food-borne-ifections-poisoning-paper2-unit-2a
... advised not to wash meat and poultry carcasses prior to cooking to help prevent water splashes and aerosols from contaminating kitchen surfaces. Any surfaces that could be potentially contaminated, such as in meat-preparation areas, as well as chopping boards, should be thoroughly disinfected after ...
... advised not to wash meat and poultry carcasses prior to cooking to help prevent water splashes and aerosols from contaminating kitchen surfaces. Any surfaces that could be potentially contaminated, such as in meat-preparation areas, as well as chopping boards, should be thoroughly disinfected after ...
Nutritional management in ebola haemorrhagic fever
... adequate protein by protein 1-1.2 g / kg of Ideal body weight by taking a high biological value protein sources such as meat, mainly in the case of patients who do not have access to food in the area with chronic food insecurity may be considered a source of protein, the simplest is the egg. As a mi ...
... adequate protein by protein 1-1.2 g / kg of Ideal body weight by taking a high biological value protein sources such as meat, mainly in the case of patients who do not have access to food in the area with chronic food insecurity may be considered a source of protein, the simplest is the egg. As a mi ...
Catabolic pathways
... is generally provided by the breakdown of ATP to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi). Note that catabolism is a convergent process that is, a wide variety of molecules are transformed into a few common end products. By contrast, anabolism is a divergent process in which a few bi ...
... is generally provided by the breakdown of ATP to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi). Note that catabolism is a convergent process that is, a wide variety of molecules are transformed into a few common end products. By contrast, anabolism is a divergent process in which a few bi ...
Macromolecules For Identification
... • A lot of lipids function as long-term energy storage. • One gram of fat stores more than twice as much energy as one gram of carbohydrates. • Lipids are also an important component of the cell membrane. Lipids consist of glycerol and fatty acids "tails". The fatty acid "tails" are long chains of c ...
... • A lot of lipids function as long-term energy storage. • One gram of fat stores more than twice as much energy as one gram of carbohydrates. • Lipids are also an important component of the cell membrane. Lipids consist of glycerol and fatty acids "tails". The fatty acid "tails" are long chains of c ...
Carbohydrates Lipids (Fats) Proteins Nucleic Acids (DNA, RNA)
... • Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur can also be found in organic compounds A lipid (a.k.a. fat) ...
... • Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur can also be found in organic compounds A lipid (a.k.a. fat) ...
iGCSE revision notes topic 2 (Part 1) Cells, animal
... alimentary canal and associated organs including mouth, salivary glands, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine: duodenum and ileum, pancreas, liver, gall bladder, large intestine: colon and rectum, anus Describe the functions of the regions of the alimentary canal listed above, in relation to ingesti ...
... alimentary canal and associated organs including mouth, salivary glands, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine: duodenum and ileum, pancreas, liver, gall bladder, large intestine: colon and rectum, anus Describe the functions of the regions of the alimentary canal listed above, in relation to ingesti ...
L10v01a_intro_to_metabolism.stamped_doc
... [00:00:01.06] SPEAKER 1: Hi. With this video we begin the second portion of the course, where we'll look at things at a more integrated systems level, rather than the molecular level which we concentrated on in the first portion. In this lecture, specifically, we'll speak about metabolism and how th ...
... [00:00:01.06] SPEAKER 1: Hi. With this video we begin the second portion of the course, where we'll look at things at a more integrated systems level, rather than the molecular level which we concentrated on in the first portion. In this lecture, specifically, we'll speak about metabolism and how th ...
Daily Essential Electrolytes, Protein, and Probiotics
... DEEP2 30™ is a delicious powder from all-natural goat milk that delivers three powerful nutritional components. The philosophy behind DEEP2 30™ is founded upon three concepts: 1. Essential Mineral/Electrolyte Support: Millions of Americans lack minerals/electrolytes in their diet. This can be attrib ...
... DEEP2 30™ is a delicious powder from all-natural goat milk that delivers three powerful nutritional components. The philosophy behind DEEP2 30™ is founded upon three concepts: 1. Essential Mineral/Electrolyte Support: Millions of Americans lack minerals/electrolytes in their diet. This can be attrib ...
Daily Essential Electrolytes, Protein, and Probiotics
... DEEP2 30™ is a delicious powder from all-natural goat milk that delivers three powerful nutritional components. The philosophy behind DEEP2 30™ is founded upon three concepts: 1. Essential Mineral/Electrolyte Support: Millions of Americans lack minerals/electrolytes in their diet. This can be attrib ...
... DEEP2 30™ is a delicious powder from all-natural goat milk that delivers three powerful nutritional components. The philosophy behind DEEP2 30™ is founded upon three concepts: 1. Essential Mineral/Electrolyte Support: Millions of Americans lack minerals/electrolytes in their diet. This can be attrib ...
I LEARN AT HOME ASSIGNMENT 4 Macromolecule Review
... carbohydrate used in food storage in plants. Potatoes, pasta and rice are rich in starch. Starches are very valuable because they provide a quick form of energy for the body. The second is glycogen. Glycogen is used for food storage in animals. The third is cellulose. Cellulose is used for st ...
... carbohydrate used in food storage in plants. Potatoes, pasta and rice are rich in starch. Starches are very valuable because they provide a quick form of energy for the body. The second is glycogen. Glycogen is used for food storage in animals. The third is cellulose. Cellulose is used for st ...
I LEARN AT HOME ASSIGNMENT 4 Macromolecule Review
... carbohydrate used in food storage in plants. Potatoes, pasta and rice are rich in starch. Starches are very valuable because they provide a quick form of energy for the body. The second is glycogen. Glycogen is used for food storage in animals. The third is cellulose. Cellulose is used for st ...
... carbohydrate used in food storage in plants. Potatoes, pasta and rice are rich in starch. Starches are very valuable because they provide a quick form of energy for the body. The second is glycogen. Glycogen is used for food storage in animals. The third is cellulose. Cellulose is used for st ...
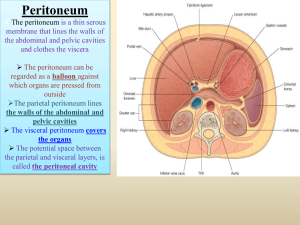
general arrangement of the abdominal viscera
... vessels and nerves. The appendix lies in the right iliac fossa its base is situated one third of the way up the line joining the right anterior superior iliac spine to the umbilicus (McBurney's point). the base of the appendix is easily found by identifying the teniae coli of the cecum and tracin ...
... vessels and nerves. The appendix lies in the right iliac fossa its base is situated one third of the way up the line joining the right anterior superior iliac spine to the umbilicus (McBurney's point). the base of the appendix is easily found by identifying the teniae coli of the cecum and tracin ...
REMOVAL OF PYRROLIDONE CARBOXYLIC ACID WITH
... cleaves peptide bonds at the carboxyl side of aspartate and glutamate in phosphate buffer, pH 7.8. With this cleavage, the aspartyl bond (generally the most labile peptide bond) is at the C-terminus, and, at worst, acid treatment will give a high background of aspartate in the first cycle only, with ...
... cleaves peptide bonds at the carboxyl side of aspartate and glutamate in phosphate buffer, pH 7.8. With this cleavage, the aspartyl bond (generally the most labile peptide bond) is at the C-terminus, and, at worst, acid treatment will give a high background of aspartate in the first cycle only, with ...
Cellular Respiration
... autotrophs) we can look at how organisms use that energy to fuel their bodies. Plants and animals both use products of photosynthesis (glucose) for metabolic fuel Heterotrophs: must take in energy from outside sources, cannot make their own e.g. animals When we take in glucose (or other carbs) ...
... autotrophs) we can look at how organisms use that energy to fuel their bodies. Plants and animals both use products of photosynthesis (glucose) for metabolic fuel Heterotrophs: must take in energy from outside sources, cannot make their own e.g. animals When we take in glucose (or other carbs) ...
NS 315 Unit 6: Proteins
... http://www.gbiosciences.com/EducationalProducts/Protein-StructureAnalysis.aspx ...
... http://www.gbiosciences.com/EducationalProducts/Protein-StructureAnalysis.aspx ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • Glucose molecules are converted to glycogen • Glycogen molecules are stored in the liver Glycogenolysis (breaking glycogen) ...
... • Glucose molecules are converted to glycogen • Glycogen molecules are stored in the liver Glycogenolysis (breaking glycogen) ...
Fermentation Quiz
... 1. Which stage of aerobic respiration occurs during fermentation? a) Glycolysis b) Krebs cycle c) Electron transport d) None of the above ...
... 1. Which stage of aerobic respiration occurs during fermentation? a) Glycolysis b) Krebs cycle c) Electron transport d) None of the above ...
Cellular Respiration
... produce H2O. Most of the water produced will be eliminated by breathing and urination. However, some sugar wil be retained in the cell. If the sugar is not needed for cellular respiration, it will be converted to glycogen or lipids for storage. ...
... produce H2O. Most of the water produced will be eliminated by breathing and urination. However, some sugar wil be retained in the cell. If the sugar is not needed for cellular respiration, it will be converted to glycogen or lipids for storage. ...
Macromolecules Worksheet #2
... 1. What is the relationship between glucose, fructose, and galactose? They are isomers of one another – They have the same chemical formula but differ in how those elements are bonded to each other within the molecule. 2. What are the structural differences between a saturated and an unsaturated fat ...
... 1. What is the relationship between glucose, fructose, and galactose? They are isomers of one another – They have the same chemical formula but differ in how those elements are bonded to each other within the molecule. 2. What are the structural differences between a saturated and an unsaturated fat ...
Powerpoint Slides for Chapter Seven
... What are the types of metabolic reactions and where do they occur? How do we get energy from glucose? What happens if we don’t have enough oxygen? Where do proteins and lipids come in? How does the system adapt to feasting? How does metabolism adjust to fasting? ...
... What are the types of metabolic reactions and where do they occur? How do we get energy from glucose? What happens if we don’t have enough oxygen? Where do proteins and lipids come in? How does the system adapt to feasting? How does metabolism adjust to fasting? ...
Deciphering Food Labels: Here`s what you need to know to
... Many cat parents ask, “What should I feed my cat?” There’s no quick answer to this, but let’s begin by looking at the unique nutritional needs of the feline: 1. In general, cats should eat high-protein, moderate-fat, low carbohydrate foods. • Cats need two to three times more protein than omnivorous ...
... Many cat parents ask, “What should I feed my cat?” There’s no quick answer to this, but let’s begin by looking at the unique nutritional needs of the feline: 1. In general, cats should eat high-protein, moderate-fat, low carbohydrate foods. • Cats need two to three times more protein than omnivorous ...
H 2 O - cloudfront.net
... • The 3 components are phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous base can be one of the following: adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, or uracil ...
... • The 3 components are phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous base can be one of the following: adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, or uracil ...
Vitamin В 1
... Vitamins – low molecular weight organic compounds that have different chemical structure and are not synthesized or are synthesized in small amount in the human organism, are not used as building material, but have marked biological effect and are necessary components of diet Hypovitaminosis – decr ...
... Vitamins – low molecular weight organic compounds that have different chemical structure and are not synthesized or are synthesized in small amount in the human organism, are not used as building material, but have marked biological effect and are necessary components of diet Hypovitaminosis – decr ...
MINERALS AND TRACE ELEMENTS - Univerzita Karlova. Prague
... compounds such fructose, ascorbic acid, citric acid, amino acids to form ferric complexes soluble in neutral pH of intestine fluid. A protein DMT1 (divalent metal transporter 1), which transports all kinds of divalent metals, then transports the iron across the cell membrane of intestinal cells. The ...
... compounds such fructose, ascorbic acid, citric acid, amino acids to form ferric complexes soluble in neutral pH of intestine fluid. A protein DMT1 (divalent metal transporter 1), which transports all kinds of divalent metals, then transports the iron across the cell membrane of intestinal cells. The ...
Digestion

Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use.In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact of saliva. Saliva, a liquid secreted by the salivary glands, contains salivary amylase, an enzyme which starts the digestion of starch in the food; the saliva also contains mucus, which lubricates the food, and hydrogen carbonate, which provides the ideal conditions of pH (alkaline) for amylase to work. After undergoing mastication and starch digestion, the food will be in the form of a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. It will then travel down the esophagus and into the stomach by the action of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach starts protein digestion. Gastric juice mainly contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin. As these two chemicals may damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by the stomach, providing a slimy layer that acts as a shield against the damaging effects of the chemicals. At the same time protein digestion is occurring, mechanical mixing occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.After some time (typically 1–2 hours in humans, 4–6 hours in dogs, 3–4 hours in house cats), the resulting thick liquid is called chyme. When the pyloric sphincter valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes with digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile juice from the liver and then passes through the small intestine, in which digestion continues. When the chyme is fully digested, it is absorbed into the blood. 95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine. Water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon (large intestine) where the pH is slightly acidic about 5.6 ~ 6.9. Some vitamins, such as biotin and vitamin K (K2MK7) produced by bacteria in the colon are also absorbed into the blood in the colon. Waste material is eliminated from the rectum during defecation.