Macromolecule Notes - Ms. Dooley`s Science Class
... End of Hydrolysis • Water breaks up into -H and –OH and attaches to make each side happy. • In the body, catabolic reactions are carried out by enzymes generally known as HYDROLASES ...
... End of Hydrolysis • Water breaks up into -H and –OH and attaches to make each side happy. • In the body, catabolic reactions are carried out by enzymes generally known as HYDROLASES ...
Lipid Metabolizması - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... very important structural (as major component of membrane structures) and functional role. In this part of discussion we will mainly focus of the digestion, transport and catabolism of triglycerides. Although other lipids like cholesterol, sphingolipids are important too but they will not be covered ...
... very important structural (as major component of membrane structures) and functional role. In this part of discussion we will mainly focus of the digestion, transport and catabolism of triglycerides. Although other lipids like cholesterol, sphingolipids are important too but they will not be covered ...
2 CCT - 2u 9
... This is in response to your letter of September 15,200O to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) pursuant to 21 U.S.C. 343(r)(6) (section 403(r)(6) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (the Act)). Your submission states that you are making the following claim, among others, for the product F ...
... This is in response to your letter of September 15,200O to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) pursuant to 21 U.S.C. 343(r)(6) (section 403(r)(6) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (the Act)). Your submission states that you are making the following claim, among others, for the product F ...
21:120:360 Biochemistry
... makeup for any exam, please notify me as soon as possible so that there is sufficient time for me to approve the request. Do not assume you will be able to receive a makeup exam unless it is confirmed by me. Please note: There will be no makeup exams, special assignments etc. to improve your grade. ...
... makeup for any exam, please notify me as soon as possible so that there is sufficient time for me to approve the request. Do not assume you will be able to receive a makeup exam unless it is confirmed by me. Please note: There will be no makeup exams, special assignments etc. to improve your grade. ...
Chapter 6
... intestinal cells and get to the blood. Digestion of proteins involves clipping the protein chains into single amino acids, dipeptides and tripeptides which are small enough to be absorbed. Then, they travel through the blood and cells can take up the amino acids to make the proteins they need. A sid ...
... intestinal cells and get to the blood. Digestion of proteins involves clipping the protein chains into single amino acids, dipeptides and tripeptides which are small enough to be absorbed. Then, they travel through the blood and cells can take up the amino acids to make the proteins they need. A sid ...
Chem 464 Biochemistry
... and sheets. Just to be different, tell me about turns. What are they, how many types of turns are there, and what can you tell me about the Amino acids that are usually found in turns. In globular proteins about 1/3 of the residues are involved in turns or loops where the protein structure reverses ...
... and sheets. Just to be different, tell me about turns. What are they, how many types of turns are there, and what can you tell me about the Amino acids that are usually found in turns. In globular proteins about 1/3 of the residues are involved in turns or loops where the protein structure reverses ...
Ch 3 organic molecules
... evolved a mechanism to digest cellulose most carnivores have not what do they eat? How is this related to corn fuels?? ...
... evolved a mechanism to digest cellulose most carnivores have not what do they eat? How is this related to corn fuels?? ...
Macromolecules Vocabulary and Concepts
... Polysaccharide (Polymers of Glucose) o Ring form of glucose comes in two forms: alpha and beta glucose o Starch: polymer of alpha glucose, energy storage in plants, digested by animals o Glycogen: polymer of alpha glucose, energy storage in animals o Cellulose: polymer of beta glucose, structural ...
... Polysaccharide (Polymers of Glucose) o Ring form of glucose comes in two forms: alpha and beta glucose o Starch: polymer of alpha glucose, energy storage in plants, digested by animals o Glycogen: polymer of alpha glucose, energy storage in animals o Cellulose: polymer of beta glucose, structural ...
Final Review
... 1. What is the cellular organelle associated with energy production? Mitochondrion 2. The ultimate source of energy for all but a very few biochemical reactions is The sun – through the process of photosynthesis 3. The biochemical process in which simple molecules are combined to make larger ones is ...
... 1. What is the cellular organelle associated with energy production? Mitochondrion 2. The ultimate source of energy for all but a very few biochemical reactions is The sun – through the process of photosynthesis 3. The biochemical process in which simple molecules are combined to make larger ones is ...
Chem 2B
... 1. What is the cellular organelle associated with energy production? Mitochondrion 2. The ultimate source of energy for all but a very few biochemical reactions is The sun – through the process of photosynthesis 3. The biochemical process in which simple molecules are combined to make larger ones is ...
... 1. What is the cellular organelle associated with energy production? Mitochondrion 2. The ultimate source of energy for all but a very few biochemical reactions is The sun – through the process of photosynthesis 3. The biochemical process in which simple molecules are combined to make larger ones is ...
Proteolytic Enzymes in Detergents: Evidence of Their
... assisting in the removal of protein-based stains such as blood and many types of food. Some of these enzymes break all peptide bonds, whereas there are other more specific proteases that only cleave those peptide bonds in which a particular amino acid is involved.3 The most widely used protease is su ...
... assisting in the removal of protein-based stains such as blood and many types of food. Some of these enzymes break all peptide bonds, whereas there are other more specific proteases that only cleave those peptide bonds in which a particular amino acid is involved.3 The most widely used protease is su ...
Gastric Adenoma
... and bulky, frothy, greasy, yellow or clay-colored stools. Diarrhea can be classified into four major categories: • Secretory diarrhea is characterized by isotonic stool and persists during fasting. • Osmotic diarrhea, such as that occurring with lactase deficiency, is due to osmotic forces exerted b ...
... and bulky, frothy, greasy, yellow or clay-colored stools. Diarrhea can be classified into four major categories: • Secretory diarrhea is characterized by isotonic stool and persists during fasting. • Osmotic diarrhea, such as that occurring with lactase deficiency, is due to osmotic forces exerted b ...
Biochem Molecules Presentation
... Proteins are synthesized by bonding amino acids Regents Biology ...
... Proteins are synthesized by bonding amino acids Regents Biology ...
Diverticular disease - Bowen Rayner Medicine
... section should not be joined together immediately. This is because the join will not heal until the intestine has completely recovered from the infection or strangulation. In this situation, a temporary 'colostomy' will be formed. A colostomy is an opening in the large intestine to the outside of th ...
... section should not be joined together immediately. This is because the join will not heal until the intestine has completely recovered from the infection or strangulation. In this situation, a temporary 'colostomy' will be formed. A colostomy is an opening in the large intestine to the outside of th ...
Seeds and Seed Germination
... The action of the enzyme also limited by substrate Once all the starch in an amyloplast is hydrolysed the enzyme stops work Therefore the release of the stored food is adjusted to suite the demand ...
... The action of the enzyme also limited by substrate Once all the starch in an amyloplast is hydrolysed the enzyme stops work Therefore the release of the stored food is adjusted to suite the demand ...
Enzymes and their effect on amino acid nutrition
... where trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase and several other exo-proteases are present to complete the process of protein digestion. The secreted proteases are very effective in degrading dietary proteins and as a result are potentially dangerous as they could digest the animal’s gastrointestinal (GI) tr ...
... where trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase and several other exo-proteases are present to complete the process of protein digestion. The secreted proteases are very effective in degrading dietary proteins and as a result are potentially dangerous as they could digest the animal’s gastrointestinal (GI) tr ...
Vitamin A - Denton ISD
... Fat is broken down into glycerol and fatty acids. 1 gram = 9 Calories 2. Essential fatty acids found in vegetable oils 3. Help body absorb certain vitamins 4. Used to produce 1. Cell membranes 2. Myelin sheaths 3. Hormones ...
... Fat is broken down into glycerol and fatty acids. 1 gram = 9 Calories 2. Essential fatty acids found in vegetable oils 3. Help body absorb certain vitamins 4. Used to produce 1. Cell membranes 2. Myelin sheaths 3. Hormones ...
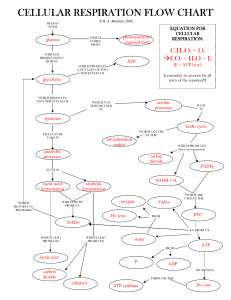
Chapter 7 – How Cells Release Stored Energy
... ATP synthases NADH is shuttled down the e- carriers Oxygen is the final e- (H) acceptor forming H2O Proteins shuttle H+ across the membrane The greater the gradient the more potential E H+ are passed through ATP synthase which catalyzes the formation of about 34 ATP ...
... ATP synthases NADH is shuttled down the e- carriers Oxygen is the final e- (H) acceptor forming H2O Proteins shuttle H+ across the membrane The greater the gradient the more potential E H+ are passed through ATP synthase which catalyzes the formation of about 34 ATP ...
4-Carbohydrate metabolism
... Particularly important dietary carbohydrates include starch and disaccharides such as lactose and sucrose. None of these molecules can be absorbed for the simple reason that they cannot cross cell membranes, unlike the situation for monosaccharides, there are no transporters to carry them across. ...
... Particularly important dietary carbohydrates include starch and disaccharides such as lactose and sucrose. None of these molecules can be absorbed for the simple reason that they cannot cross cell membranes, unlike the situation for monosaccharides, there are no transporters to carry them across. ...
Chapter 3 Biological Molecules
... Chitin (polymer of modified glucose units) • Found in the outer coverings of insects, crabs, and spiders • Found in the cell walls of many fungi ...
... Chitin (polymer of modified glucose units) • Found in the outer coverings of insects, crabs, and spiders • Found in the cell walls of many fungi ...
ANATOMY THEME SESSION: Oesophagus, Stomach
... Duodenum. On prosections of the duodenum and pancreas, identify the 4 parts of the duodenum (superior, descending, horizontal/inferior, ascending), and the greater and lesser duodenal papillae. Name the ducts that drain into the duodenum at these papillae? ...
... Duodenum. On prosections of the duodenum and pancreas, identify the 4 parts of the duodenum (superior, descending, horizontal/inferior, ascending), and the greater and lesser duodenal papillae. Name the ducts that drain into the duodenum at these papillae? ...
Digestion

Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use.In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact of saliva. Saliva, a liquid secreted by the salivary glands, contains salivary amylase, an enzyme which starts the digestion of starch in the food; the saliva also contains mucus, which lubricates the food, and hydrogen carbonate, which provides the ideal conditions of pH (alkaline) for amylase to work. After undergoing mastication and starch digestion, the food will be in the form of a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. It will then travel down the esophagus and into the stomach by the action of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach starts protein digestion. Gastric juice mainly contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin. As these two chemicals may damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by the stomach, providing a slimy layer that acts as a shield against the damaging effects of the chemicals. At the same time protein digestion is occurring, mechanical mixing occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.After some time (typically 1–2 hours in humans, 4–6 hours in dogs, 3–4 hours in house cats), the resulting thick liquid is called chyme. When the pyloric sphincter valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes with digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile juice from the liver and then passes through the small intestine, in which digestion continues. When the chyme is fully digested, it is absorbed into the blood. 95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine. Water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon (large intestine) where the pH is slightly acidic about 5.6 ~ 6.9. Some vitamins, such as biotin and vitamin K (K2MK7) produced by bacteria in the colon are also absorbed into the blood in the colon. Waste material is eliminated from the rectum during defecation.