Neck Lymph Nodes Levels - CT Anatomy
... to any names, marks, products, or services of third parties or hypertext links to thirdparty sites or information are provided solely as a convenience to you and do not in any way constitute or imply ECR's endorsement, sponsorship or recommendation of the third party, information, product or service ...
... to any names, marks, products, or services of third parties or hypertext links to thirdparty sites or information are provided solely as a convenience to you and do not in any way constitute or imply ECR's endorsement, sponsorship or recommendation of the third party, information, product or service ...
Gross Anatomy of the Skull by K. Dacre - AAEP Focus 2006
... Blood is supplied to brachydont teeth via the pulp and thus enters the tooth through the apical foramen. An extensive capillary network forms, particularly in the coronal aspect of the pulp. Blood is drained from the tooth via an intricate venous network that exits at the apical foramen.10 Vessels o ...
... Blood is supplied to brachydont teeth via the pulp and thus enters the tooth through the apical foramen. An extensive capillary network forms, particularly in the coronal aspect of the pulp. Blood is drained from the tooth via an intricate venous network that exits at the apical foramen.10 Vessels o ...
13 Management of Cervical Lymph Nodes in Differentiated Thyroid
... of cervical lymphadenopathy in differentiated thyroid cancer is controversial. There is currently no role in using PET to detect occult metastases in the N0 neck but it maybe useful in detecting recurrent neck disease in the presence of an elevated serum thyroglobulin with negative 131I scans and an ...
... of cervical lymphadenopathy in differentiated thyroid cancer is controversial. There is currently no role in using PET to detect occult metastases in the N0 neck but it maybe useful in detecting recurrent neck disease in the presence of an elevated serum thyroglobulin with negative 131I scans and an ...
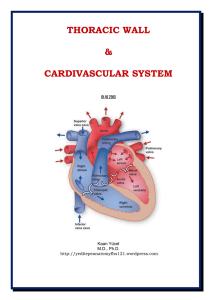
Dr.Kaan Yücel yeditepeanatomyfhs121.wordpress.com Thoracic
... The heart has two sides. The right side of the heart (right heart) receives poorly oxygenated (venous) blood from the body through the superior vena cava (SVC) and inferior vena cava (IVC) and pumps it through the pulmonary trunk and arteries to the lungs for oxygenation. The left side of the heart ...
... The heart has two sides. The right side of the heart (right heart) receives poorly oxygenated (venous) blood from the body through the superior vena cava (SVC) and inferior vena cava (IVC) and pumps it through the pulmonary trunk and arteries to the lungs for oxygenation. The left side of the heart ...
1 Chapter 6: The pleura and lungs The Pleura Each pleural sac is a
... bronchi divide and redivide until their diameter is less than 1 mm after which they are known as bronchioles, the walls of which lack mucous glands and cartilaginous plates. The bronchioles subdivide and form respiratory bronchioles whose walls, lined by nonciliated columnar epithelium, contain smoo ...
... bronchi divide and redivide until their diameter is less than 1 mm after which they are known as bronchioles, the walls of which lack mucous glands and cartilaginous plates. The bronchioles subdivide and form respiratory bronchioles whose walls, lined by nonciliated columnar epithelium, contain smoo ...
ct-based definition of thoracic lymph node
... Committee on Cancer. Methods and Materials: A dedicated thoracic radiologist, thoracic surgeon, medical physicist, and three radiation oncologists were gathered to generate a three-dimensional radiologic description for the mediastinal and hilar nodal regions on axial CT scans. This paper proposes a ...
... Committee on Cancer. Methods and Materials: A dedicated thoracic radiologist, thoracic surgeon, medical physicist, and three radiation oncologists were gathered to generate a three-dimensional radiologic description for the mediastinal and hilar nodal regions on axial CT scans. This paper proposes a ...
pharyngitis: to treat or not to treat
... Midline of the neck Behind : to From skull base The Nose esophagus The of Mouth In front upper 6 The vertebra larynx Cervical ...
... Midline of the neck Behind : to From skull base The Nose esophagus The of Mouth In front upper 6 The vertebra larynx Cervical ...
File
... protein molecules that leak out of the pulmonary capillaries • Transfer fluids back into the circulatory system ...
... protein molecules that leak out of the pulmonary capillaries • Transfer fluids back into the circulatory system ...
Development of the Respiratory System
... However, the muscles and cartilage arise from the 4th and the 6th arches. The development of these structures will be discussed in a later. Trachea: The trachea develops caudal to the larynx. The epithelium develops from the endoderm and the tracheal cartilage and muscles develop from splanchnic m ...
... However, the muscles and cartilage arise from the 4th and the 6th arches. The development of these structures will be discussed in a later. Trachea: The trachea develops caudal to the larynx. The epithelium develops from the endoderm and the tracheal cartilage and muscles develop from splanchnic m ...
Upper extremity arteries & veins
... Microscopic, very thin-walled vessels comprised of endothelium with basement membrane; allows for filtration and reabsorption Found in all tissues of the body except for those that are “avascular” Usually form branching networks (“capillary beds”) within tissues for increased surface area bl ...
... Microscopic, very thin-walled vessels comprised of endothelium with basement membrane; allows for filtration and reabsorption Found in all tissues of the body except for those that are “avascular” Usually form branching networks (“capillary beds”) within tissues for increased surface area bl ...
LECTURE OUTLINE “SCALP (layers, vessels and nerves)” Learning
... The emissary veins do not have valves and open in the loose areolar tissue; therefore, infection can be transmitted from the scalp to the cranial cavity. The layer of loose areolar tissue is known as the dangerous area of the scalp. ...
... The emissary veins do not have valves and open in the loose areolar tissue; therefore, infection can be transmitted from the scalp to the cranial cavity. The layer of loose areolar tissue is known as the dangerous area of the scalp. ...
Angiography_Anatomy_Part_1
... body tissues White Blood Cells are Leukocytes and are produced in the medullary cavity of some bones (yellow bone marrow) and lymph system. It’s job is to protect against infection and disease Platelets originate from bone marrow They repair tears in blood vessel wall and promote blood clott ...
... body tissues White Blood Cells are Leukocytes and are produced in the medullary cavity of some bones (yellow bone marrow) and lymph system. It’s job is to protect against infection and disease Platelets originate from bone marrow They repair tears in blood vessel wall and promote blood clott ...
The peritoneum 腹膜
... frequently adhered together, and are found wrapped about the organs in the upper part of the abdomen ...
... frequently adhered together, and are found wrapped about the organs in the upper part of the abdomen ...
Body Regions Review Anatomical Position Supine versus Prone
... Liver- consists of two lobes, converts glucose into glycogen and detoxifies Pancreas – secretes enzymes into the duodenum via pancreatic duct Small Intestine – site where digestion is completed and virtually all absorption occurs Duodenum – first part of the small intestine Colon – regions of the la ...
... Liver- consists of two lobes, converts glucose into glycogen and detoxifies Pancreas – secretes enzymes into the duodenum via pancreatic duct Small Intestine – site where digestion is completed and virtually all absorption occurs Duodenum – first part of the small intestine Colon – regions of the la ...
1 Anatomy – Thorax
... Vagus nerve → right and left vagus → right or left recurrent laryngeal nerves Oesophagus, Thoracic duct (duck between 2 gooses – ayzGOUS and oesophaGOUS) Anterior mediastinum potential space between pericardium and sternum Contents - Thymus, Sternopericardial ligaments, Lymph nodes, Branches of the ...
... Vagus nerve → right and left vagus → right or left recurrent laryngeal nerves Oesophagus, Thoracic duct (duck between 2 gooses – ayzGOUS and oesophaGOUS) Anterior mediastinum potential space between pericardium and sternum Contents - Thymus, Sternopericardial ligaments, Lymph nodes, Branches of the ...
THORACIC CAVITY
... peanuts, and parts of chicken bones and toys have all found their way into the bronchi. Parts of teeth may be inhaled while a patient is under anesthesia during a difficult dental extraction. Because the right bronchus is the wider and more direct continuation of the trachea , foreign bodies tend to ...
... peanuts, and parts of chicken bones and toys have all found their way into the bronchi. Parts of teeth may be inhaled while a patient is under anesthesia during a difficult dental extraction. Because the right bronchus is the wider and more direct continuation of the trachea , foreign bodies tend to ...
Gluteal Region (17).
... -gluteal veins are tributaries of the internal iliac veins that rain blood from the gluteal region -superior & inferior gluteal veins accompany the corresponding arteries through the greater sciatic foramen, superior and inferior to the piriformis, respectively *communicate with tributaries of the f ...
... -gluteal veins are tributaries of the internal iliac veins that rain blood from the gluteal region -superior & inferior gluteal veins accompany the corresponding arteries through the greater sciatic foramen, superior and inferior to the piriformis, respectively *communicate with tributaries of the f ...
ORAL REGION ORAL CAVITY Mouth consists of ORAL VESTIBULE
... Soft palate can be elevated so that it is in contact with posterior wall of the pharynx—closes isthmus of the pharynx, so that you have to breathe through your mouth Soft palate can also be drawn inferiorly so that it is in contact with posterior part of tongue Closes isthmus of the fauces, so ...
... Soft palate can be elevated so that it is in contact with posterior wall of the pharynx—closes isthmus of the pharynx, so that you have to breathe through your mouth Soft palate can also be drawn inferiorly so that it is in contact with posterior part of tongue Closes isthmus of the fauces, so ...
Anatomy Block 5 Oral Quiz Review
... Referred pain is simply the presentation of pain that reflects an injurious stimulus elsewhere, usually in the viscera. Note, this is not pain radiation. Referred pain happens when nerve fibers from regions of high sensory input (such as the skin) and nerve fibers from regions of normally low sensor ...
... Referred pain is simply the presentation of pain that reflects an injurious stimulus elsewhere, usually in the viscera. Note, this is not pain radiation. Referred pain happens when nerve fibers from regions of high sensory input (such as the skin) and nerve fibers from regions of normally low sensor ...
Pelvic lymphadenectomy in cervical cancer—surgical anatomy and
... Pelvic lymph node sampling is variably defined, either as the removal of a certain minimal number of lymph nodes, or based on anatomic criteria [13]. Irrespective on the definition, lymphatic tissue removal is limited to easily accessible pelvic regions and does not address all nodal groups. The numbe ...
... Pelvic lymph node sampling is variably defined, either as the removal of a certain minimal number of lymph nodes, or based on anatomic criteria [13]. Irrespective on the definition, lymphatic tissue removal is limited to easily accessible pelvic regions and does not address all nodal groups. The numbe ...
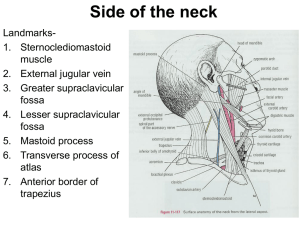
Side of the neck
... lymph nodes. Lipoma, cystic hygroma or lymphangioma, pharyngeal pouch or a cervical rib. Supraclavicular lymph nodes are commonly enlarged in tuberculosis, Hodgkin’s disease and in malignant growth of the breast, arm or chest. 2. Left supraclavicular nodes or Virchow’s or Scalene nodes are mostly in ...
... lymph nodes. Lipoma, cystic hygroma or lymphangioma, pharyngeal pouch or a cervical rib. Supraclavicular lymph nodes are commonly enlarged in tuberculosis, Hodgkin’s disease and in malignant growth of the breast, arm or chest. 2. Left supraclavicular nodes or Virchow’s or Scalene nodes are mostly in ...
Gastro40-HALabPracticalReview
... Spleen (part of it) and body of pancreas are mostly visible at L1, also superior mesenteric artery is observed to arise from the anterior portion of the aorta and is visible posterior to pancreas. THIS IS QUITE ...
... Spleen (part of it) and body of pancreas are mostly visible at L1, also superior mesenteric artery is observed to arise from the anterior portion of the aorta and is visible posterior to pancreas. THIS IS QUITE ...
The supratrochlear and supraorbital veins
... mandibular vein , just below the parotid gland , to from the external jugular vein 4. • The occipital vein : drains into the suboccipital venous plexus , which lies beneath the floor of the upper part of the posterior triangle ; the plexus in turn drains into the vertebral veins or the internal jugu ...
... mandibular vein , just below the parotid gland , to from the external jugular vein 4. • The occipital vein : drains into the suboccipital venous plexus , which lies beneath the floor of the upper part of the posterior triangle ; the plexus in turn drains into the vertebral veins or the internal jugu ...
Anatomy of thyroid gland Introduction • Brownish
... “false capsule” formed by pretracheal fascia Right and left lobes United by a narrow isthmus, which extends across the trachea anterior to second and third tracheal cartilages In some people a thi ...
... “false capsule” formed by pretracheal fascia Right and left lobes United by a narrow isthmus, which extends across the trachea anterior to second and third tracheal cartilages In some people a thi ...
Lymphatic system

The lymphatic system is part of the circulatory system and a vital part of the immune system, comprising a network of lymphatic vessels that carry a clear fluid called lymph (from Latin lympha meaning water) directionally towards the heart. The lymphatic system was first described in the seventeenth century independently by Olaus Rudbeck and Thomas Bartholin. Unlike the cardiovascular system, the lymphatic system is not a closed system. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma while leaving the blood cells. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered plasma are reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres remain in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymph system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres.The other main function is that of defense in the immune system. Lymph is very similar to blood plasma: it contains lymphocytes and other white blood cells. It also contains waste products and debris of cells together with bacteria and protein. Associated organs composed of lymphoid tissue are the sites of lymphocyte production. Lymphocytes are concentrated in the lymph nodes. The spleen and the thymus are also lymphoid organs of the immune system. The tonsils are lymphoid organs that are also associated with the digestive system. Lymphoid tissues contain lymphocytes, and also contain other types of cells for support. The system also includes all the structures dedicated to the circulation and production of lymphocytes (the primary cellular component of lymph), which also includes the bone marrow, and the lymphoid tissue associated with the digestive system.The blood does not come into direct contact with the parenchymal cells and tissues in the body (except in case of an injury causing rupture of one or more blood vessels), but constituents of the blood first exit the microvascular exchange blood vessels to become interstitial fluid, which comes into contact with the parenchymal cells of the body. Lymph is the fluid that is formed when interstitial fluid enters the initial lymphatic vessels of the lymphatic system. The lymph is then moved along the lymphatic vessel network by either intrinsic contractions of the lymphatic passages or by extrinsic compression of the lymphatic vessels via external tissue forces (e.g., the contractions of skeletal muscles), or by lymph hearts in some animals. The organization of lymph nodes and drainage follows the organization of the body into external and internal regions; therefore, the lymphatic drainage of the head, limbs, and body cavity walls follows an external route, and the lymphatic drainage of the thorax, abdomen, and pelvic cavities follows an internal route. Eventually, the lymph vessels empty into the lymphatic ducts, which drain into one of the two subclavian veins, near their junction with the internal jugular veins.