Contrasting C3, C4 and CAM Photosynthesis
... fixation of CO2 from the actual fixation of CO2 by RuBisCO, in order to concentrate it, what actually is the difference ...
... fixation of CO2 from the actual fixation of CO2 by RuBisCO, in order to concentrate it, what actually is the difference ...
Chemistry Unit 1
... is also important to realize that hydroxides which react with both acids and bases are described as amphoteric substances. For example, aluminium hydroxide, Al(OH)3, reacts with both acids and bases to form salt and water. So, Al(OH)3, is amphoteric in nature. What is the common characteristic of ac ...
... is also important to realize that hydroxides which react with both acids and bases are described as amphoteric substances. For example, aluminium hydroxide, Al(OH)3, reacts with both acids and bases to form salt and water. So, Al(OH)3, is amphoteric in nature. What is the common characteristic of ac ...
Net Ionic Equation Powerpoint Tutorial
... might occur: the formation of a weak acid. An acid is a compound that has an H+ ion bonded to some negative ion: HNO3 for example is nitric acid. HF is hydrofluoric acid. All acids fall into one of two categories: strong acids and weak acids. A strong acid is one that dissociates 100% in water. That ...
... might occur: the formation of a weak acid. An acid is a compound that has an H+ ion bonded to some negative ion: HNO3 for example is nitric acid. HF is hydrofluoric acid. All acids fall into one of two categories: strong acids and weak acids. A strong acid is one that dissociates 100% in water. That ...
Cellular Respiration - Kania´s Science Page
... ancient pathway which harvests energy where energy transfer first evolved transfer energy from organic molecules to ATP still is starting point for ALL cellular respiration ...
... ancient pathway which harvests energy where energy transfer first evolved transfer energy from organic molecules to ATP still is starting point for ALL cellular respiration ...
Lipoteichoic Acid Synthesis and Function in Gram
... has significantly diverged from the LtaS enzyme. In Bacillus spp., which contain four LTA synthase enzymes, these proteins are more closely related to each other and the LtaS protein of L. monocytogenes than to LtaP. Disaccharide-containing glycolipids are often the predominant glycolipids and are pr ...
... has significantly diverged from the LtaS enzyme. In Bacillus spp., which contain four LTA synthase enzymes, these proteins are more closely related to each other and the LtaS protein of L. monocytogenes than to LtaP. Disaccharide-containing glycolipids are often the predominant glycolipids and are pr ...
Amino Acid Neurotransmitters
... form of GluR5 (GluR5-Q) is functional. Homomeric GluR7 receptors (both a and b) can form functional channels but these display a very low affinity for glutamate. GluR7a receptors are insensitive to AMPA. Also, despite a very high affinity for domoate, GluR7a receptors are functionally insensitive to thi ...
... form of GluR5 (GluR5-Q) is functional. Homomeric GluR7 receptors (both a and b) can form functional channels but these display a very low affinity for glutamate. GluR7a receptors are insensitive to AMPA. Also, despite a very high affinity for domoate, GluR7a receptors are functionally insensitive to thi ...
BioFiles v5 n1 - Sigma
... carboxylic acid group at the C1 position (see Figure 1). Because of the carboxylic acid group, sialic acids have an inherent negative charge. The most common sialic acids are N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac, NeuNAc or NANA), N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Glc), and N-acetyl-9-O-acetylneuraminic acid ...
... carboxylic acid group at the C1 position (see Figure 1). Because of the carboxylic acid group, sialic acids have an inherent negative charge. The most common sialic acids are N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac, NeuNAc or NANA), N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Glc), and N-acetyl-9-O-acetylneuraminic acid ...
Substrate-Promoted Formation of a Catalytically Competent
... i.e., water/hydroxide ligands, coordinated to one or both metal ions. While it is at present not possible to unambiguously distinguish between these two possibilities, a reaction mechanism is proposed whereby the terminally bound H2O/OH- acts as the nucleophile, activated via hydrogen bonding by the ...
... i.e., water/hydroxide ligands, coordinated to one or both metal ions. While it is at present not possible to unambiguously distinguish between these two possibilities, a reaction mechanism is proposed whereby the terminally bound H2O/OH- acts as the nucleophile, activated via hydrogen bonding by the ...
9 biological oxidation, electron transfer chain and oxidative
... cytochromes. It is the terminal component of the chain of respiratory carriers found in mitochondria and transfers electrons resulting from the oxidation of substrate molecules by dehydrogenases to their final acceptor, oxygen. The enzyme is poisoned by carbon monoxide, cyanide, and hydrogen sulfide ...
... cytochromes. It is the terminal component of the chain of respiratory carriers found in mitochondria and transfers electrons resulting from the oxidation of substrate molecules by dehydrogenases to their final acceptor, oxygen. The enzyme is poisoned by carbon monoxide, cyanide, and hydrogen sulfide ...
BEL β-trefoil: A novel lectin with antineoplastic properties in king
... called lectins (Sharon 2007). In general, ligand binding precedes the fulfillment of an important biological function, which in some cases is still not known. Some members of this family are also called agglutinins because of their ability to agglutinate red blood cells, but this term does not necess ...
... called lectins (Sharon 2007). In general, ligand binding precedes the fulfillment of an important biological function, which in some cases is still not known. Some members of this family are also called agglutinins because of their ability to agglutinate red blood cells, but this term does not necess ...
Protein Nutrition of Dairy Cattle – An Overview
... reflects a deepening understanding of microbial protein synthesis in the rumen and the amino acid composition of ruminant products. In contrast, estimates of amino acid requirements for maintenance have remained elusive. Our comprehension of amino acid (and protein) metabolism and requirements for ...
... reflects a deepening understanding of microbial protein synthesis in the rumen and the amino acid composition of ruminant products. In contrast, estimates of amino acid requirements for maintenance have remained elusive. Our comprehension of amino acid (and protein) metabolism and requirements for ...
Physiology of the thermophilic acetogen Moorella - The Keep
... metabolism (e.g., ethanol and butyrate fermentations yield 2 and 3 ATPSLP per hexose, respectively). Although the acetyl-‐CoA pathway (i.e., reduction of 2 molecules of CO2 to acetate) does not increase the ...
... metabolism (e.g., ethanol and butyrate fermentations yield 2 and 3 ATPSLP per hexose, respectively). Although the acetyl-‐CoA pathway (i.e., reduction of 2 molecules of CO2 to acetate) does not increase the ...
17 - Stanford University
... residue, such as Asp or Glu found in aminotransferases, or with a polar residue, Ser or Thr, in enzymes of the tryptophan synthase family.2,3,8 The pyridinium ion of PLP acts as an effective electron sink, stabilizing the carbanion intermediate by forming a quinonoid species, which can be easily cha ...
... residue, such as Asp or Glu found in aminotransferases, or with a polar residue, Ser or Thr, in enzymes of the tryptophan synthase family.2,3,8 The pyridinium ion of PLP acts as an effective electron sink, stabilizing the carbanion intermediate by forming a quinonoid species, which can be easily cha ...
topological changes in the cyp3a4 active site probed with
... CYP3A4 is the most abundant P450 enzyme in the human liver and plays a significant role in the metabolism of a wide variety of drugs (Guengerich, 1999; Nebert and Russell, 2002). Because of its pharmacological significance and the potential for drug-drug interactions, CYP3A4 has been the subject of ...
... CYP3A4 is the most abundant P450 enzyme in the human liver and plays a significant role in the metabolism of a wide variety of drugs (Guengerich, 1999; Nebert and Russell, 2002). Because of its pharmacological significance and the potential for drug-drug interactions, CYP3A4 has been the subject of ...
21. glycolysis
... The major function of carbohydrates in metabolism is as a fuel to be oxidized and provide energy for other metabolic processes. The carbohydrate is utilized by cells mainly as glucose. The 3 principal monosaccharides resulting from digestive processes are glucose, fructose and galactose. Much of the ...
... The major function of carbohydrates in metabolism is as a fuel to be oxidized and provide energy for other metabolic processes. The carbohydrate is utilized by cells mainly as glucose. The 3 principal monosaccharides resulting from digestive processes are glucose, fructose and galactose. Much of the ...
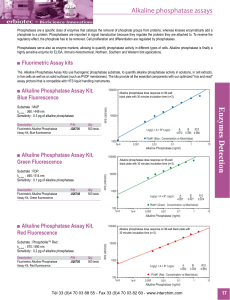
Enzymes Detection
... much more sensitive than the currently available fluorimetric assay for this enzyme activity. This method eliminates the interference that occurs in some biological samples and can be readily used to detect lysyl oxidase activity in cell culture experiments. ...
... much more sensitive than the currently available fluorimetric assay for this enzyme activity. This method eliminates the interference that occurs in some biological samples and can be readily used to detect lysyl oxidase activity in cell culture experiments. ...
Attachment 2 - Food Standards Australia New Zealand
... via the shikimate metabolic pathway. This metabolic pathway is present in all plants, bacteria and fungi (Haslam, 1993). Plant variants of the EPSPS enzyme are inhibited by the herbicide glyphosate, however, bacterial variants of the EPSPS enzyme are, in general, not inhibited due to reduced binding ...
... via the shikimate metabolic pathway. This metabolic pathway is present in all plants, bacteria and fungi (Haslam, 1993). Plant variants of the EPSPS enzyme are inhibited by the herbicide glyphosate, however, bacterial variants of the EPSPS enzyme are, in general, not inhibited due to reduced binding ...
6 theoretical problems 2 practical problems
... The bound iron(III) ion at each binding site is surrounded by six donor atoms from various ligands. Thus, two oxygen atoms of a carbonate anion coordinate to the metal, and the following amino acid side chains from the protein primary structure also coordinate to the iron(III) ion with one potential ...
... The bound iron(III) ion at each binding site is surrounded by six donor atoms from various ligands. Thus, two oxygen atoms of a carbonate anion coordinate to the metal, and the following amino acid side chains from the protein primary structure also coordinate to the iron(III) ion with one potential ...
Clinical Chemistry Evaluations in Toxicity Studies
... the kidney has two functionally distinct parts: the glomerulus and the tubule system. The glomerulus acts as a semipermeable diffusion membrane while the tubule system acts on the glomerular ultrafiltrate to maintain water and solute homeostasis in the animal. Quantitative and qualitative serum and/ ...
... the kidney has two functionally distinct parts: the glomerulus and the tubule system. The glomerulus acts as a semipermeable diffusion membrane while the tubule system acts on the glomerular ultrafiltrate to maintain water and solute homeostasis in the animal. Quantitative and qualitative serum and/ ...
Clinical Chemistry Evaluations in Toxicity Studies
... the kidney has two functionally distinct parts: the glomerulus and the tubule system. The glomerulus acts as a semipermeable diffusion membrane while the tubule system acts on the glomerular ultrafiltrate to maintain water and solute homeostasis in the animal. Quantitative and qualitative serum and/ ...
... the kidney has two functionally distinct parts: the glomerulus and the tubule system. The glomerulus acts as a semipermeable diffusion membrane while the tubule system acts on the glomerular ultrafiltrate to maintain water and solute homeostasis in the animal. Quantitative and qualitative serum and/ ...
subset seed extension to protein blast
... algorithm designing subset seed attempt to extract information about the structure of the family from this set, and use it to produce alignments for the entire family. In the first phase a hierarchical tree is constructed that represents similarities of amino acids. Then, a seed alphabet is designed ...
... algorithm designing subset seed attempt to extract information about the structure of the family from this set, and use it to produce alignments for the entire family. In the first phase a hierarchical tree is constructed that represents similarities of amino acids. Then, a seed alphabet is designed ...
Exam 1
... A. It undergoes an addition reaction with hydrogen to form propane. B. It undergoes a polymerisation reaction expelling water in the process. C. Weak dispersion forces act between propene molecules and consequently it is a gas at room temperature. D. One propene molecule will react with excess oxyge ...
... A. It undergoes an addition reaction with hydrogen to form propane. B. It undergoes a polymerisation reaction expelling water in the process. C. Weak dispersion forces act between propene molecules and consequently it is a gas at room temperature. D. One propene molecule will react with excess oxyge ...
14steriod
... 1- structural lipid present in membrane. 2- precursors of steroidal hormones. - 27 C of cholesterol is derived from acetate. ...
... 1- structural lipid present in membrane. 2- precursors of steroidal hormones. - 27 C of cholesterol is derived from acetate. ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.