- decomposition occurs much faster in the presence of oxygen, insects may also thrive, aerobic degradation is generally faster than anaerobic degradation. Fungal growt ...
... decompose the corpse. The microorganisms will also die faster once there are insufficient carbon sources to sustain them. Air content- decomposition occurs much faster in the presence of oxygen, insects may also thrive, aerobic degradation is generally faster than anaerobic degradation. Fungal growt ...
Lecture 6 - TCA cycle I - University of Lethbridge
... Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge ...
... Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge ...
Rumen Protected Fat
... More beneficial when the animal's requirement for protein is not met through microbial protein In early lactation period of high yielders (15 kg/day) In rapidly growing (1 kg/day) calves Animals thriving on poor quality roughages ...
... More beneficial when the animal's requirement for protein is not met through microbial protein In early lactation period of high yielders (15 kg/day) In rapidly growing (1 kg/day) calves Animals thriving on poor quality roughages ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.