Introductory Biology Primer - A computational tour of the human
... which in turn each turn on many proteins, ... ...
... which in turn each turn on many proteins, ... ...
Lecture 3
... The binding site forms when amino acids from within the protein come together in the folding The remaining sequences may play a role in regulating the protein’s activity ...
... The binding site forms when amino acids from within the protein come together in the folding The remaining sequences may play a role in regulating the protein’s activity ...
Ch 4: Cellular Metabolism
... 2 letter word: 2 bases = 1 aa how many possibilities? 3 letter word: 3 bases = 1 aa how many possibilities? ...
... 2 letter word: 2 bases = 1 aa how many possibilities? 3 letter word: 3 bases = 1 aa how many possibilities? ...
26.4 The ureo cyde
... positive nitrogen balance-fhe excretion of less nitrogen than is consumed.The nitrogen balanceis positive becausechildren are growing and their cells are making new proteins and other nitrogen compounds. Several conditions result in a negative nitrogen balance-the excretion of more nitrogen than is ...
... positive nitrogen balance-fhe excretion of less nitrogen than is consumed.The nitrogen balanceis positive becausechildren are growing and their cells are making new proteins and other nitrogen compounds. Several conditions result in a negative nitrogen balance-the excretion of more nitrogen than is ...
Genetics Learning Goals
... Score 4: Student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications of the learning goal(s) and can reconstruct and apply their knowledge from limited information: A/B4) Describe important discoveries that led to today’s model of DNA structure and explain how the development of the DNA model exhibits ...
... Score 4: Student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications of the learning goal(s) and can reconstruct and apply their knowledge from limited information: A/B4) Describe important discoveries that led to today’s model of DNA structure and explain how the development of the DNA model exhibits ...
Pretest and Post Test Questions
... C) 44 D) 56 E) 72 Answer: A 8) Where does DNA replication occur in eukaryotes? A) cytoplasm B) ribosome C) nucleus D) vacuole E) rough endoplasmic reticulum Answer: C 9) Where does DNA replication occur in prokaryotes? A) cytoplasm B) ribosome C) nucleus D) vacuole E) rough endoplasmic reticulum Ans ...
... C) 44 D) 56 E) 72 Answer: A 8) Where does DNA replication occur in eukaryotes? A) cytoplasm B) ribosome C) nucleus D) vacuole E) rough endoplasmic reticulum Answer: C 9) Where does DNA replication occur in prokaryotes? A) cytoplasm B) ribosome C) nucleus D) vacuole E) rough endoplasmic reticulum Ans ...
Biochemistry
... than the original elements Compound composition given in chemical formula – Examples: ______________ ...
... than the original elements Compound composition given in chemical formula – Examples: ______________ ...
General Amino Acid Metabolism
... The first step in the catabolism of most amino acids is the transfer of their α - amino group to α -ketoglutarate where the products are α - ketoacids and glutamate. This transfer of amino groups from one carbon skeleton to another is catalyzed by a family of transaminases which are also called amin ...
... The first step in the catabolism of most amino acids is the transfer of their α - amino group to α -ketoglutarate where the products are α - ketoacids and glutamate. This transfer of amino groups from one carbon skeleton to another is catalyzed by a family of transaminases which are also called amin ...
Unti 8-9 - DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
... Score 4: Student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications of the learning goal(s) and can reconstruct and apply their knowledge from limited information: A/B4) Describe important discoveries that led to today’s model of DNA structure and explain how the development of the DNA model exhibits ...
... Score 4: Student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications of the learning goal(s) and can reconstruct and apply their knowledge from limited information: A/B4) Describe important discoveries that led to today’s model of DNA structure and explain how the development of the DNA model exhibits ...
Organic Molecules Jeopardy
... Earwax and cholesterol are lipids. What is another example of a lipid in our body? ...
... Earwax and cholesterol are lipids. What is another example of a lipid in our body? ...
Slide 1
... Store energy, provide barriers Fats, oils & waxes Fatty acids, glycerol & other compounds Prevents water loss from plants Needed to carry out body functions Saturated (will not accept H’s) & unsaturated ...
... Store energy, provide barriers Fats, oils & waxes Fatty acids, glycerol & other compounds Prevents water loss from plants Needed to carry out body functions Saturated (will not accept H’s) & unsaturated ...
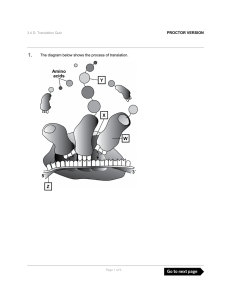
Translation is simply the decoding of nucleotide sequences on
... in genes (DNA).The synthesis of every protein molecule in a cell is directed by an mRNA, originally copied from DNA. Synthesis of RNA from DNA template is called transcription and the process is catalyzed by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. Next step is the synthesis of polypeptide (protein) from mR ...
... in genes (DNA).The synthesis of every protein molecule in a cell is directed by an mRNA, originally copied from DNA. Synthesis of RNA from DNA template is called transcription and the process is catalyzed by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. Next step is the synthesis of polypeptide (protein) from mR ...
Biochemistry Presentation Notes Pre-AP 14-15
... 1. bad cholesterol – LDL (low density lipoprotein) – goes to cells, excess deposited in arteries 2. good cholesterol – HDL (high density lipoprotein) – gets rid of excess LDL’s in arteries ...
... 1. bad cholesterol – LDL (low density lipoprotein) – goes to cells, excess deposited in arteries 2. good cholesterol – HDL (high density lipoprotein) – gets rid of excess LDL’s in arteries ...
8.4 Enzymes speed up metabolic reactions by
... active site and is held there by weak interactions Side chains (R groups) of a few of the amino acids that make up the active site catalyze the conversion of substrate to product Product departs Repeats Most metabolic reactions are reversible and an enzyme can catalyze both forwards and backwards Th ...
... active site and is held there by weak interactions Side chains (R groups) of a few of the amino acids that make up the active site catalyze the conversion of substrate to product Product departs Repeats Most metabolic reactions are reversible and an enzyme can catalyze both forwards and backwards Th ...
final review
... 1. Diagram the hierarchy of structural levels in biological organization from the simplest to the most complex level. 2. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 3. Distinguish between positive and negative feedback. 4. What is homeostasis? 5. What are the three domains of life? 6. List ...
... 1. Diagram the hierarchy of structural levels in biological organization from the simplest to the most complex level. 2. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 3. Distinguish between positive and negative feedback. 4. What is homeostasis? 5. What are the three domains of life? 6. List ...
7.013 Problem Set 1 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... An eye lens is comprised of cells that are created when an eye is formed and are retained for its lifetime. These cells lack organelles and can be regarded as “sacs” that are filled with a loose uniform arrangement of water-soluble structural proteins called crystallins. The uniform distribution of ...
... An eye lens is comprised of cells that are created when an eye is formed and are retained for its lifetime. These cells lack organelles and can be regarded as “sacs” that are filled with a loose uniform arrangement of water-soluble structural proteins called crystallins. The uniform distribution of ...
3.2 Carbohydrates, lipids annd proteins
... between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides; between fatty acids, glycerol and triglycerides; and between amino acids and polypeptides. ...
... between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides; between fatty acids, glycerol and triglycerides; and between amino acids and polypeptides. ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.























