intestine rectum aorta vena cava
... The teniae coli, thickened bands of smooth muscle represenAng most of the longitudinal coat, begin at the base of the appendix as the thick longitudinal layer of the appendix separates into three bands. ...
... The teniae coli, thickened bands of smooth muscle represenAng most of the longitudinal coat, begin at the base of the appendix as the thick longitudinal layer of the appendix separates into three bands. ...
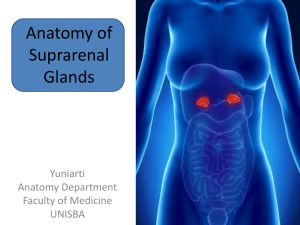
Location of Suprarenal Glands
... •The pyramidal right gland is more apical (situated over the superior pole) relative to the right kidney, lies anterolateral to the right of the diaphragm, and makes contact with the IVC anteromedially and the liver anterolaterally ...
... •The pyramidal right gland is more apical (situated over the superior pole) relative to the right kidney, lies anterolateral to the right of the diaphragm, and makes contact with the IVC anteromedially and the liver anterolaterally ...
Roundworm cloze notes
... Large numbers of filarial worms may block the passage of fluids within lymph vessels and cause _____________________________________. Ascarid Worms Ascaris lumbricoides is a serious parasite of humans and many other ___________________________ animals. It absorbs digested food from the host’s ______ ...
... Large numbers of filarial worms may block the passage of fluids within lymph vessels and cause _____________________________________. Ascarid Worms Ascaris lumbricoides is a serious parasite of humans and many other ___________________________ animals. It absorbs digested food from the host’s ______ ...
a glossary of terms related to oral
... THORACIC VERTEBRAE Twelve vertebra that are part of the vertebral or spinal column (which consists of a total of 32-33 individual vertebrae, joined together by intervertebral cartilages and a complex system of ligaments); distinctive from other vertebrae by the articular facets on their transverse p ...
... THORACIC VERTEBRAE Twelve vertebra that are part of the vertebral or spinal column (which consists of a total of 32-33 individual vertebrae, joined together by intervertebral cartilages and a complex system of ligaments); distinctive from other vertebrae by the articular facets on their transverse p ...
Pleural Cavity and Lungs - Dr. Sholley
... Lymphatic vessels on the surface of the lung (deep plexus) can be seen as blackened intersecting lines due to the presence of inhaled dust and carbon particles. Lymph fluid from these plexi travel to pulmonary nodes, which are located in the substance of the lung and can be observed as blackened ...
... Lymphatic vessels on the surface of the lung (deep plexus) can be seen as blackened intersecting lines due to the presence of inhaled dust and carbon particles. Lymph fluid from these plexi travel to pulmonary nodes, which are located in the substance of the lung and can be observed as blackened ...
Liver& biliary
... portal vein ( 70 % ). The hepatic artery brings oxygenated blood to the liver and the portal vein brings venous blood rich in the products of digestion which have been absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The arterial and venous blood is conducted to the central veins drain into the right & lef ...
... portal vein ( 70 % ). The hepatic artery brings oxygenated blood to the liver and the portal vein brings venous blood rich in the products of digestion which have been absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The arterial and venous blood is conducted to the central veins drain into the right & lef ...
Kidney, suprarenal, posterior abdominal wall
... The inferior suprarenal artery: this comes off the renal arteries, and it supplies the inferior portions of the adrenal gland The venous drainage of the adrenal gland is simple. Why? Because it follows a simple pattern. The right suprarenal vein is short and empties directly into the IVC. The le ...
... The inferior suprarenal artery: this comes off the renal arteries, and it supplies the inferior portions of the adrenal gland The venous drainage of the adrenal gland is simple. Why? Because it follows a simple pattern. The right suprarenal vein is short and empties directly into the IVC. The le ...
الشريحة 1
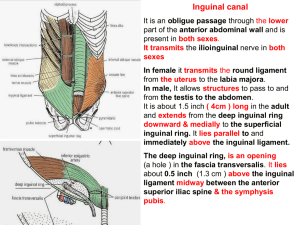
... the femoral vein. its center is located 4cm below the inguinal ligament lateral to the pubic tubercle, it is about 4cm long and 1.5 cm wide. The opening is covered by a thin and perforated fascia called ciribriform fascia. the lateral margin of the opening is sharp called the falciform margin. ...
... the femoral vein. its center is located 4cm below the inguinal ligament lateral to the pubic tubercle, it is about 4cm long and 1.5 cm wide. The opening is covered by a thin and perforated fascia called ciribriform fascia. the lateral margin of the opening is sharp called the falciform margin. ...
22-inguinal_canal2009-01-27 10:292.7 MB
... It is continuous with the fatty & membranous layers of the anterior abdominal wall. The fat is replaced by smooth muscle called dardos muscle which is innervated by sympathetic nerve fibers & is responsible for wrinkling of the overlying skin. The membranous layer ( Colles’ fascia ) is continuous in ...
... It is continuous with the fatty & membranous layers of the anterior abdominal wall. The fat is replaced by smooth muscle called dardos muscle which is innervated by sympathetic nerve fibers & is responsible for wrinkling of the overlying skin. The membranous layer ( Colles’ fascia ) is continuous in ...
Saladin, Human Anatomy 3e
... and finally large veins. Even large veins have thinner, less muscular walls than arteries of comparable size. Venous sinuses have large lumens, thin walls, and no muscle. 13. Medium veins in the limbs have valves to help produce a one-way flow of blood. 14. Although systemic blood usually passes thr ...
... and finally large veins. Even large veins have thinner, less muscular walls than arteries of comparable size. Venous sinuses have large lumens, thin walls, and no muscle. 13. Medium veins in the limbs have valves to help produce a one-way flow of blood. 14. Although systemic blood usually passes thr ...
Anatomy and Histology of the Pancreas
... pancreaticoduodenal veins lie close to their corresponding arteries and empty into the splenic or portal veins. Because of the close anatomic relationship of the splenic vein with the pancreas, inflammatory or neoplastic diseases involving the pancreatic body and tail can lead to splenic vein occlus ...
... pancreaticoduodenal veins lie close to their corresponding arteries and empty into the splenic or portal veins. Because of the close anatomic relationship of the splenic vein with the pancreas, inflammatory or neoplastic diseases involving the pancreatic body and tail can lead to splenic vein occlus ...
05 lung & pleura2012-01
... alveolar ducts, which lead into alveolar sacs. • The alveolar sacs consist of several alveoli, each alveolus is surrounded by a network of blood capillaries for gas exchange. ...
... alveolar ducts, which lead into alveolar sacs. • The alveolar sacs consist of several alveoli, each alveolus is surrounded by a network of blood capillaries for gas exchange. ...
What is anatomy?
... featured or (ii) by the manufacturer of each product to be administered, to verify the recommended dose or formula, the method and duration of administration, and contraindications. It is the responsibility of the practitioner, relying on their own experience and knowledge of the patient, to make di ...
... featured or (ii) by the manufacturer of each product to be administered, to verify the recommended dose or formula, the method and duration of administration, and contraindications. It is the responsibility of the practitioner, relying on their own experience and knowledge of the patient, to make di ...
Cardiovascular System part II
... Contained within the tissues and branch out becoming smaller and smaller. The only connection between arteries and veins. Serves the needs of the body’s cells by exchanging blood between tissue cells and blood. ...
... Contained within the tissues and branch out becoming smaller and smaller. The only connection between arteries and veins. Serves the needs of the body’s cells by exchanging blood between tissue cells and blood. ...
Development of the Mesodermal Organs in Vertebrates
... blood vessel). This epithelium becomes the endothelium of the blood vessel; the outer layers of the blood vessels are added much later in development. The blood vessels are originally laid down as a network. Those blood vessels through which the most blood is channeled develop into arteries & veins. ...
... blood vessel). This epithelium becomes the endothelium of the blood vessel; the outer layers of the blood vessels are added much later in development. The blood vessels are originally laid down as a network. Those blood vessels through which the most blood is channeled develop into arteries & veins. ...
Document
... • Thick fascial sheath surrounding the psoas muscle • Arises as the muscle enters the abdominal cavity under the medial arcuate ligament • Ends at the pelvic brim as the muscle leaves the abdomen inferior to the inguinal ligament (does not extend into the thigh) ...
... • Thick fascial sheath surrounding the psoas muscle • Arises as the muscle enters the abdominal cavity under the medial arcuate ligament • Ends at the pelvic brim as the muscle leaves the abdomen inferior to the inguinal ligament (does not extend into the thigh) ...
Practical class 2 ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS
... What structure separates the quadrate lobe from the right lobe? ...
... What structure separates the quadrate lobe from the right lobe? ...
SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE NASOPHARYNX
... - Arises from the lower part of the posterior margin of the medial pterygoid plate -Sphincter that prevents reflux into the nasopharynx and has a peristaltic function during swallowing ...
... - Arises from the lower part of the posterior margin of the medial pterygoid plate -Sphincter that prevents reflux into the nasopharynx and has a peristaltic function during swallowing ...
Nerve Supply of the Perineum and Pelvis
... Lungs - Pleura The pleura of the lungs are divided into 2 different parts: • Parietal Pleura = Adheres to the Internal thoracic wall • Visceral Pleura = Attached to the lungs ...
... Lungs - Pleura The pleura of the lungs are divided into 2 different parts: • Parietal Pleura = Adheres to the Internal thoracic wall • Visceral Pleura = Attached to the lungs ...
Gross Anatomy Lungs
... • Consists of segmental bronchus , a segmental branch of the pulmonary artery ,and a segment of the lung tissue, surrounded by a delicate connective tissue septum. • It is drained by the intersegmental part of the pulmonary vein • Refers to the portion of the lung supplied by each segmental bronchu ...
... • Consists of segmental bronchus , a segmental branch of the pulmonary artery ,and a segment of the lung tissue, surrounded by a delicate connective tissue septum. • It is drained by the intersegmental part of the pulmonary vein • Refers to the portion of the lung supplied by each segmental bronchu ...
Organs from the mesoderm
... At a somewhat later stage of development the walls of the ccelomie cavities of the right and left sides separate further (Fig. 45, B). The splanchnicdityer thickens, and begins to sur- ...
... At a somewhat later stage of development the walls of the ccelomie cavities of the right and left sides separate further (Fig. 45, B). The splanchnicdityer thickens, and begins to sur- ...
Lecture 19 - Vessels and Circulation
... Send blood into capillaries Tunica media has only a few layers of smooth muscle cells ...
... Send blood into capillaries Tunica media has only a few layers of smooth muscle cells ...
Chapter 20 Blood Vessels
... e. lumen is larger than in corresponding arteries f. venules – small diameter g. sinus or sinusoid = no smooth muscle or elastic tissue in walls h. venous reserve or reservoir - see above IV. Circulatory System - Arterial portion A. Pulmonary circuit 1. blood leaves right ventricle past pulmonary va ...
... e. lumen is larger than in corresponding arteries f. venules – small diameter g. sinus or sinusoid = no smooth muscle or elastic tissue in walls h. venous reserve or reservoir - see above IV. Circulatory System - Arterial portion A. Pulmonary circuit 1. blood leaves right ventricle past pulmonary va ...
2nd year Anatomy - Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University
... are given a prelab discussion for half an hour, before the beginning of each practical class using data show and videos to demonstrate the important structures of the dissected region(s) of the topic of the week which the student should focus on during the practical classes. In addition, a brief top ...
... are given a prelab discussion for half an hour, before the beginning of each practical class using data show and videos to demonstrate the important structures of the dissected region(s) of the topic of the week which the student should focus on during the practical classes. In addition, a brief top ...
Lymphatic system

The lymphatic system is part of the circulatory system and a vital part of the immune system, comprising a network of lymphatic vessels that carry a clear fluid called lymph (from Latin lympha meaning water) directionally towards the heart. The lymphatic system was first described in the seventeenth century independently by Olaus Rudbeck and Thomas Bartholin. Unlike the cardiovascular system, the lymphatic system is not a closed system. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma while leaving the blood cells. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered plasma are reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres remain in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymph system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres.The other main function is that of defense in the immune system. Lymph is very similar to blood plasma: it contains lymphocytes and other white blood cells. It also contains waste products and debris of cells together with bacteria and protein. Associated organs composed of lymphoid tissue are the sites of lymphocyte production. Lymphocytes are concentrated in the lymph nodes. The spleen and the thymus are also lymphoid organs of the immune system. The tonsils are lymphoid organs that are also associated with the digestive system. Lymphoid tissues contain lymphocytes, and also contain other types of cells for support. The system also includes all the structures dedicated to the circulation and production of lymphocytes (the primary cellular component of lymph), which also includes the bone marrow, and the lymphoid tissue associated with the digestive system.The blood does not come into direct contact with the parenchymal cells and tissues in the body (except in case of an injury causing rupture of one or more blood vessels), but constituents of the blood first exit the microvascular exchange blood vessels to become interstitial fluid, which comes into contact with the parenchymal cells of the body. Lymph is the fluid that is formed when interstitial fluid enters the initial lymphatic vessels of the lymphatic system. The lymph is then moved along the lymphatic vessel network by either intrinsic contractions of the lymphatic passages or by extrinsic compression of the lymphatic vessels via external tissue forces (e.g., the contractions of skeletal muscles), or by lymph hearts in some animals. The organization of lymph nodes and drainage follows the organization of the body into external and internal regions; therefore, the lymphatic drainage of the head, limbs, and body cavity walls follows an external route, and the lymphatic drainage of the thorax, abdomen, and pelvic cavities follows an internal route. Eventually, the lymph vessels empty into the lymphatic ducts, which drain into one of the two subclavian veins, near their junction with the internal jugular veins.