Remember: Condensation makes bonds: Hydrolysis breaks bonds.
... • “Organic compounds are based on carbon and are found in living things.” (1) 2. List three carbon-containing groups or molecules that are not organic. There are many organic molecules in living things. The same (or very similar) molecules are used in many different living things for the same purpos ...
... • “Organic compounds are based on carbon and are found in living things.” (1) 2. List three carbon-containing groups or molecules that are not organic. There are many organic molecules in living things. The same (or very similar) molecules are used in many different living things for the same purpos ...
Cell Structure
... archaebacteria were together in the kingdom Monera. Because of discoveries over the last 20 years scientists have decided that they are so different that they should have their own kingdom. ...
... archaebacteria were together in the kingdom Monera. Because of discoveries over the last 20 years scientists have decided that they are so different that they should have their own kingdom. ...
Ch.24Pt.4_000
... TAGs are partially hydrolyzed: 2 of the 3 F.A.s have ester linkages hydrolyzed and are released. Monoacylglycerol remains = glycerol and 1 fatty acid ...
... TAGs are partially hydrolyzed: 2 of the 3 F.A.s have ester linkages hydrolyzed and are released. Monoacylglycerol remains = glycerol and 1 fatty acid ...
Lecture#7 Microbial Biotechnology
... Microbial Biotechnology in Agriculture and Food • development of genetically engineered plants with internal resistance to drought, frost, insect pests and infestation • reduction in dependency of plants on chemical fertilizers and identification of alternatives to expensive fertilizers • replaceme ...
... Microbial Biotechnology in Agriculture and Food • development of genetically engineered plants with internal resistance to drought, frost, insect pests and infestation • reduction in dependency of plants on chemical fertilizers and identification of alternatives to expensive fertilizers • replaceme ...
Other ways to make ATP
... • Without O2 as an e- acceptor, NADH cannot be re-oxidized to NAD. • Even though aerobic metabolism can produce ~36 ATP from 1 glucose, the 2 ATP from glycolysis is enough. • But glycolysis requires that NAD be reduced to NADH; what happens when ALL the NAD becomes NADH with no O2 to accept the H? • ...
... • Without O2 as an e- acceptor, NADH cannot be re-oxidized to NAD. • Even though aerobic metabolism can produce ~36 ATP from 1 glucose, the 2 ATP from glycolysis is enough. • But glycolysis requires that NAD be reduced to NADH; what happens when ALL the NAD becomes NADH with no O2 to accept the H? • ...
Gastro17-GITractPt1
... Clinical Vignette: If a patient has a gall bladder stone and it gets inflamed and perforates posteriorly, the stones can get inside the duodenum. If the stone is large enough, it can obstruct the duodenum. It also stains the anterior surface of the duodenum postmortem Neck of the pancreas is l ...
... Clinical Vignette: If a patient has a gall bladder stone and it gets inflamed and perforates posteriorly, the stones can get inside the duodenum. If the stone is large enough, it can obstruct the duodenum. It also stains the anterior surface of the duodenum postmortem Neck of the pancreas is l ...
Unit 04 Enzymes and respiration Review
... 10. Summarize in order the parts of aerobic respiration ( Krebs cycle, glycolysis, ETC). Tell what is produced in each part. 11. When do we notice plants using respiration pathways? Is this the only time they respire? 12. How could we tell that plants were using respiration? 13. Name an organism tha ...
... 10. Summarize in order the parts of aerobic respiration ( Krebs cycle, glycolysis, ETC). Tell what is produced in each part. 11. When do we notice plants using respiration pathways? Is this the only time they respire? 12. How could we tell that plants were using respiration? 13. Name an organism tha ...
Slide 1
... • There is a rapid period of growth during this phase due to the fact that: • Bacteria have developed the necessary enzymes and there are plenty of nutrients. • There are few waste products being produced. • The rate of cell division is currently at its maximum with the number of bacteria doubling a ...
... • There is a rapid period of growth during this phase due to the fact that: • Bacteria have developed the necessary enzymes and there are plenty of nutrients. • There are few waste products being produced. • The rate of cell division is currently at its maximum with the number of bacteria doubling a ...
All the following is correct about ribosomes EXCEPT
... Carbon chains form the skeletons of most organic molecules, the skeletons may be a. straight only b. branched only c. arranged in closed rings only d. All of them ...
... Carbon chains form the skeletons of most organic molecules, the skeletons may be a. straight only b. branched only c. arranged in closed rings only d. All of them ...
Protein foods - Deans Community High School
... Our bodies need certain amino acids to keep us healthy. We get these amino acids by eating protein in animal and plant foods. We have the same problem with eating protein as we do with eating starch. Protein molecules are too big to get into our blood. This means that our bodies have to break the pr ...
... Our bodies need certain amino acids to keep us healthy. We get these amino acids by eating protein in animal and plant foods. We have the same problem with eating protein as we do with eating starch. Protein molecules are too big to get into our blood. This means that our bodies have to break the pr ...
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... • Nucleotides are linked together by phosphodiester linkages – Covalent bond between a phosphate group and a sugar • This creates the sugarphosphate backbone • One end will have a phosphate attached to a 5’ carbon; the other will have a hydroxyl group on a 3’ carbon (these are the ends of DNA and th ...
... • Nucleotides are linked together by phosphodiester linkages – Covalent bond between a phosphate group and a sugar • This creates the sugarphosphate backbone • One end will have a phosphate attached to a 5’ carbon; the other will have a hydroxyl group on a 3’ carbon (these are the ends of DNA and th ...
Marvelous Macromolecules - Pregitzersninjascienceclasses
... Used in energy storage then broken down as needed in the cell Also used to maintain structure in cells ...
... Used in energy storage then broken down as needed in the cell Also used to maintain structure in cells ...
Slide ()
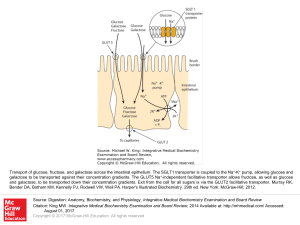
... Transport of glucose, fructose, and galactose across the intestinal epithelium. The SGLT1 transporter is coupled to the Na+-K+ pump, allowing glucose and galactose to be transported against their concentration gradients. The GLUT5 Na+-independent facilitative transporter allows fructose, as well as ...
... Transport of glucose, fructose, and galactose across the intestinal epithelium. The SGLT1 transporter is coupled to the Na+-K+ pump, allowing glucose and galactose to be transported against their concentration gradients. The GLUT5 Na+-independent facilitative transporter allows fructose, as well as ...
Unit 3: Chapter 6
... - Carry ____________ _______________ - _____________ for _________________ - The order of nitrogenous bases (A, T, G, C) determines the _______ of _____________ - The order of amino acids determines the protein ...
... - Carry ____________ _______________ - _____________ for _________________ - The order of nitrogenous bases (A, T, G, C) determines the _______ of _____________ - The order of amino acids determines the protein ...
functional group
... 1. Happens by hydrolysis 2. Polymers are broken down into monemers by adding a water. 3. Energy is not used 4. Enzymes are required. Example: digestion ...
... 1. Happens by hydrolysis 2. Polymers are broken down into monemers by adding a water. 3. Energy is not used 4. Enzymes are required. Example: digestion ...
Topic 3.2: Carbohydrates, Lipids, and Proteins
... Often transported from leaves of plants to other locations in plants by vascular tissue ...
... Often transported from leaves of plants to other locations in plants by vascular tissue ...
Figure 5-2
... 40. ______________ Gylcogen is a plant based polysaccharide that is also known as fiber. 41. ______________ Glucose is a monosaccharide used as an immediate supply of energy for cells. 42. ______________ Lipids contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. 43. ______________ Nitrogen is an ...
... 40. ______________ Gylcogen is a plant based polysaccharide that is also known as fiber. 41. ______________ Glucose is a monosaccharide used as an immediate supply of energy for cells. 42. ______________ Lipids contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. 43. ______________ Nitrogen is an ...
How Does Life Use Energy?
... That matter and structure can persist during drying or freezing when all processes cease. Life processes can resume upon restoration of water or thawing. ...
... That matter and structure can persist during drying or freezing when all processes cease. Life processes can resume upon restoration of water or thawing. ...
Organic vs. Inorganic
... •Enzymes become denatured with temperatures that are too high or pH levels not 7. The active site changes shape. •Examples of Enzymes•Lactase, the enzyme breaks down lactose •Protease and peptidase - A protease is any enzyme that can break down a long protein into smaller chains called peptides • Am ...
... •Enzymes become denatured with temperatures that are too high or pH levels not 7. The active site changes shape. •Examples of Enzymes•Lactase, the enzyme breaks down lactose •Protease and peptidase - A protease is any enzyme that can break down a long protein into smaller chains called peptides • Am ...
Macs Notes
... that BREAK DOWN molecules.) Water is used during the process. Why? b/c now you have to break up one or more of the covalent links. This leaves unhappy atoms with electrons that need to be shared. So... ...water breaks up into –H and –OH and attaches to make each side happy. In the body these r ...
... that BREAK DOWN molecules.) Water is used during the process. Why? b/c now you have to break up one or more of the covalent links. This leaves unhappy atoms with electrons that need to be shared. So... ...water breaks up into –H and –OH and attaches to make each side happy. In the body these r ...
Digestion

Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use.In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact of saliva. Saliva, a liquid secreted by the salivary glands, contains salivary amylase, an enzyme which starts the digestion of starch in the food; the saliva also contains mucus, which lubricates the food, and hydrogen carbonate, which provides the ideal conditions of pH (alkaline) for amylase to work. After undergoing mastication and starch digestion, the food will be in the form of a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. It will then travel down the esophagus and into the stomach by the action of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach starts protein digestion. Gastric juice mainly contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin. As these two chemicals may damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by the stomach, providing a slimy layer that acts as a shield against the damaging effects of the chemicals. At the same time protein digestion is occurring, mechanical mixing occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.After some time (typically 1–2 hours in humans, 4–6 hours in dogs, 3–4 hours in house cats), the resulting thick liquid is called chyme. When the pyloric sphincter valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes with digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile juice from the liver and then passes through the small intestine, in which digestion continues. When the chyme is fully digested, it is absorbed into the blood. 95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine. Water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon (large intestine) where the pH is slightly acidic about 5.6 ~ 6.9. Some vitamins, such as biotin and vitamin K (K2MK7) produced by bacteria in the colon are also absorbed into the blood in the colon. Waste material is eliminated from the rectum during defecation.