How Cells Harvest Energy from Food
... In both plants and animals, and in fact in almost all organisms, the energy for living is obtained by breaking down the organic molecules originally produced in plants. The ATP energy and reducing power invested in building the organic molecules are retrieved by stripping away the energetic electron ...
... In both plants and animals, and in fact in almost all organisms, the energy for living is obtained by breaking down the organic molecules originally produced in plants. The ATP energy and reducing power invested in building the organic molecules are retrieved by stripping away the energetic electron ...
Rumen Protected Fat
... More beneficial when the animal's requirement for protein is not met through microbial protein In early lactation period of high yielders (15 kg/day) In rapidly growing (1 kg/day) calves Animals thriving on poor quality roughages ...
... More beneficial when the animal's requirement for protein is not met through microbial protein In early lactation period of high yielders (15 kg/day) In rapidly growing (1 kg/day) calves Animals thriving on poor quality roughages ...
Carbohydrates
... Carbohydrates perform numerous roles in living organisms: Polysaccharides serve for the storage of energy (e.g., starch and glycogen), and as structural components (e.g., cellulose in plants and chitin in arthropods). The 5-carbon monosaccharide ribose is an important component of coenzymes (e.g., A ...
... Carbohydrates perform numerous roles in living organisms: Polysaccharides serve for the storage of energy (e.g., starch and glycogen), and as structural components (e.g., cellulose in plants and chitin in arthropods). The 5-carbon monosaccharide ribose is an important component of coenzymes (e.g., A ...
BOOK NOTES ch9_sec3
... • The cells of most organisms transfer energy found in organic compounds, such as those in foods, to ATP. • The primary fuel for cellular respiration is glucose. Fats can be broken down to make ATP. • Proteins and nucleic acids can also be used to make ATP, but they are usually used for building imp ...
... • The cells of most organisms transfer energy found in organic compounds, such as those in foods, to ATP. • The primary fuel for cellular respiration is glucose. Fats can be broken down to make ATP. • Proteins and nucleic acids can also be used to make ATP, but they are usually used for building imp ...
15Nitrogen metabolism
... of L-glutamate. Glutamate can be used as a donor of amino group in the biosynthesis of non-essential a.a - In hepatocytes, glutamate is transported from the cytosol into mitochondria, where it undergoes Oxidative deamination catalyzed by L-glutamate ...
... of L-glutamate. Glutamate can be used as a donor of amino group in the biosynthesis of non-essential a.a - In hepatocytes, glutamate is transported from the cytosol into mitochondria, where it undergoes Oxidative deamination catalyzed by L-glutamate ...
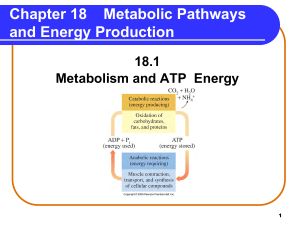
Metabolic Pathways and Energy Production
... • begin digestion in the mouth, where salivary amylase breaks down polysaccharides to smaller polysaccharides (dextrins), maltose, and some glucose. • continue digestion in the small intestine, where pancreatic amylase hydrolyzes dextrins to maltose and glucose. • maltose, lactose, and sucrose are h ...
... • begin digestion in the mouth, where salivary amylase breaks down polysaccharides to smaller polysaccharides (dextrins), maltose, and some glucose. • continue digestion in the small intestine, where pancreatic amylase hydrolyzes dextrins to maltose and glucose. • maltose, lactose, and sucrose are h ...
New Insights into the Interaction of Carbohydrate and Fat
... During exercise at approximately 80 % VO2max in moderately active individuals, the majority of energy is derived from carbohydrate use and particularly from muscle glycogen during the first 20–30 min. Exercising at this high intensity in the presence of artificially elevated FFA levels decreased net ...
... During exercise at approximately 80 % VO2max in moderately active individuals, the majority of energy is derived from carbohydrate use and particularly from muscle glycogen during the first 20–30 min. Exercising at this high intensity in the presence of artificially elevated FFA levels decreased net ...
The Glucose/Fatty Acid Cycle 1963–2003
... Glucose and fatty acids are the major fuels for mammalian metabolism and it is clearly essential that mechanisms exist for mutual co-ordination of their utilization. The glucose–fatty acid cycle, as it was proposed in 1963, describes one set of mechanisms by which carbohydrate and fat metabolism int ...
... Glucose and fatty acids are the major fuels for mammalian metabolism and it is clearly essential that mechanisms exist for mutual co-ordination of their utilization. The glucose–fatty acid cycle, as it was proposed in 1963, describes one set of mechanisms by which carbohydrate and fat metabolism int ...
PDF - Oxford Academic
... species could, in part, account for the increased specific activities observed. When [14C]HCO3 was added to a dark heterotrophic culture of C fritschii, a steady rate of incorporation was observed, which was approx. 1% that obtained with a photoheterotrophic culture. Presumably the supply of NADPH a ...
... species could, in part, account for the increased specific activities observed. When [14C]HCO3 was added to a dark heterotrophic culture of C fritschii, a steady rate of incorporation was observed, which was approx. 1% that obtained with a photoheterotrophic culture. Presumably the supply of NADPH a ...
Towards Controlling the Glycoform: A Model Framework Linking
... Biotechnological products, including bioengineered vaccines and recombinant proteins, constitute 19% of the pharmaceutical market with a total sales value of $142bn as of 2011 and substantial anticipated growth [1]. Glycoproteins represent the largest group of biologically-derived medicines, constit ...
... Biotechnological products, including bioengineered vaccines and recombinant proteins, constitute 19% of the pharmaceutical market with a total sales value of $142bn as of 2011 and substantial anticipated growth [1]. Glycoproteins represent the largest group of biologically-derived medicines, constit ...
Citrate Cycle
... The citrate cycle captures energy using redox reactions Acetyl-CoA, derived from pyruvate (from glycolysis), is the “normal” entry substrate into the cycle Pyruvate can also be derived from amino acid catabolism, and acetyl-CoA can be derived from both amino a acids and fatty acids. ...
... The citrate cycle captures energy using redox reactions Acetyl-CoA, derived from pyruvate (from glycolysis), is the “normal” entry substrate into the cycle Pyruvate can also be derived from amino acid catabolism, and acetyl-CoA can be derived from both amino a acids and fatty acids. ...
Perry et al., 2008
... oxidase IV (electron transport chain) — reflecting increases in the capacity for fat and carbohydrate oxidation; (iii) increase the content of skeletal muscle fatty acid, glucose, and lactate transport proteins; and (iv) decrease skeletal muscle glycogenolysis and substrate phosphorylation from glyc ...
... oxidase IV (electron transport chain) — reflecting increases in the capacity for fat and carbohydrate oxidation; (iii) increase the content of skeletal muscle fatty acid, glucose, and lactate transport proteins; and (iv) decrease skeletal muscle glycogenolysis and substrate phosphorylation from glyc ...
Sample Questions Chapters 9-10
... e. neither gains nor loses electrons, but gains or loses energy. ____ ...
... e. neither gains nor loses electrons, but gains or loses energy. ____ ...
1 CHRONIC LIVER DISEASES DERANGEMENTS OF HEPATIC
... The liver functions to maintain normal levels of blood sugar by a combination of glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycolysis. These pathways are regulated by a number of hormones including insulin, glucagon, growth hormone and catecholamines. The exquisite sensitivity of the hepatocyte ...
... The liver functions to maintain normal levels of blood sugar by a combination of glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycolysis. These pathways are regulated by a number of hormones including insulin, glucagon, growth hormone and catecholamines. The exquisite sensitivity of the hepatocyte ...
Expression of phosphofructokinase in Neisseria meningitidis
... appear to occur at a high rate. None of the above-mentioned types of PFK are present in N. meningitidis. If it is assumed that N. meningitidis once had a functional PFK and that during the evolution of the species this activity was lost (Bapteste et al., 2003), the question of why N. meningitidis lo ...
... appear to occur at a high rate. None of the above-mentioned types of PFK are present in N. meningitidis. If it is assumed that N. meningitidis once had a functional PFK and that during the evolution of the species this activity was lost (Bapteste et al., 2003), the question of why N. meningitidis lo ...
TCA Cycle - eCurriculum
... The function of these reactions is to compensate for the efflux of intermediates from the TCA cycle into other pathways. The carbon skeleton of some amino acids comes from intermediates of the TCA cycle. In nervous tissue "Ketoglutarate is transformed to glutamate and GABA, both neurotransmitter ...
... The function of these reactions is to compensate for the efflux of intermediates from the TCA cycle into other pathways. The carbon skeleton of some amino acids comes from intermediates of the TCA cycle. In nervous tissue "Ketoglutarate is transformed to glutamate and GABA, both neurotransmitter ...
Acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylases: Versatile targets for
... in response to dietary changes and altered nutritional requirements in animals, for example during exercise, and therefore plays a key role in controlling the switch between carbohydrate and fatty acid utilization in liver and skeletal muscle [Harwood, 2005]. Malonyl-CoA may also act centrally to co ...
... in response to dietary changes and altered nutritional requirements in animals, for example during exercise, and therefore plays a key role in controlling the switch between carbohydrate and fatty acid utilization in liver and skeletal muscle [Harwood, 2005]. Malonyl-CoA may also act centrally to co ...
File - Groby Bio Page
... Used to reduce NAD and FAD. Three reduced NAD are produced and 1 reduced FAD per cycle. NAD = Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide FAD = Flavine adenine dinucleotide ...
... Used to reduce NAD and FAD. Three reduced NAD are produced and 1 reduced FAD per cycle. NAD = Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide FAD = Flavine adenine dinucleotide ...
Energy Transformation — Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... 5. How many metabolic pathways are there in cellular aerobic respiration? In anaerobic respiration? (Please see pictures 4 and 5.) 6. What are the reactants and products of cellular respiration? (Please see pictures 4 and 5) 7. About how many ATP molecules does a cell obtain from the breakdown of on ...
... 5. How many metabolic pathways are there in cellular aerobic respiration? In anaerobic respiration? (Please see pictures 4 and 5.) 6. What are the reactants and products of cellular respiration? (Please see pictures 4 and 5) 7. About how many ATP molecules does a cell obtain from the breakdown of on ...
Heriot-Watt University The effect of sodium acetate ingestion on the
... (i.e., 100–140%) had minimal effect upon the calculated rates of fat and carbohydrate oxidation at this time and did not influence the overall conclusions presented within this study. Carbohydrate and fat oxidation rates were calculated according to Frayn (1983) at rest and Jeukendrup and Wallis (20 ...
... (i.e., 100–140%) had minimal effect upon the calculated rates of fat and carbohydrate oxidation at this time and did not influence the overall conclusions presented within this study. Carbohydrate and fat oxidation rates were calculated according to Frayn (1983) at rest and Jeukendrup and Wallis (20 ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.