Amino Acids - Abbott Nutrition
... mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF, nuclear factor; ROS, reactive oxygen species; eIF, eukaryotic initiation factor; P, phosphorylated; HMB, βHydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate; EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid. *Effects on protein degradation and synthesis in the presence of HMB/EPA. Eley HL, et al. Am J Physiol ...
... mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF, nuclear factor; ROS, reactive oxygen species; eIF, eukaryotic initiation factor; P, phosphorylated; HMB, βHydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate; EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid. *Effects on protein degradation and synthesis in the presence of HMB/EPA. Eley HL, et al. Am J Physiol ...
finalcarbohydrat met..
... VI. Digestion of cellulose: A. Cellulose contains β(1-4) bonds between glucose molecules. ...
... VI. Digestion of cellulose: A. Cellulose contains β(1-4) bonds between glucose molecules. ...
Can you describe the various methods of cell membrane transport?
... The death rates from diseases such as bacterial pneumonia and surgical infections dropped substantially once antibiotics were widely available.• ...
... The death rates from diseases such as bacterial pneumonia and surgical infections dropped substantially once antibiotics were widely available.• ...
Protein and Amino Acid Analysis
... The amount of tryptophan in a single 4-ounce serving of turkey (350 milligrams) is also lower than the amount typically used to induce sleep. The recommendations for tryptophan supplements to help you sleep are 500 to 1,000 milligrams. ...
... The amount of tryptophan in a single 4-ounce serving of turkey (350 milligrams) is also lower than the amount typically used to induce sleep. The recommendations for tryptophan supplements to help you sleep are 500 to 1,000 milligrams. ...
HMH 2.3 notes
... • Many carbon-based molecules are made of many small subunits bonded together. – Monomers are the individual subunits. – Polymers are made of many monomers. ...
... • Many carbon-based molecules are made of many small subunits bonded together. – Monomers are the individual subunits. – Polymers are made of many monomers. ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... use by a phosphorolytic reaction catalyzed by glycogen/starch phosphorylase. This enzyme catalyze an attack by Pi on the (a14) glycosidic linkage from the nonreducing end, generating glucose 1phosphate and a polymer one glucose unit shorter. ...
... use by a phosphorolytic reaction catalyzed by glycogen/starch phosphorylase. This enzyme catalyze an attack by Pi on the (a14) glycosidic linkage from the nonreducing end, generating glucose 1phosphate and a polymer one glucose unit shorter. ...
Lab Module 8: Phenol-Red Carbohydrate Fermentation Broths
... of types of by-products. Lactobacillus (and human muscle cells) forms lactic acid as a fermentation by-product. Acetobacter forms acetic acid. Many bacteria form mixtures of products including liquids and gases. The particular types of by-products depends on the particular enzyme systems used to per ...
... of types of by-products. Lactobacillus (and human muscle cells) forms lactic acid as a fermentation by-product. Acetobacter forms acetic acid. Many bacteria form mixtures of products including liquids and gases. The particular types of by-products depends on the particular enzyme systems used to per ...
Carbohydrates
... • includes starches, sugars and cellulose (fiber) • most are plant materials produced by photosynthesis ...
... • includes starches, sugars and cellulose (fiber) • most are plant materials produced by photosynthesis ...
Cellular Respiration
... The remaining acceptors pump out two more H+ pairs to outer chamber by using energy of downhill moving electron pair. Therefore, 3 proton pairs are pumped by using the energy of 1 NADH. 3 H+ pairs or 1 NADH produce 3 ATP molecules. O2 is the ultimate acceptor for electrons and H+. ETC and Krebs Cycl ...
... The remaining acceptors pump out two more H+ pairs to outer chamber by using energy of downhill moving electron pair. Therefore, 3 proton pairs are pumped by using the energy of 1 NADH. 3 H+ pairs or 1 NADH produce 3 ATP molecules. O2 is the ultimate acceptor for electrons and H+. ETC and Krebs Cycl ...
Protein Overview
... training. Don’t train hungry! Consume protein after work out…up to 3 hours post exercise ...
... training. Don’t train hungry! Consume protein after work out…up to 3 hours post exercise ...
Sample exam questions Chapter 11 Carbohydrates
... A. The ATP produced/glucose degraded ratio would be the same as for normal cells B. The ATP produced/glucose degraded ratio would be one-half that of normal cells * C. The ATP produced/glucose degraded ratio would be zero. D. The ATP produced/glucose degraded ratio would be twice that of a normal ce ...
... A. The ATP produced/glucose degraded ratio would be the same as for normal cells B. The ATP produced/glucose degraded ratio would be one-half that of normal cells * C. The ATP produced/glucose degraded ratio would be zero. D. The ATP produced/glucose degraded ratio would be twice that of a normal ce ...
Microbiology of the Rumen - Iowa State University: Animal Science
... Limitations of Fiber Analysis NDF and ADF should be done sequentially on the same sample. Not done this way in most commercial labs. Pectin solubilized in ND soln, but not soluble in the AD soln. Should report NDF and ADF on an organic basis. Minerals, especially soil, are not solubilized in the de ...
... Limitations of Fiber Analysis NDF and ADF should be done sequentially on the same sample. Not done this way in most commercial labs. Pectin solubilized in ND soln, but not soluble in the AD soln. Should report NDF and ADF on an organic basis. Minerals, especially soil, are not solubilized in the de ...
metabolism - anatomymodelimages
... -a. Complete proteins – animal sources; meat; eggs; dairy -b. Incomplete proteins - plant sources -c. Essential amino acids – must be obtained from diet 2. Use in body – structure; function (enzymes, hemoglobin); fuel if needed 3. Deficits – tissue wasting; growth retardation; anemia 4. Excesses – o ...
... -a. Complete proteins – animal sources; meat; eggs; dairy -b. Incomplete proteins - plant sources -c. Essential amino acids – must be obtained from diet 2. Use in body – structure; function (enzymes, hemoglobin); fuel if needed 3. Deficits – tissue wasting; growth retardation; anemia 4. Excesses – o ...
Proteins
... Incomplete proteins also supply all of the EAAs, but usually one AA is limiting (low) “low quality” Plant-based ...
... Incomplete proteins also supply all of the EAAs, but usually one AA is limiting (low) “low quality” Plant-based ...
ANN 303 PRINCIPLES OF ANIMAL NUTRITION (A)
... The dry matter of food is divided into organic and inorganic material. There is however no sharp distraction between them. This is because many organic compound contain mineral element as structural component e.g carbohydrate contains phosphorus. The animal body contain very low carbohydrate. Howeve ...
... The dry matter of food is divided into organic and inorganic material. There is however no sharp distraction between them. This is because many organic compound contain mineral element as structural component e.g carbohydrate contains phosphorus. The animal body contain very low carbohydrate. Howeve ...
glucose, faKy acids, amino acids
... • Happens in muscle of humans and other animals in the absence of oxygen ( anaerobic) • LacDc acid and CO2 are produced • Does not produce ATP, but it does allow glycolysis to occur again and ...
... • Happens in muscle of humans and other animals in the absence of oxygen ( anaerobic) • LacDc acid and CO2 are produced • Does not produce ATP, but it does allow glycolysis to occur again and ...
high energy bond
... Buildup of bigger molecules Products are large molecules Protein, peptidoglycan, DNA, RNA Mediated by enzymes E required (endergonic) ...
... Buildup of bigger molecules Products are large molecules Protein, peptidoglycan, DNA, RNA Mediated by enzymes E required (endergonic) ...
ENDODERMAL DERIVATIVES, FORMATION OF THE GUT AND ITS
... the chorionic cavity but the folding of the embryo and its fusion along the ventral midline incorporates this space into the embryo as the intraembryonic coelom. The splanchnopleuric membrane forms an overcoat around the gut tube and gives rise to the muscle and fibrous connective tissue of the bowe ...
... the chorionic cavity but the folding of the embryo and its fusion along the ventral midline incorporates this space into the embryo as the intraembryonic coelom. The splanchnopleuric membrane forms an overcoat around the gut tube and gives rise to the muscle and fibrous connective tissue of the bowe ...
4. MP and MPM that contain iridoids
... glycosides (genciopikrin, eritrocentaurin, eritritaurin); flavonovyy glycoside of centaurin, oleanolovuyu and ascorbic acids, essential oil, resins Pharmacological activity: Preparations of centaury as bitter taste is excited ...
... glycosides (genciopikrin, eritrocentaurin, eritritaurin); flavonovyy glycoside of centaurin, oleanolovuyu and ascorbic acids, essential oil, resins Pharmacological activity: Preparations of centaury as bitter taste is excited ...
Lactic Acid System - PhysicalEducationatMSC
... produces lactate and hydrogen ions - for each lactate molecule, one hydrogen ion is formed. The presence of hydrogen ions, not lactate, makes the muscle acidic that will eventually halt muscle function. As hydrogen ion concentrations, increase the blood and muscle become acidic. This acidic environm ...
... produces lactate and hydrogen ions - for each lactate molecule, one hydrogen ion is formed. The presence of hydrogen ions, not lactate, makes the muscle acidic that will eventually halt muscle function. As hydrogen ion concentrations, increase the blood and muscle become acidic. This acidic environm ...
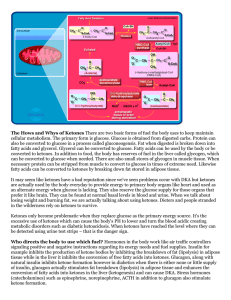
Pathology Ketone bodies are created at moderate
... can be converted to glucose when needed. There are also small stores of glycogen in muscle tissue. When necessary protein can be stripped from muscle to convert to glucose in times of extreme need. Likewise fatty acids can be converted to ketones by breaking down fat stored in adipose tissue. It may ...
... can be converted to glucose when needed. There are also small stores of glycogen in muscle tissue. When necessary protein can be stripped from muscle to convert to glucose in times of extreme need. Likewise fatty acids can be converted to ketones by breaking down fat stored in adipose tissue. It may ...
Cellular Respiration
... 1. Have you ever stopped to think about how the foods you consume on a daily basis are broken down to produce energy? Not only do you eat food on a regular basis, but you usually drink some type of water-based beverage with your meal & you breathe in oxygen too. 2. All cells must do work to stay ali ...
... 1. Have you ever stopped to think about how the foods you consume on a daily basis are broken down to produce energy? Not only do you eat food on a regular basis, but you usually drink some type of water-based beverage with your meal & you breathe in oxygen too. 2. All cells must do work to stay ali ...
ATP powers cellular work
... ATP stores energy obtained from food and releases it as needed at a later time ...
... ATP stores energy obtained from food and releases it as needed at a later time ...
NEHRU ARTS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE, TM PALAYALAM
... 2. Write a detailed account on nutritional types of microorganisms with examples 3. Compare the physiology of Chemoautotrophs and photoautotrophs 4. Write in detail about transport of nutrients in the cell. ...
... 2. Write a detailed account on nutritional types of microorganisms with examples 3. Compare the physiology of Chemoautotrophs and photoautotrophs 4. Write in detail about transport of nutrients in the cell. ...
Digestion

Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use.In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact of saliva. Saliva, a liquid secreted by the salivary glands, contains salivary amylase, an enzyme which starts the digestion of starch in the food; the saliva also contains mucus, which lubricates the food, and hydrogen carbonate, which provides the ideal conditions of pH (alkaline) for amylase to work. After undergoing mastication and starch digestion, the food will be in the form of a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. It will then travel down the esophagus and into the stomach by the action of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach starts protein digestion. Gastric juice mainly contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin. As these two chemicals may damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by the stomach, providing a slimy layer that acts as a shield against the damaging effects of the chemicals. At the same time protein digestion is occurring, mechanical mixing occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.After some time (typically 1–2 hours in humans, 4–6 hours in dogs, 3–4 hours in house cats), the resulting thick liquid is called chyme. When the pyloric sphincter valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes with digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile juice from the liver and then passes through the small intestine, in which digestion continues. When the chyme is fully digested, it is absorbed into the blood. 95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine. Water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon (large intestine) where the pH is slightly acidic about 5.6 ~ 6.9. Some vitamins, such as biotin and vitamin K (K2MK7) produced by bacteria in the colon are also absorbed into the blood in the colon. Waste material is eliminated from the rectum during defecation.