Metabolic fuels: regulating fluxes to select mix
... constituent amino acids, with values that generally fall between lipids and carbohydrates (Fig.1B–E). Here, the inclusion of proteins is for comparison only and does not imply that they are used preferentially at intermediate intensities. In reality, animals usually try to curtail the use of protei ...
... constituent amino acids, with values that generally fall between lipids and carbohydrates (Fig.1B–E). Here, the inclusion of proteins is for comparison only and does not imply that they are used preferentially at intermediate intensities. In reality, animals usually try to curtail the use of protei ...
The Protein Data Bank (PDB) & PDB Files
... • Text file, viewed/modified in editor (TextPad) • a.k.a. structure file • Contains position of every atom in the file as well as some information about the structure • Holds all the information needed to reconstruct a 3D model of a molecule – view in RASMOL or DeepView • At first, contents are inti ...
... • Text file, viewed/modified in editor (TextPad) • a.k.a. structure file • Contains position of every atom in the file as well as some information about the structure • Holds all the information needed to reconstruct a 3D model of a molecule – view in RASMOL or DeepView • At first, contents are inti ...
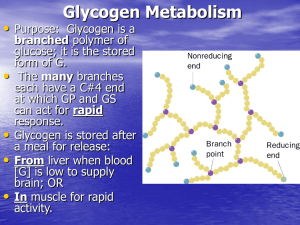
Glycogen Metabolism - http://www.utm.edu
... catalyzed by phosphoprotein phosphatase 1 (PP1). In muscle, phosphorylation of a regulatory glycogen binding protein, GM in response to insulin (which causes dephosphorylation of other Es) at site 1 activates PP1. This results in the opposite activities to the above (GS active to store the plentiful ...
... catalyzed by phosphoprotein phosphatase 1 (PP1). In muscle, phosphorylation of a regulatory glycogen binding protein, GM in response to insulin (which causes dephosphorylation of other Es) at site 1 activates PP1. This results in the opposite activities to the above (GS active to store the plentiful ...
FLAVIN MONONUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHATASE FROM GOAT LIVER: A POSSIBLE TARGET FOR
... essential coenzyme form of the vitamin riboflavin, and occurs widespread in plant and animal organisms [1, 34]. FMN and FAD are formed from riboflavin in liver, intestinal mucosa and other tissues. A great number of mammalian enzymes require FMN or Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) as coenzymes for ...
... essential coenzyme form of the vitamin riboflavin, and occurs widespread in plant and animal organisms [1, 34]. FMN and FAD are formed from riboflavin in liver, intestinal mucosa and other tissues. A great number of mammalian enzymes require FMN or Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) as coenzymes for ...
Ch - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... ● Gycolysis and the Krebs cycle are major intersections to various catabolic and anabolic pathways ...
... ● Gycolysis and the Krebs cycle are major intersections to various catabolic and anabolic pathways ...
Document
... A living system’s free energy is energy that can do work when temperature and pressure are uniform, as in a living cell ...
... A living system’s free energy is energy that can do work when temperature and pressure are uniform, as in a living cell ...
Chapter 6 Power Points
... A living system’s free energy is energy that can do work when temperature and pressure are uniform, as in a living cell ...
... A living system’s free energy is energy that can do work when temperature and pressure are uniform, as in a living cell ...
chapter 15 acids and bases
... Oftentimes, assumptions such as these are valid if K is very small. A very small value of K means that a very small amount of reactants go to products. Hence, x is small. If we did not make this assumption, we would have to solve a quadratic equation. ...
... Oftentimes, assumptions such as these are valid if K is very small. A very small value of K means that a very small amount of reactants go to products. Hence, x is small. If we did not make this assumption, we would have to solve a quadratic equation. ...
Chapter 1 - Research Explorer
... 1998). The degradation of these compounds results in the formation of important metabolites, which are vital in biochemical processes (e.g. in the biosynthesis of lipids), as well as in energy production (via the Krebs cycle and ketone body production). The degradation of the BCAAs starts with their ...
... 1998). The degradation of these compounds results in the formation of important metabolites, which are vital in biochemical processes (e.g. in the biosynthesis of lipids), as well as in energy production (via the Krebs cycle and ketone body production). The degradation of the BCAAs starts with their ...
Glucose
... complete, but insulin effects persist and blood glucose falls. The body interprets this hypoglycemic state as starvation and secretes counterregulatory hormones to release free fatty acids from fat cells. Fatty acids are packed into transport lipoproteins (very-low-density lipoproteins [VLDLs) in th ...
... complete, but insulin effects persist and blood glucose falls. The body interprets this hypoglycemic state as starvation and secretes counterregulatory hormones to release free fatty acids from fat cells. Fatty acids are packed into transport lipoproteins (very-low-density lipoproteins [VLDLs) in th ...
Computer-Assisted Molecular Modeling of Benzodiazepine and
... the turnover of substrates, vitamins, and hormones. In mammalian species, the active forms are Tq and its more potent deiodinated metabolite, T3 (1). Facilitated carrier-mediated transport allows the hormones to cross the cell membrane and then to interact with cytosolic, enzymatic, mitochondrial, m ...
... the turnover of substrates, vitamins, and hormones. In mammalian species, the active forms are Tq and its more potent deiodinated metabolite, T3 (1). Facilitated carrier-mediated transport allows the hormones to cross the cell membrane and then to interact with cytosolic, enzymatic, mitochondrial, m ...
Design and Synthesis of RGD Mimetics as Potent Inhibitors of
... Strategy of Rational Drug Design: Peptides to Peptidomimetics. Current efforts in drug development are aimed at developing non-peptidic inhibitors that mimic the structure and function of bioactive peptides. Known as peptidomimetics, these compounds have many advantages over their parent peptides.4 ...
... Strategy of Rational Drug Design: Peptides to Peptidomimetics. Current efforts in drug development are aimed at developing non-peptidic inhibitors that mimic the structure and function of bioactive peptides. Known as peptidomimetics, these compounds have many advantages over their parent peptides.4 ...
Patterns of prokaryotic lateral gene transfers affecting
... Full list of author information is available at the end of the article ...
... Full list of author information is available at the end of the article ...
Carbon dioxide metabolism and ecological significance
... Euryarchaeota exhibit this C metabolic pathway. Here, one CO2 molecule is reduced to CO and other to a methyl group. Subsequently, acetyl-CoA is synthesized from CO and the methyl group. This pathway is the most energetically favourable autotrophic carbon fixation pathway. However, it is restricted ...
... Euryarchaeota exhibit this C metabolic pathway. Here, one CO2 molecule is reduced to CO and other to a methyl group. Subsequently, acetyl-CoA is synthesized from CO and the methyl group. This pathway is the most energetically favourable autotrophic carbon fixation pathway. However, it is restricted ...
File
... 4. At which stage is it the most difficult to tell the embryos apart? (I, II, or III) I 5. Describe at least one similarity in the structure of these embryos Eyes, spinal cord, begin life with a tail 6. How do these similarities support the evidence of ancestry? The embryo begins with very similar c ...
... 4. At which stage is it the most difficult to tell the embryos apart? (I, II, or III) I 5. Describe at least one similarity in the structure of these embryos Eyes, spinal cord, begin life with a tail 6. How do these similarities support the evidence of ancestry? The embryo begins with very similar c ...
document
... terms of amylase. This colder temperature, however has not been observed to greatly affect the reaction of amylase with starch. (6,7) Some theories suggest that amylase evolved to be able to survive in colder temperatures. It is believed that those enzymes which could not stand the cold died off, al ...
... terms of amylase. This colder temperature, however has not been observed to greatly affect the reaction of amylase with starch. (6,7) Some theories suggest that amylase evolved to be able to survive in colder temperatures. It is believed that those enzymes which could not stand the cold died off, al ...
Avian-to-human transmission of the PB1 gene of influenza A viruses in the 1957 and 1968 pandemics
... of new subtypes of influenza A viruses can lead to pandemics in humans. For example, the virus A/Singapore/i/57 (H2N2) (Sing/57), whose HA and NA differed from those of previously circulating viruses, emerged in the 1957 pandemic. Another virus, A/Hong Kong/1/68 (H3N2), with a different HA subtype f ...
... of new subtypes of influenza A viruses can lead to pandemics in humans. For example, the virus A/Singapore/i/57 (H2N2) (Sing/57), whose HA and NA differed from those of previously circulating viruses, emerged in the 1957 pandemic. Another virus, A/Hong Kong/1/68 (H3N2), with a different HA subtype f ...
Biosynthesis of Glucosyl Glycerol, a Compatible Solute, Using
... pustule disease in soybeans, showed a very strong deduced amino acid homology with various ASases [17]. However, it only displayed sucrose hydrolysis activity without any glucosyltransferase or isomerization activities [18]. α-D-Glucosyl glycerol (GG) was formerly known as the main compatible solute ...
... pustule disease in soybeans, showed a very strong deduced amino acid homology with various ASases [17]. However, it only displayed sucrose hydrolysis activity without any glucosyltransferase or isomerization activities [18]. α-D-Glucosyl glycerol (GG) was formerly known as the main compatible solute ...
Problem Set #3 Key
... 4 Succinyl-CoA synthetase (GTP) 4 Succinate Dehydrogenase (FADH2) 4 Malate Dehydrogenase (NADH) ...
... 4 Succinyl-CoA synthetase (GTP) 4 Succinate Dehydrogenase (FADH2) 4 Malate Dehydrogenase (NADH) ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.