Biyokimyaya Giriş
... • Biochemistry is the study of the molecules and chemical reactions of life. • The Biochemist uses physical and chemical principles to explain biology at the molecular level. ...
... • Biochemistry is the study of the molecules and chemical reactions of life. • The Biochemist uses physical and chemical principles to explain biology at the molecular level. ...
4) Protein Evolution
... o Metal chelate affinity chromatography, Zn2+ or Ni2+ are attached to matrix, bind to polyHis tags (6xHis) ...
... o Metal chelate affinity chromatography, Zn2+ or Ni2+ are attached to matrix, bind to polyHis tags (6xHis) ...
Chapter 4
... • Simple – composed only of amino acid residues • Conjugated – contain prosthetic groups (metal ions, co-factors, lipids, carbohydrates) Example: Hemoglobin – Heme ...
... • Simple – composed only of amino acid residues • Conjugated – contain prosthetic groups (metal ions, co-factors, lipids, carbohydrates) Example: Hemoglobin – Heme ...
Proteins synthesisand expression
... of subunits (like a chain) that tells how to build a protein • A protein is a sequence of subunits – a chain of amino acids. ...
... of subunits (like a chain) that tells how to build a protein • A protein is a sequence of subunits – a chain of amino acids. ...
Aalborg Universitet Christiansen, Gunna; Sennels, Lau; Stensballe, Allan; Birkelund, Svend
... The coding capacity of the chlamydial genome was revealed by genome sequencing of strain D/UW-Cx (Stephens et al. 1998). Of the 894 likely protein-coding genes 255 (28%) were not similar to any known proteins indicating the uniqueness of the genus Chlamydia. Since then multiple chlamydial and parach ...
... The coding capacity of the chlamydial genome was revealed by genome sequencing of strain D/UW-Cx (Stephens et al. 1998). Of the 894 likely protein-coding genes 255 (28%) were not similar to any known proteins indicating the uniqueness of the genus Chlamydia. Since then multiple chlamydial and parach ...
Bioinorganic_chemistry
... Introduction Bioinorganic chemistry is concerned with the roles of inorganic elements in biological processes. Metal ions can have structural roles, catalytic roles, or both. Metals that have catalytic roles will be present at the active site of the biomolecule which will likely be a metalloprotein ...
... Introduction Bioinorganic chemistry is concerned with the roles of inorganic elements in biological processes. Metal ions can have structural roles, catalytic roles, or both. Metals that have catalytic roles will be present at the active site of the biomolecule which will likely be a metalloprotein ...
Chapter 4
... increase if each one had multiple shapes • Proteins usually have only one useful conformation because otherwise it would not be efficient use of the energy available to the system • Natural selection has eliminated proteins that do not perform a specific function in the cell ...
... increase if each one had multiple shapes • Proteins usually have only one useful conformation because otherwise it would not be efficient use of the energy available to the system • Natural selection has eliminated proteins that do not perform a specific function in the cell ...
File
... pH of the blood. It is a tertiary protein that bonds to iron, which gives it its red hue when carrying oxygen. ...
... pH of the blood. It is a tertiary protein that bonds to iron, which gives it its red hue when carrying oxygen. ...
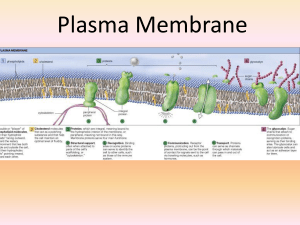
Plasma Membrane
... A. They can act as a channel, allowing the transport of ions across the membrane. B. They often require ATP to actively transport materials across the membrane against a concentration gradient. C. They may be receptor proteins that bind specific molecules from the surrounding solution, which trigger ...
... A. They can act as a channel, allowing the transport of ions across the membrane. B. They often require ATP to actively transport materials across the membrane against a concentration gradient. C. They may be receptor proteins that bind specific molecules from the surrounding solution, which trigger ...
Protein
... – The structure of the protein affects the process also. Most proteins denature at temps between 47 and 67 degrees C, as in eggs and milk. – The denaturation of beef takes a much higher temp. ...
... – The structure of the protein affects the process also. Most proteins denature at temps between 47 and 67 degrees C, as in eggs and milk. – The denaturation of beef takes a much higher temp. ...
From the Cradle to the grave: molecular chaperones that may
... 3D structure of the Amino Acid chain This 3D structure is produced after translation Proteins are constantly under threat of unfolding due to chemical and cellular stress Hydrogen bonds may be disrupted by change in temperature and varying pH levels ...
... 3D structure of the Amino Acid chain This 3D structure is produced after translation Proteins are constantly under threat of unfolding due to chemical and cellular stress Hydrogen bonds may be disrupted by change in temperature and varying pH levels ...
Biological Molecules
... grow hair, ligaments and fingernails; and let you see (the lens of your eye is pure crystallised protein). ...
... grow hair, ligaments and fingernails; and let you see (the lens of your eye is pure crystallised protein). ...
SG-Glutamic-C™ (Cat. # 786-15)
... highly specific for the cleavage of peptide bonds at the carboxy side of either aspartic or glutamic acid, depending on the buffer used. In ammonium bicarbonate or Tris-HCl buffer, in particular in the absence of phosphate ions, the enzyme is specific for the glutamyl site. Recommended buffers for f ...
... highly specific for the cleavage of peptide bonds at the carboxy side of either aspartic or glutamic acid, depending on the buffer used. In ammonium bicarbonate or Tris-HCl buffer, in particular in the absence of phosphate ions, the enzyme is specific for the glutamyl site. Recommended buffers for f ...
Protein Lab 2012 PDF
... specific amino acids that are linked together in the chain. These amino acids react with each other and cause the protein chain to twist and fold up into a large 3-D shape, forming a globular protein. The “R” groups (or side groups) of each amino acid can be either hydrophobic (water-fearing) or hyd ...
... specific amino acids that are linked together in the chain. These amino acids react with each other and cause the protein chain to twist and fold up into a large 3-D shape, forming a globular protein. The “R” groups (or side groups) of each amino acid can be either hydrophobic (water-fearing) or hyd ...
The Human Cell Poster Introduction
... rise to a particular protein provides us with some insight into that protein, but a deeper investigation of how the protein is made, where it is located, and how much of it is present in different cell types is required to enable a true understanding of its function. As mentioned above, changes to t ...
... rise to a particular protein provides us with some insight into that protein, but a deeper investigation of how the protein is made, where it is located, and how much of it is present in different cell types is required to enable a true understanding of its function. As mentioned above, changes to t ...
WHAT THEY DO
... Proteins are made of long chains (polymers) made of monomers. All proteins are made of the monomer… ...
... Proteins are made of long chains (polymers) made of monomers. All proteins are made of the monomer… ...
Document
... The genetic code is redundant - most amino acids are coded by more than one of the 64 possible codons. The genetic code is not ambiguous - no codon codes for more than one amino acid. The genetic code is universal - all organisms use the same code, indicating that the code evolved once, early in the ...
... The genetic code is redundant - most amino acids are coded by more than one of the 64 possible codons. The genetic code is not ambiguous - no codon codes for more than one amino acid. The genetic code is universal - all organisms use the same code, indicating that the code evolved once, early in the ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... The genetic code is redundant - most amino acids are coded by more than one of the 64 possible codons. The genetic code is not ambiguous - no codon codes for more than one amino acid. The genetic code is universal - all organisms use the same code, indicating that the code evolved once, early in the ...
... The genetic code is redundant - most amino acids are coded by more than one of the 64 possible codons. The genetic code is not ambiguous - no codon codes for more than one amino acid. The genetic code is universal - all organisms use the same code, indicating that the code evolved once, early in the ...
Packet 2- Chemistry of Life
... ii. Secondary structure: The string is folded in some way (beta pleated sheets or alpha helices) iii. Tertiary structure: The folded shape FOLDS on itself iv. Quaternary structure: More than one protein with tertiary structure COMBINES B. Exposure to acids or bases (or heat) can affect the abili ...
... ii. Secondary structure: The string is folded in some way (beta pleated sheets or alpha helices) iii. Tertiary structure: The folded shape FOLDS on itself iv. Quaternary structure: More than one protein with tertiary structure COMBINES B. Exposure to acids or bases (or heat) can affect the abili ...
Chapter 4 - WordPress.com
... • Glucose is the primary source of energy. • Glucose can be stored as glycogen, and converted to and stored as fat. • Glucose can be catabolized anaerobically and aerobically. Anaerobically, glucose is incompletely broken down (glycolysis) into lactic acid and small amounts of ATP. Aerobically, gluc ...
... • Glucose is the primary source of energy. • Glucose can be stored as glycogen, and converted to and stored as fat. • Glucose can be catabolized anaerobically and aerobically. Anaerobically, glucose is incompletely broken down (glycolysis) into lactic acid and small amounts of ATP. Aerobically, gluc ...
Biochemistry-lab-identifying
... composed of several amino acids (N-H) molecule groups that are linked together. Proteins have different functions; they can provide structure (ligaments, fingernails, hair), help in digestion (stomach enzymes), aid in movement (muscles), help us fight off infection and disease and play a part in our ...
... composed of several amino acids (N-H) molecule groups that are linked together. Proteins have different functions; they can provide structure (ligaments, fingernails, hair), help in digestion (stomach enzymes), aid in movement (muscles), help us fight off infection and disease and play a part in our ...